- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Electric Current and OHM’s Law Question and Answers
- Kirchhoff’s Laws and Electrical Measurement Question and Answers
- Electric Energy and Power Question and Answers
- Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetism Question and Answers
- Magnetic Properties of Materials Question and Answers
- Alternating Current Question and Answers
- Eletromagnetic Wave
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Reflection of Light Question and Answers
- Refraction of Light Question and Answers
- Refraction of Light At Spherical Surface: Lens Question and Answers
- Dispersion and Scattering of Light Question and Answers
- Optical Instruments Question and Answers
- Light Wave and Interference of Light Question and Answers
- Diffraction and Polarisation of Light Question and Answers
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- Quantum Theory Question and Answers
- Atoms And Nucel
- Atom Question and Answers
- Atomic Nucleus Question and Answers
- Electronic Devices
- Semiconductors and Electronics Question and Answers
- Digital Circuits Question and Answers
- Communication Systems
- Communication System Question and Answers
 Sainavle
Sainavle
WBBSE Class 8 History Chapter 2 Hyderbad Ayodhya And Bengal And The Battle Of Plassey Long Answer Questions
Chapter 2 Rise Of Regional Powers Topic A Rise Of Regional Powers Hyderbad Ayodhya And Bengal And The Battle Of Plassey Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Discuss in detail the causes of the decline of the Mughal Empire.
Answer:
Mughal Empire Introduction:
The decline of the Mughal empire began with Aurangzeb’s death in 1707. After going through continuous wear and tear in the next fifty years the empire now became confined to Delhi, Agra, and their neighboring areas.
Then for a long time, it continued to exist in name only and the emperors were merely nominal heads.
Causes for the downfall of the Mughal Empire-
1. Jagirdari crisis:
Towards the end of the Mughal rule, the number of Mansabdars increased but the amount of land did not. Since the Jagirdars were unable to obtain
a product that was equivalent to their remuneration, they did not maintain the required number of soldiers and horses. So an administrative crisis arose which hastened the fall of the empire.
Class 8 History WBBSE
2. Conflict among courtiers:
The Mughal aristocrats were divided into three groupsIrani, Turani, and Hindustani. The conflict among them became so acute during the rule of the weak later Mughals that it shook the foundation of the government.
3. Erroneous policy of Aurangzeb:
Aurangzeb kept himself engaged in wars during a major period of his reign and thus drained the wealth, power, and energy of the kingdom.
His erroneous Rajput policy, Deccan policy, and orthodox religious policy brought about the downfall of the Mughal empire.
4. Peasant unrest:
The immense pressure created on the peasants as a result of the economic crisis made them desperate and they rose in rebellion. The Jat rebellion (1669),
the Satnami revolt (1672), and other Sikh revolts were the results of the financial crisis and Aurangzeb’s religious policies. Continuous peasant rebellions led to the decline of the Mughal empire.
5 Rise ofregional powers:
Many independent kingdoms arose taking advantage of the internal weakness of the Mughal empire.
Some of these kingdoms were Hyderabad under Nizam ulmulk, Ayodhya under Sadat Khan, and Bengal under Murshid Quli Khan.
Though they verbally owed loyalty to the emperor, their attitude and behavior helped in the rise of separatist tendencies.
6. Foreign invasions:
The invasion of Nadir Shah gave a death blow to the Mughal empire which was already weakened by an internal crisis. Nadir Shah invaded India in 1739 created a massacre and plundered enormous wealth.
Question 2. Discuss briefly the tribal revolts that took place in the frontier during Aurangzeb’s reign.
Answer:
Aurangzeb’s Reign Introduction:
During the reign of Aurangzeb, the tribals living on the Northwest frontier became rebellious and created chaos. Aurangzeb tried to subjugate them by using money and power.
Class 8 History WBBSE
Tribal Revolts In The Frontier During Aurganzeb’s Reign-
1. Bhagu revolt:
The people of the Yusufjai tribe attacked the Mughal officers under the leadership of Bhagu in 1667. They were cruelly suppressed by the Mughal general Amin Khan.
2. Revolt of Akmal Khan:
The Afridi tribe created much disturbance under the leadership of Akmal Khan in 1672. It is said that they killed 10,000 Mughal soldiers, imprisoned 20,000, and plundered wealth of about rupees 2 crore.
3. Revolt of Kushhal Khan:
The Khatak tribes joined the revolt of the Afridis under the leadership of Kushhal Khan. Many people who were attracted by the brilliant and charismatic personality of Kushhal Khan, joined the revolt.
However, the Mughal general Aghar Khan bribed the poor people and created dissension among them. This weakened the revolt.
Aurangzeb’s reign Results:
- Aurangzeb failed to get the supply of forces from the Afghan tribes during his war with the Rajputs.
- Besides, much of the wealth of the Mughal treasury was drained due to these frontier wars.
- Since Aurangzeb was busy with these frontier revolts the separatists in different areas increased their power.
Aurangzeb’s reign Significance: Aurangzeb had to send his army to suppress the frontier revolts and this brought much relief to Shivaji while carrying out his campaigns against the Mughals.
Question 3. Discuss the rise of Bengal as a provincial power.
Answer:
The Rise Of Bengal As A Provincial Power:-
Introduction:
After the death of rapidly Aurangzeb the Mughal Empire proceeded toward its downfall. The weak and inefficient rulers failed to keep the empire integrated and conduct the administration smoothly.
So chaos reigned everywhere and a number of regional powers arose.
Rise Of Independent KinG doms-
1. Subah of Bengal:
The Mughals had established their power in Bengal after defeating Daud Khan (the last Karrani Sultan) during the reign of Akbar. Since then Bengal was ruled by the Subedars appointed by the Mughal emperor.
2. Murshid Quli Khan as the Diwan of Bengal:
Aurangzeb sent Murshid Quli Khan, who had already attained much reputation as the Diwan of Berar in the Deccan, as the Diwan of Hyderabad, and then the Diwan of Bengal.
He was given the title of Murshid Quli for his achievements as the Diwan of Bengal.
During this time Azim-us-Shaan, Aurangzeb’s grandson, was the subedar of Bengal. However, the weakness of the Subedar helped Murshid Quli Khan to show his genius.
3 Murshid Quli Khan as the Subedar of Bengal:
After Aurangzeb’s death, the Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah first transferred Murshid Quli Khan to Deccan but after two years he appointed him again as the Diwan of Bengal.
Afterward, emperor Faruksiyar appointed him as the Subedar of Bengal.
Murshid Quli Khan showed ceremonious loyalty to the Mughal emperor and sent him regular taxes. However, in practice, he ruled over Bengal independently.
He founded an independent kingdom of Bengal taking advantage of the chaos prevailing in the Mughal empire.
Class 8 History WBBSE
Question 4. Discuss the emergence of Hyderabad as a regional power.
Answer:
The Emergence Of Hyderabad As A Regional Power:-
Introduction:
The decay of the Mughal empire began with the death of Aurangzeb. As a result, a number of regional or provincial powers arose in different parts of India.
Though they owed allegiance to the Mughal emperor they were practically independent. One such independent kingdom was Hyderabad.
Emergence Of Independent Hyderabad-
1. Rise of the Nizam:
The Turanis were an important elite group in the Mughal court. Mir Qamaruddin Khan Siddiqui was a member of this group during Aurangzeb’s time and was conferred the title of Chin Qilich Khan by the emperor.
He was also given the titles of Nizam-ul-Mulk and Asaf Jha by Emperor Faruksiyar and Emperor Muhammad Shah respectively.
He maintained a cordial relationship with all these emperors and started ruling over Hyderabad independently.

2. Defeat of Mubariz Khan:
The provincial Mughal ruler Mubariz Khan was appointed in Hyderabad almost as an independent ruler. He proceeded against the Nizam in 1724 by the order of emperor Muhammad Shah.
Mubariz Khan was killed and the Mughal army was routed out in the battle of Shakar-kheda. So Muhammad Shah accepted the Nizam as the ruler of the Deccan by a treaty.
3. Foundation of the Kingdom of Hyderabad:
Though the foundation of the independent kingdom of Hyderabad was laid under Nizam he never declared his independence officially.
The coins were circulated in the name of the Mughal emperor and the Khutba was also read in his name. So the Mughal emperor was never disturbed by the existence of Hyderabad.
In the meantime, the Nizam got an opportunity to lay the foundation of an independent kingdom.
Class 8 History WBBSE
4. Emergence of independent Hyderabad:
The administration of Hyderabad was formally based on the Mughal structure but the substantial modification was done internally.
These changes included making the Jagirs hereditary, appointing new officials, decentralization of administrative power, and so on.
In this way, Hyderabad began to emerge as an independent kingdom under Nizam.
Question 5. Discuss the emergence of Ayodhya as a regional power.
Answer:
The Emergence Of Ayodhya As A Regional Power:-
Introduction:
After Aurangzeb’s death, the Mughal empire began to disintegrate. As a result, the central administration became slack. A number of independent kingdoms arose in different parts of the country taking advantage of the situation.
Ayodhya was one such kingdom to assert its independence.

Rise Of Independent Ayodhya
1. Role of Sadat Khan:
Sadat Khan was appointed the Subedar of Ayodhya by the Mughal emperor.
Sadat Khan first suppressed the revolts of the local rulers and clan chiefs of Ayodhya ruthlessly and introduced a benevolent system of administration.
He treated the Hindus, who formed the majority, genially and appointed them to high posts. He also made the post of the Nawab hereditary. Moreover, he expanded his kingdom by adding Varanasi and Allahabad to it.
So he turned Ayodhya into almost an independent kingdom before his death.
2. Role of SafdarJung:
Sadat Khan maintained a cordial relationship with the Mughal emperor by virtue of which he placed his son-in-law Safdar Jung as the administrator of Ayodhya. Safdar Jung became the ruler after the death of Sadat Khan.
He suppressed the rebellious Ruphela Zamindar and the Pathans and established peace in his kingdom. He also introduced a secular type of administration in Ayodhya.
Though he owed allegiance to the Mughal ruler, he ruled over Ayodhya independently. Like Sadat Khan he also remained involved in court politics but, at the same time, established Ayodhya as an independent kingdom.
Question 6. Give an account of the background and outcome of granting data to the British East India Company.
Answer:
Background And Outcome Of Granting Data To The British East India Company:-
Introduction:
The Mughal emperor Faruksiyar gave the British East India Company the right to free trade in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa in lieu of an annual payment of rupees three thousand. This was called dastak.Background of receiving data
Background Of Receiving Dastak
The British East India Company also made its chief trading center in Bengal in 1651 like other

European trading companies. They received zamindari rights over the three villages of Kolkata, Sutanuti, and Gobindapur after prospering in their trade.
In order to gain more facilities they sent a delegation to emperor Faruksiyar in 1715 under the leadership of John Surman. Consequently, Faruksiyar issued his Firman (a royal decree) by which
the company received data on the right to free trade in Bengal in lieu of an annual payment of rupees three thousand in 1717.
Results Of Receiving Dastak-
1. Government recognition:
The facilities which the Company had so long been enjoying in the trade now came to be recognized by the government.
2. Enjoying additional facilities: The Company now began to enjoy some additional facilities. One such facility was that the chairman of
the English trading center could grant permission or data for free trade to his nominated business representative. On presenting this document no English ship would be checked by the officers of the Nawab.
3. Advancement of commercial competition:
In comparison to other European trading companies, the English Company progressed greatly in trade by virtue of the data.
Again, the native traders were unable to compete with the English Company since they could not carry on tax-free trade.
So they were adversely affected while the English Company made much headway.
Question 7. What do you know, about Clive’s conspiracy over the throne of Bengal?
Answer:
CIives’s Conspiracy
The first party to conspiracy-The British: The relationship between the British Company and Nawab Siraj Abdullah was never very cordial. The Company realized that Siraj aimed at uprooting the British power in India.
So, under the leadership of Clive, they targeted Siraj as their chief enemy and regarded it as their foremost duty to overthrow him.

The second party to the conspiracy-Relatives and officers of the Nawab:
The conspiracy of Plassey was mainly a creation of the nobles of Murshidabad.
When Siraj asked Jagat Seth to help him to suppress Shaukat Jung, the ruler of Purnia he refused and threatened Jagat Seth that he would convert him.
Again, Rai Durlabh and Mir Jafar were removed from the posts of Diwan and Bakshi respectively and they were offended by Siraj. Moreover, Siraj was young and not farsighted.
His rudeness offended his relatives who joined hands with the royal officials and the Seths to depose him and place Mir Jafar on the throne.
Clive took the opportunity and tried to remove the mortal enemy of the Company through a plot.
Secret agreement:
Clive made a secret agreement with Mir Jafar, Manikchand, Jagat Seth, Yar Latif, Rai Durlabh, Umichand, and other influential persons. The agreement contained that
After deposing Siraj Mir Jafar would become the Nawab
In lieu of the favor, the English Company would get sole power and maximum commercial facilities in Bengal and adjoining areas.
Question 8. Discuss the causes of the Battle of Plassey.
Answer:
Introduction:
The relationship Reasons for conflict between Siraj and the company deteriorated considerably and this culminated in the battle of Plassey.
Reasons For Conflict Between Siraj And The Company-
1. Defiance of the Nawab:
When Siraj became the Nawab, the Dutch, the French, and the Zamindars of Bengal showed their respect by sending him gifts but the British Company did not show any such respect and this offended Siraj.
2. Misuse of data:
The British East India Company got data on the right to free trade by virtue of Faruksiyar’s Firman. The company officials used data for personal business defying Nawab’s orders and depriving him of his due taxes.
3. Assisting the conspiracy:
Many royal officers and relatives could not accept Siraj as the Nawab and entered into a competition to usurp power. Clive utilized this internal conflict to build up a conspiracy against Siraj.

4. Insulting Siraj’s messenger:
Krishnadas amassed 53 lakh rupees of the dead Nawab of Dhaka and sought shelter at the English headquarters in Kolkata. When Siraj learned about it he sent his messenger Narayan Das asking
the British Company to hand over Krishna Das to him but Governor Drek insulted Narayan Das and drove him away.
5. Fortification of Kolkata:
During Siraj’s reign, the French and the English began to build forts in Chandannagar and Calcutta respectively. Siraj ordered them to stop the fortification. The French obeyed but the English did not.
Question 9. Discuss the Black Hole Tragedy briefly.
Answer:
Black Hole Tragedy
Background:
Siraj was highly enraged when the English neither handed over Krishna Das, the son of Rajballav, the Diwan of Dhaka nor stopped the construction of Fort William. Therefore, Siraj occupied Fort William on 20th June 1756.
Governor Drek, the English general, and other English lords managed to escape but many of them were captured by Siraj.
Account of Holwell:
According to Holwell, a British official, Siraj occupied Fort William and imprisoned 146 English people in a room, 18 ft long and 14ft and 10 inches wide, for an entire night. About 123 of them died of suffocation.

Imaginary tale:
Subsequently, it proved that the event was a piece of Holwell’s imagination. There was no possibility of 146 British people staying at the fort then, and it was also not possible to accommodate
So many people in such a small room. Maybe a few people were imprisoned there.
Dispute:
There is much controversy among historians and scholars regarding this incident. Jadunath Sarkar thinks that there were about 60-70 English people rather than 146. Again, the Nawab had nothing to do with the incident.
If happened due to the negligence of the officials. According to Akshay Kumar Maitra, the list of names of dead Englishmen given by Holwell was not true because most of them had either died earlier or lived on after the incident.
Anne Besant made an interesting comment on this incident “Geometry has proved that the arithmetical sum was wrong”.
Class 8 History Solution WBBSE
Question 10. What was the significance of the Battle of Plassey?
Answer:
Introduction:
The Battle of Plassey which took place between Siraj ud-daullah, the last independent Nawab of Bengal, and the British forces under Robert Clive had far-reaching effects.
According to historian Maleson, “No other battle had a such widespread, conspicuous, and permanent effect as the Battle of Plassey”.
Significance Of The Battle Of Plassey-
1. Establishment of Company’s authority over Bengal:
After gaining victory in the Battle of Plassey the British East India Company established its political authority over Bengal. Now they aimed at establishing their superiority all over India.
2. Establishment of authority over India:
Through the consolidation of power over Bengal the British government tried to establish its superiority over the whole of India. They utilized the resources of Bengal to bring other regions of India under colonial rule.
3. Authority over trade:
After winning the Battle of Plassey the Company started using data, i.e., the right to free trade. In this way, they established a monopoly over the trade and commerce of Bengal.
4. Drain of resources:
After the Battle of Massey the Company and its officials sent huge amounts of wealth and resources to England both legally and illegally. The historian Brooke Adams referred to this as the ‘Plassey plunder’.
5. Kingmakers:
The British now virtually became the kingmakers and appointed Mir Jafar, Mir Qasim, and Najm ud-daulah as Nawabs in exchange for a huge amount of money. The Nawabs now became mere puppets in the hands of the British.
6. Initiation of a new era:
The Indian society and civilization under British rule experienced a renaissance under the influence of Western education and a trend of thought. So the medieval period ended and the modern period set in.

Conclusion:
The Company crossed the first step towards colonial rule through the Battle of Plassey. According to Tarachand, ‘The defeat of Plassey has made the weakness of India conspicuous.
Class 8 History Solution WBBSE
Question 11. Focus on the dispute over Plassey’s plunder.
Answer:
Introduction:
The British East India Company sent huge wealth and resources from India to England after winning the Battle of Plassey.
They did not send these things in lieu of old, silver, or other commodities and so it was termed as ‘plunder’ by several scholars.
The historian Brooke Adams called this incident the ‘Plassey plunder’ or ‘Plassey loot’.
Dispute Over Plassey Plunder
Methods of Plassey Plunder: The Plassey Plunder took place in two ways. The first one was through Company officials and the second one was through the commercial, economic, and revenue policies of the Company.
Description of the plunder:
At this time the Company authority and the officials had dispatched rupees 50 crores to England. As a prior agreement, they got rupees one and a half crore by placing Mir Jafar on the throne of Bengal.
The chief hands behind the plunder, i.e., Robert Clive, Johnston Senior, and Sykes returned to England laden with wealth.
Difference of opinion:
There is a difference of opinion among historians regarding the exact amount of wealth and resources dispatched to England.
According to Holden Ferber, it was pounds 18 lacks between 1757-90, according to professor P. J. Marshal it was 5 lakh pounds annually and according to Dr. Amalesh Tripathi, it was 25-30 lakh rupees annually.
Result:
The Company met its administrative expenses from the wealth plundered from India.
They also built up a vast empire with the help of this wealth. Again, this wealth was used in fostering the Industrial Revolution and for the construction of modern England.
Question 12. Suppose you are a resident of Bengal during the reign of Siraj ud-daullah. Write a diary entry on your reaction to the defeat of Siraj in the Battle of Plassey.
Answer:
July 3, 1757, The English East India Company came to India for trade purposes but their activities are no more confined to trade and commerce. They are eager to interfere in the politics of Bengal.
Siraj ud-daullah has succeeded Alivardi Khan as the Nawab. Now the members of the royal family are conspiring against Siraj.
Jagat Seth, Raj Ballabh, Rai Durlabh, Umichand, Mir Jafar, and Miran have joined hands with Robert Clive, the chief official of the Company.
I have heard that they want to place Mir Jafar on the throne of the Nawab. Most probably Siraj is aware of the plot but I do not understand why he is not taking any action to crush his opponents.
This passivity on his part has now led to the Battle of Plassey. Now Nawab’s 70,000 soldiers faced the 3,000 soldiers of the Company on 23rd June 1757.
Astonishingly Nawab’s chiefs like Mir Jafar, Rai Durlabh, and Yar Latif remained absolutely inactive in the war and gave no instructions to The army.
Only two of the chiefs Mir Madan and Mohanlal fought bravely and died in the battle.
The entire army disintegrated due to betrayal on the part of Mir Jafar. Siraj was defeated in the battle. Now the rule of the British has started in Bengal.
I have heard that Miran, the son of Mir Jafar, has killed Siraj. Mir Jafar’s greed for Nawab’s throne brought about the sunset of Bengal’s independence.
I think it will no more be possible to stop the advancement of British power in India in the forthcoming days.
WBBSE Class 8 History Chapter 2 Rise Of Regional Powers Multiple Choice Questions
Chapter 2 Rise Of Regional Powers Topic A Rise Of Regional Powers Hyderbad Ayodhya And Bengal And The Battle Of Plassey Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. When did the Persians under the leadership of Nadir Shah attack Delhi?
- 1707-08
- 1738-39
- 1765-66
- 1757-58
Answer: 3. 1738-39
Question 2. Under whose leadership the Afghans attacked and destroyed the city of Delhi?
- Ahmed Shah Abdali
- Nadir Shah
- Mir Qasim
- Alauddin Khilji
- Sadat Khan
Answer: 1. Nadir Shah
Question 3. Who took the title of Asaf Jah?
- Alivardi Khan
- Sadat Khan
- Mir Qamar ud din Khan Siddiqi
- Mir Jafar
Answer: 3. Mir Qamar ud din Khan Siddiqi
Question 4. After capturing Kolkata, Siraj renamed it
- Sirajnagar
- Alipore
- Alinagar
- Sirajabad
Answer: 3. Alinagar
Class 8 History Solution WBBSE
Question 5. Aurangzeb appointed Murshid Quli Khan as Bengal’s
- Nazim
- Faujdar
- Diwan
- Ulema
Answer: 1. Nazim
Question 6. Who led the British army to reoccupy
- Lord Wellesley
- Lord Cornwallis
- Lord Clive
- Lord Dalhousie
Answer: 3. Lord Clive
Question 7. Who propagated the story of the ‘Black Hole tragedy’?
- Roger Drake
- Akshay Kumar Maitra
- Holwell
- Robert Clive
Answer: 3. Holwell
Question 8. Mir Qasim was the son-in-law of
- Alivardi Khan
- Mir Jafar
- Mir Qamar ud-din Khan Siddiqi
- Miran
Answer: 2. Mir Jafar
Question 9. Who was the Nawab when the Maratha Cavalry attacked Bengal?
- Murshid Quli Khan
- Alivardi Khan
- Siraj ud Abdallah
- Shuja ud din
Answer: 2. Alivardi Khan
Question 10. The last independent Nawab of Bengal was
- Siraj ud-Abdallah
- Mir Jafar
- Mir Qasim
- Alivardi Khan
Answer: 1. Siraj ud-Abdallah
Chapter 2 Rise Of Regional Powers Topic A Rise Of Regional Powers Hyderbad Ayodhya And Bengal And The Battle Of Plassey Select The Most Appropriate Expla Nation For The Following Statement
Question 1. The Mughal rulers who succeeded Aurangzeb could not retain the empire.
- The economic basis of the empire collapsed.
- The strength of the empire rapidly declined after the death of Aurangzeb.
- The administrative crisis could be noticed in the empire.
Answer: 2. The strength of the empire rapidly declined after the death of Aurangzeb.
Question 2. Internal revolts and external aggressions created a rift in the empire towards the end.
- The military power of the Mughals weakened.
- The aristocrats were involved in mutual rivalries.
- The war for succession had reached its climax.
Answer: 1 The military power of the Mughals weakened.
Question 3. The administrative structure of the Mughals collapsed after the reign of emperor Aurangzeb.
- The rate of revenue was considerably reduced.
- There were conflicts over the capturing of high administrative posts.
- There was much crisis in the Jaigirdari and Mansabdari systems.
Answer: 3. There was much crisis in the Jaigirdari and Mansabdari systems.
Question 4. Many regional powers arose by the middle of the 18th century. Explanation
- The authority and administrative structure of the vast Mughal empire weakened.
- Efficient provincial leaders emerged in different regions.
- The residents of different regions tried their best to have their demands fulfilled.
- Answer: 1. The authority and administrative structure of the vast Mughal empire weakened.
Question 5. The British East India Company involved the Jagat Seths in the conspiracy against Siraj.
- The Jagat Seths had great financial capacity.
- The Jagat Seths had much influence over the court of the Nawab of Bengal in Murshidabad.
- The Jagat Seths were all experienced and judicious.
Answer: 2. The Jagat Seths had much influence over the court of the Nawab of Bengal in Murshidabad.
Class 8 WBBSE History Question Answer
Question 6. The Mughals lost their control over the subah of Bengal during the regime of Alivardi Khan.
- The Mughal emperor granted independence to the subah of Bengal.
- Alivardi Khan won the strife against the Mughals.
- The Mughal ruler was not provided with any administrative information.
Answer: 3. The Mughal ruler was not provided with any administrative information.
Question 7. Faruksiyar’s Firman created a conflict between the British and the Nawab of Bengal.
- Faruksiyar’s Firman declared that a specific financial grant was to be given to the British Company.
- The Company began to carry on unlimited trade in Bengal taking advantage of the exemption of taxes as granted by Faruksiyar’s firman.
- Faruksiyar’s firman had inhibited the trading rights of European countries other than the British.
Answer: 2. The Company began to carry on unlimited trade in Bengal taking advantage of the exemption of taxes as granted by Faruksiyar’s firman.
Question 8. The relationship between the English company and Murshid Quli Khan the Nawab of Bengal had deteriorated.
- The English traders misused the data for personal trade and evaded the taxes which were due to the Nawab. Explanation
- The English traders built forts disobeying the instructions of the Nawab. Explanation
- The English traders got involved in a conflict with the officials of the Nawab.
Answer: 1. The English traders misused the data for personal trade and evaded the taxes which were due to the Nawab. Explanation
Question 9. Statement The relationship between the British company and Alivardi Khan, the Nawab Bengal, deteriorated.
- Alivardi Khan killed some clerks of the British company.
- Alivardi Khan ordered the British traders to leave Bengal.
- Alivardi Khan demanded rupees thirty lacks from the British company which refused to pay it.
Answer: 3. Alivardi Khan demanded rupees thirty lacks from the British company which refused to pay it.
Question 10. Statement The relationship between the British East India Company and Siraj ud- Abdallah, the Nawab of Bengal, deteriorated. Explanation
- Siraj demanded a lot of money from the British trading company for the development of trade.
Explanation - The British company fortified Calcutta defying Siraj’s orders. Explanation
- There was a conflict between Nawab’s officials and British officials.
Answer: 2. The British company fortified Calcutta defying Siraj’s orders. Explanation
Question 11. Statement The political powers in the Indian subcontinent were in continuous conflict during the 18th century.
- They were all war-mongers. Explanation
- They wanted to display their military powers before each other. Explanation
- Each of them endeavored to increase their jurisdiction and resources.
Answer: 3. Each of them endeavored to increase their jurisdiction and resources.
Chapter 2 Rise Of Regional Power Topic B Battle Of Buxar And British Resident System Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The Company abolished the dual system of administration in
- 1757
- 1772
- 1780
- 1792
Answer: 2.1772
Question 2. The policy of Subsidiary Alliance was introduced by
- Lord Wellesley
- Lord Dalhousie
- Lord Clive
- Lord Verelst
Answer: 1. Lord Wellesley
Question 3. The Treaty of Salbai was signed in
- 1770
- 1782
- 1792
- 1799
Answer: 2. 1782
Question 4. The French governor of Pondicherry was
- Robert Clive
- Dupleix
- Vasco da Gama
- Magallen
Answer: 2. Dupleix
Question 5. To become Nawab with British support, MirQasim had to pay almost
- 25 lakhs
- 27 lakhs
- 29 lakhs
- 31 lakhs
Answer: 3. 1.29 lakhs
Question 6. The Governor of Kolkata at the time of the grant of Diwani was
- Robert Clive
- Henry Drek
- Cartier
- Verelst
Answer: 1. Robert Clive
Question 7. The year 1770 is famous in history for
- famine
- Diwani
- dual government
- war
Answer: 1. famine
Question 8. Who became the Nawab of Bengal after Mir Jafar?
- Najm ud-Abdallah
- Mir Qasim
- Alivardi Khan
- Siraj ud-Abdallah
Answer: 2. Mir Qasim
WBBSE Class 9 History Multiple Choice Questions
- Chapter 1 Some Aspects Of The French Revolution Multiple Choice Question And Answers
- Chapter 2 Revolutionary Ideals, Napoleonic Empire And Nationalism Multiple Choice Question And Answers
- Chapter 3 Europe In The 19th Century Multiple Choice Question And Answers
- Chapter 4 Industrial Revolution, Colonialism And Imperialism Multiple Choice Question And Answers
- Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Multiple Choice Questions
- Chapter 6 The Second World War And Its Aftermath Multiple Choice Questions
- Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Multiple Choice Questions
WBBSE Class 9 History Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 1 Some Aspects Of The French Revolution Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 2 Revolutionary Ideals, Napoleonic Empire And Nationalism Very Short Question and Answers
- Chapter 3 Europe In The 19th Century Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 4 Industrial Revolution, Colonialism And Imperialism Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 6 The Second World War And Its Aftermath Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Very Short Answer Questions
WBBSE Class 9 History Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 1 Some Aspects Of The French Revolution Very Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 2 Revolutionary Ideals, Napoleonic Empire And Nationalism Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 3 Europe In The 19th Century Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 4 Industrial Revolution, Colonialism And Imperialism Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 6 The Second World War And Its Aftermath Short Answer Questions
- Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Short Answer Questions
WBBSE Class 9 History Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 1 Some Aspects Of The French Revolution Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 2 Revolutionary Ideals, Napoleonic Empire And Nationalism Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 3 Europe In The 19th Century Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 4 Industrial Revolution, Colonialism And Imperialism Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Long Answer Questions
- Chapter 6 The Second World War And Its Aftermath Long Answer Questions
WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 History Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Multiple Choice Questions
Class 9 History Chapter 7 WBBSE The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic A Foundation and Organisation of the League of Nation Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The League of Nations was formed after-
1. First World War
2. Second World War
3. First Balkan War
4. Second Balkan War
Answer: 1. First World War
Question 2. President Wilson belonged to-
1. France
2. USA
3. Italy
4. Spain
Answer: 2. USA
Question 3. Which of the following personalities was most active in the establishment of the League of Nations?
1. Woodrow Wilson
2. Clemenceau
3. Lloyd George
4. Orlando
Answer: 1. Woodrow Wilson
Question 4. The country which did not join the League of Nations was-
1. Germany
2. Britain
3. America
4. Spain
Answer: 3. America
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 History Multiple Choice Questions
Question 5. The session of the League of Nations was held in a year-
1. Once
2. Twice
3. Thrice
4. Weekly
Answer: 1. Once
Class 9 History Chapter 5 WBBSE
Question 6. The executive body of the League of Nations was called-
1. Security Council
2. Secretariat
3. Executive Board
4. Board of Directors
Answer: 1. Security Council
Question 7. The highest officer of the Secretariat of the League of Nations was called-
1. Secretary General
2. Chairman
3. General Secretary
4. Collector
Answer: 1. Secretary General
Question 8. Russia joined the League of Nations in
1. 1933
2. 1934
3. 1936
4. 1938
Answer: 2. 1934
Question 9. Japan gave up the membership of League of Nations in
1. 1933
2. 1938
3. 1992
4. 1900
Answer: 1. 1933
Question 10. Which treaty set up the League of Nations?
1. Treaty of Sevres
2. Treaty of Versailles
3. Treaty of St. Germain
4. Treaty of Trianon
Answer: 2. Treaty of Versailles
Class 9 History West Bengal Board
Question 11. The prestige of the League of Nations was generally satisfactory till –
1. 1920
2. 1930
3. 1940
4. 1950
Answer: 2. 1930
Question 12. In the beginning, the country which was not allowed membership was-
1. France
2. Britain
3. Britain
4. Canada
Answer: 2. Britain
Question 13. Which nation was a member of the League of Nations during its entire existence?
1. Japan
2. France
3. Germany
4. Russia
Answer: 2. France
Question 14. Which of the following is not associated with the organisation of the League?
1. A secretariat
2. A world bank
3. A court of international justice
4. An assembly
Answer: 2. A world bank
Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic B United Nations: Charter and Organisation Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
Question 1. The UNO was founded on-
1. 24 October 1945
2. 29 October 1946
3. 24 October 1947
4. 25 October 1946
Answer: 1. 24 October 1945
Question 2. The number of judges in the International Court of Justice is-
1. 15
2. 16
3. 17
4. 18
Answer: 1. 15
Class 9 History West Bengal Board
Question 3. The UN Charter was finalised and became effective-
1. San Francisco, 24 October, 1945
2. Paris, 5 March 1944
3. Yalta, 2 February 1945
4. None of these.
Answer: 1. San Francisco, 24 October 1945
Question 4. Trygve Lie, the first Secretary General of UNO, was from-
1. USA
2. Norway
3. Korea
4. France
Answer: 2. Norway
Question 5. The term of office of a judge of the International Court of Justice is-
1. 6 years
2. 8 years
3. 7 years
4. 9 years
Answer: 4. 9 years
Question 6. The number of principal organs of the United Nations is-
1. 6
2. 5
3. 4
4. 3
Answer: 1. 6
Question 7. The following is not associated with the UN-
1. ILO
2. WHO
3. ASEAN (Association for South East Asian Nations)
4. IMF
Answer: 3. ASEAN (Association for South East Asian Nations)
Question 8. Which of the following is not a chief organ of the UNO?
1. International Labour Organisation
2. Security Council
3. International Court of Justice
4. General Assembly
Answer: 1. International Labour Organisation
Question 9. The full form of ILO is-
1. Internal Labour Organisation
2. International Labour Organisation
3. International Lawyers’ Organisation
4. Internal Labour Office
Answer: 2. International Labour Organisation
Question 10. UNO was established after-
1. Russo-Japanese war
2. First World War
3. Second World War
4. The Battle of Waterloo
Answer: 3. Second World War
Question 11. Atlantic Charter was declared by-
1. Roosevelt and Churchill
2. Churchill and Stalin
3. Jawaharlal Nehru and Stalin
4. None of the above
Answer: 1. Roosevelt and Churchill
Question 12. The UN Charter was ratified in 1945 by-
1. 25 nations
2. 33 nations
3. 51 nations
4. 37 nations
Answer: 3. 51 nations
WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 History Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Very Short Answer Questions
Class 9 History WBBSE Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic A Foundation and Organisation of the League of Nation Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Question 1. What were the three principal organs of the League of Nations?
Answer:
The three principal organs of the League of Nations were:
[1] The Assembly.
[2] The Council and
[3] The Secretariat.
Question 2. Who could become members of the General Assembly of the League of Nations?
Answer: All the states which were members of the League of Nations were essentially members of the General Assembly.
Question 3. How were new members admitted in the League Assembly?
Answer: Any member could be admitted in the League Assembly by a vote of assent by of the existing members.
Question 4. Name the two great powers which were not members of the League in the beginning.
Answer: The two great powers which were not members of the League, in the beginning, were USA and Germany.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 History Very Short Answer Questions
Question 5. Who elected the temporary members of the League Council?
Answer: The temporary members of the League Council were elected by the League Assembly.
Question 6. Name the countries which first elected as members of the League Council.
Answer: The countries which were first elected as members of the League Council were England, France, Italy and Japan.
Class 9 History WBBSE
Question 7. What were the two autonomous bodies of the League of Nations?
Answer:
The two autonomous bodies of the League of Nations were:
[1] The Permanent Court of International Justice and
[2] The International Labour Organisation.
Question 8. When was the first session of the League convened?
Answer: The first session of the League was convened in 1920.
Question 9. Where was the first session of the League of Nations held?
Answer: The first session of the League of Nations was held in the city of Geneva, Switzerland.
Question 10. When was the last session of the League of Nations held?
Answer: The last session of the League of Nations was held on 14th December 1939.
Question 11. What is Covenant?
Answer: The Constitution of the League of Nations is called Covenant.
Question 12. How was the Secretary General of the League of Nations appointed?
Answer: The Secretary General of the League of Nations was appointed by the Council through the formal approval of the Assembly was necessary.
Question 13. When was the Permanent Court of International Justice opened and where?
Answer: The Permanent Court of International Justice was opened in 1922 in Hague, the erstwhile capital of Holland.
Question 14. What was the function of the Permanent Court of International Justice?
Answer: The function of the Permanent Court of International Justice was to settle international disputes which might be referred to it by the Council of the League and interpret international treaties and other legal complications.
Question 15. In which year the Aland Islands issue was settled by the League of Nations?
Answer: In 1921 the Aland Islands issue was settled by the League of Nations.
Class 9 History WBBSE
Question 16. Which commission was appointed by the League of Nations to determine the cause of the Japanese invasion of Manchuria?
Answer: The Lytton Commission was appointed by the League of Nations to determine the cause of the Japanese invasion of Manchuria.
History Class 9 WBBSE Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic B United Nations: Charter and Organisation Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
Question 1. Who selected the name United Nations Organisation?
Answer: The name United Nations Organisation was selected by the American President Franklin Roosevelt.
Question 2. From where did Franklin Roosevelt select the name United Nations Organisation?
Answer: Franklin Roosevelt selected the name United Nations Organisation from Lord Byron’s poem ‘The Childe Harold’s Pilgrimage’.
Question 3. When was the UNO established and where?
Answer: The UNO was first established on 24 October 1945, in New York, USA.
Question 4. For how many years and by whom are the members of the Security Council elected?
Answer: The members of the Security Council are elected for two years by the members of the General Assembly.
Question 5. How are new members admitted in the UNO?
Answer: New members are admitted in the UNO on the recommendation of the Security Council and by a vote of assent by 2/3 of the existing members of the General Assembly.
Question 6. How many members are there in the Security Council of the UNO at present?
Answer: There are 15 members in the Security Council of the UNO at present.

Question 7. What is the seventh principle enumerated in the UN Charter?
Answer: The seventh principle enumerated in the UN Charter is that the UN would not interfere in matters strictly within the domestic jurisdiction of any state.
Question 8. How many principles have been mentioned in the UN Charter?
Answer: Seven principles have been mentioned in the UN Charter.
Question 9. How many charter members were there in the UNO?
Answer: There were 51 charter members in the UNO.
History Class 9 WBBSE
Question 10. Which countries are the five members of the Security Council with the power of Veto?
Answer: The five members of the Security Council who have the power of Veto are the USA, USSR, England, France and China.
Question 11. What is the judicial organ of the United Nations?
Answer: The judicial organ of the United Nations is the International Court of Justice.
Question 12. How many judges are there in the International Court of Justice?
Answer: There are 15 judges in the International Court of Justice.
Question 13. How are the judges of the International Court of Justice elected?
Answer: The judges of the International Court of Justice are elected by the General Assembly and the Security Council.
Question 14. Name two organisations under the Economic and Social Council.
Answer: The two organisations under the Economic and Social Council are UNESCO (United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organisation) and FAO (Food and Agricultural Organisation).
Question 15. What does UNICEF stand for?
Answer: UNICEF stands for United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund.
Question 16. Where is the headquarters of WHO?
Answer: The headquarters of WHO is in Geneva.
Question 17. What does WHO stand for?
Answer: WHO stands for World Health Organisation.
Question 18. What does UNESCO stand for?
Answer: UNESCO stands for United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation.
History Class 9 WBBSE
Question 19. What is the composition of the Trusteeship Council?
Answer: The Trusteeship Council is composed of the representatives of permanent members of the Security Council, representatives of all those states which hold the administration of colonies and some representatives elected by the General Assembly.
Question 20. How is the head of the Secretariat of UNO appointed?
Answer: The head of the Secretariat, the Secretary-General, is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council.
Question 21. Who is the present secretary general of UNO?
Answer: The present secretary general of UNO is Antonio Guterres.
Question 22. When and where was the United Nations Declaration signed?
Answer: On 1 January 1942 the United Nations Declaration was signed in Washington.
Question 23. Where is the headquarter of Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)?
Answer: The headquarter of the Food and Agriculture Organisation is located in Rome.
WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 History Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Short Answer Questions
Class 9 History Book West Bengal Board WBBSE Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic A Foundation and Organisation of the League of Nation Short Answer Questions
Question 1. How was the League of Nations founded?
Answer:
League Of Nations Founded:-
The terrible repercussion of the First World War (1914-18) made a strong impact on the minds of the people and made them cry out for peace. President Woodrow Wilson of the United States of America took the initiative and made a plan to establish a world peace organisation known as the League of Nations which would solve disputes peacefully. The League of Nations was thus not only an expression of the call to peace, but it was also a means of promoting the call to peace.

Question 2. With what aim was the League of Nations founded?
Answer:
Aim Of The League Of Nations Founded:-
After the First World War (1914-18) an international peace organisation known as the League of Nations was established in 1920 with the following aims in view:
[1] To prevent armed conflict and to promote international peace and cooperation,
[2] To establish honourable relations among different nations,
[3] To promote international disarmament in order to reduce tension and
[4] To find out ways and means for peaceful settlement of international disputes.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 History Short Answer Questions

Question 3. Describe the structure of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Class 9 History WBBSE Structure Of The League Of Nations:-
The League of Nations had four main. organs, the first of which was the Assembly consisting of representatives of every member state, meeting once a year at Geneva.
The second organ was the Council i.e, the executive committee composed of one representative from each of the five permanent states (Great Britain, France, Germany, Italy and Japan) and temporarily of nine other member states, chosen by the Assembly.
The third was the permanent Secretariat, located at Geneva the main function of which was to prepare reports for the consideration of the Assembly and the Council. The fourth organ was the Permanent Court of International Justice which was a court of arbitration for the settlement of international disputes with its office at Hague.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
Question 4. Write a note on the Covenant of the As United States did not accept the League of Nations.
Answer: The Constitution of the League of Nations called the Covenant consisted of 26 articles among which the tenth, twelfth and sixteenth articles were of great significance.
[1] Under the tenth article of the Covenant, the members of the League of Nations promised to respect the political independence and territorial integrity of the member countries of the League.
[2] According to the twelfth article, the members unanimously decided to solve their problems, through mutual negotiations.
[3] The sixteenth article made it clear that if any member country of the League of Nations declared war and violated settlements, that country would be declared the enemy of all nations and her aggression would be faced with all might.
Question 5. Give an account of the General Assembly of the new permanent members. The function of the League of Nations.
Answer: The League of Nations functioned through a number of organs, the most important of which was the Assembly. All the states which were members of the League were essentially members of the Assembly. Every member state could send three representatives, although no state had more than one vote.
The function of the Assembly of the League was:
[1] To establish world peace.
[2] To resolve international disputes.
[3] To extend international security and
[4] To work for safeguarding the interests of minorities.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
Question 6. Who were the members of the League Council?
Answer:
The members of the League Council were divided into two divisions:
[1] Permanent members and
[2] Temporary members.
There were five permanent members of the Council, viz, Great Britain, USA, France, Italy and Japan. As the United States did not accept membership of the League of Nations, the number of permanent members remained at only four.
The number of temporary members were four. Later on, the number of permanent members were increased to six and temporary members to nine. Germany and Russia became the new permanent members.
Question 7. Give an account of the Council of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Council Of The League Of Nations:-
The League Council comprised nine four temporary members. The five permanent members of which five were permanent and members were Great Britain, the USA, France, Italy membership of the League, the number of and Japan. As the USA did not accept the on number of permanent members were permanent members remained only four. Later increased to six. Germany and Russia became the new permanent members.
The function of the League Council were:
[1] To discuss about various international disputes and to resolve them.
[2] To make efforts to stop a war and to reduce armament.
[3] Summoning of international conferences to resolve disputes.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
Question 8. Who are the permanent members of the League Council?
Answer:
Permanent Members Of The League Council:-
The Council of the League consisted of four permanent members. Later the number of members were increased to six. England, France, Italy and Japan were permanent members. Later on, Russia and Germany were admitted as permanent members.
Question 9. What were the main functions of the League Council?
Answer:
The main functions, of the League Council, were:
[1] To discuss about various international disputes and to resolve them.
[2] To make efforts to stop war and to reduce armaments.
[3] Summoning of international conferences to resolve disputes.
Question 10. What was the function of the Secretariat and their obligations to the League. of the League of Nations?
Answer:
The function of the Secretariat of the League of Nations were:
[1] To list the subjects to be considered in the Assembly.
[2] To preserve the documents and necessary papers regarding the minutes of the meetings, settlements and treaties concluded among the member states,
[3] To offer necessary suggestions for effecting modifications in the treaties.
Class 9 History WBBSE
Question 11. Mention any two causes of the failure of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Two causes for the failure of the League of Nations were:
[1] the League was never able to make itself truly ‘representative of the entire world. Countries like USA, Germany, Russia, Italy and Japan were not members of the League at different stages and no international organisation can be really successful if some of the great powers remain outside of it.
[2] The League had no army, navy or air force of its own nor was it in a position to apply economic sanction on the Great Powers which looked after their own interests instead of fulfilling
Question 12. Who is known as the ‘Father of the League of Nations? Who was the first secretary-general of the league?
Answer:
1. US President Woodrow Wilson is known as the ‘Father of the League of Nations’.
2. The first secretary general of the League of Nations was Eric Drummond.
Question 13. Mention two features of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Two features of the League of Nations were:
[1] To settle international disputes by peaceful means.
[2] To settle all international legal disputes among the members of the league.
Class 9 History WBBSE Chapter 7 The League Of Nations And The United Nations Organisation Topic B United Nations: Charter and Organisation Short Answer (SA) Type Questions Answer
Question 1. How did the United Nations Organisation come into being?
Answer:
United Nations Organisation:-
The League of Nations collapsed under the impact of the Second World War and the allied powers felt the need of a world peace organisation. Winston Churchill, Prime Minister of Britain and Franklin Roosevelt, President of the USA announced the Atlantic Charter where the term ‘United Nations’ was first adopted.
In the Moscow Conference (1943) Britain, the USA, Russia and China were unanimous that an international peace organisation should be set up. This resolution was confirmed in the Dumberton Oaks Conference (1944) and Yalta Conference (1945). Representatives of 50 nations met at San Francisco (1945) and prepared a Charter for world peace called UN Charter. On 24 October 1945, the United Nations Organisation (UNO) came into existence.
Question 2. What are the principal aims (objectives) of the UNO?
Answer:
The principal aims (objectives) of the UNO established after the Second World War are:
[1] to maintain world peace, prevent armed conflict among nations, promote the peaceful settlement of international disputes and to remove international tension.
[2] to promote education, culture and health of mankind and to promote the economic condition of the poor and underdeveloped nations.

Question 3. What is the UN Charter?
Answer:
UN Charter:-
Between April and June 1945 representatives of 50 nations who were directly or indirectly involved in the war against the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy and Japan) met at a conference at San Francisco. The Big Four (Britain, France, USA, and Russia) dominated the conference and prepared a charter for world peace called the UN Charter.
Class 9 History WBBSE
Question 4. What are the basic principles of UNO?
Answer:
The basic principles of UNO are:
[1] All the members, big or small, in order to enjoy the rights and benefits would sincerely carry out their duties as per the UNO charter.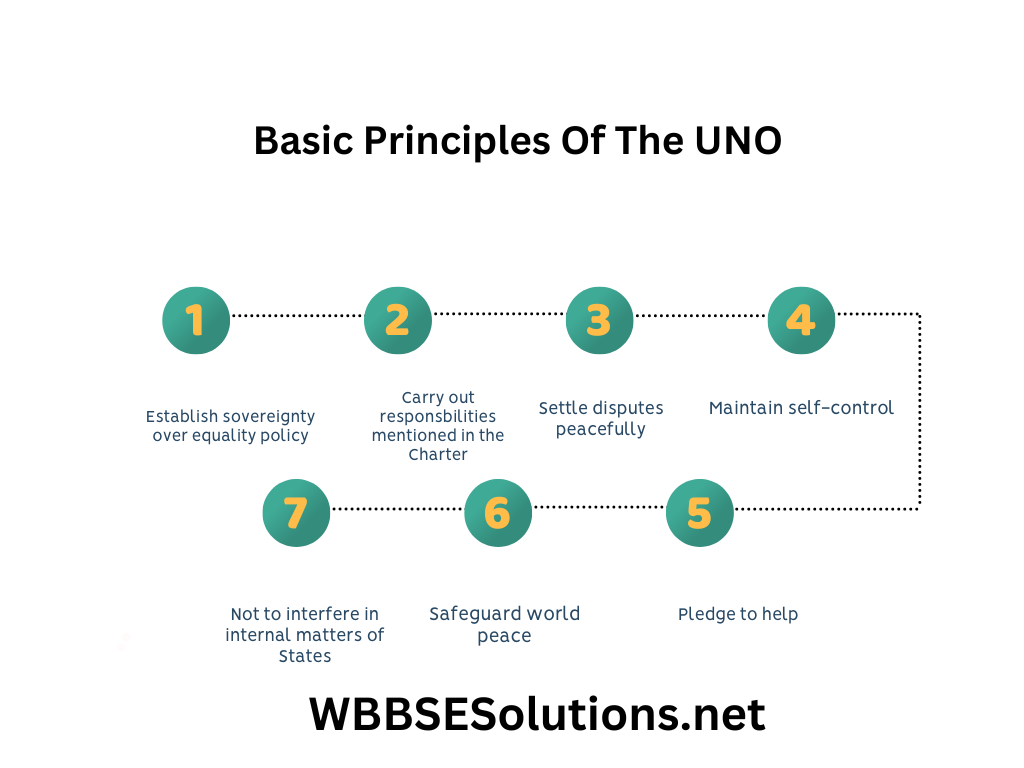
[2] All the members shall settle international disputes by peaceful means.
[3] UNO would not interfere in the internal affairs of any country.
[4] All members would enjoy the same sovereign status.
[5] All members pledge to help.
[6] All members would safeguard world peace.
Question 5. Write a note on membership of the UNO.
Answer:
Membership Of The UNO:-
[1] The membership of the UNO is open to all peace-loving nations of the world which accept the obligation of the UNO and are willing to carry out these obligations.
[2] 51 states who signed the UN Charter are the original members of the UN.
[3] Any member could be admitted in the UN on the recommendation of the Security Council and by a vote of assent by of the existing members of the General Assembly.
[4] America, England, France, Russia and China are the permanent members of the UN Security Council.
[5] If member countries persistently violate the principles of the Charter they may be expelled by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council.
Question 6. What is the function of the International Court of Justice?
Answer:
Function Of The International Court Of Justice:-
The function of the International Court of Justice is to solve the legal disputes that arise between different countries e.g. interpretation of treaties, application of principles of international law to a particular dispute or situation and settles issues of commensurate compensation for breach of international law etc. It also gives legal advice to the Security Council and the General Assembly.
Class 9 History WBBSE
Question 7. What is FAO and WHO?
Answer:
FAO And WHO:-
FAO and WHO are two specialised agencies of the Economic and Social Council. FAO is Food and Agricultural Organisation and WHO is World Health Organisation.
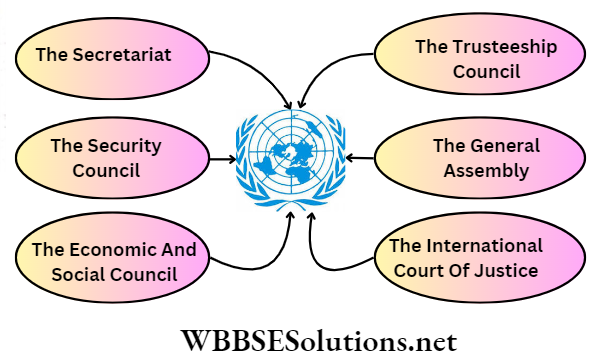
Question 8. What are the six main organs of the UNO?
Answer:
The six main organs of the United Nations organisation are:
[1] The General Assembly.
[2] The Security Council.
[3] The Economic and Social Council.
[4] The Trusteeship Council.
[5] The International Court of Justice and
[6] The Secretariat.
Question 9. Why is 24 October celebrated as United Nations Day?
Answer:
24 October Celebrated As United Nations Day:-
Between April and June of 1945, representatives of 50 nations who were directly or indirectly involved in the war against the Axis Powers met at a conference led by Britain, France, the USA and Russia at San Francisco and prepared a charter for world peace called the UN Charter. The Charter became officially effective on 24 October. So this day is celebrated as the United Nations Day.
Question 10. What is ‘Veto’?
Answer:
Veto:-
The foremost responsibility of the Security Council is the maintenance of international peace and security. All the five permanent members of the Security Council (USA, USSR, UK, France and China) must agree on all important issues. A negative vote by any one permanent member is called a ‘Veto’. If the Veto is exercised, then the proposal or resolution is considered not passed. So on this issue, the Security Council cannot take any action.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
Question 11. What are the different specialised agencies of the Economic and Social Council?
Answer:
The different specialised agencies of the Economic and Social Council are:
[1] ILO (International Labour Organisation).
[2] UNESCO (United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organisation).
[3] WHO (World Health Organisation).
[4] FAO (Food and Agricultural Organisation).
[5] IMF(International Monetary Fund)
Question 12. What is the composition of the General Assembly?
Answer:
Composition Of The General Assembly:-
The General Assembly of the UNO consists of all member states of the United Nations Organisation. Each member state can send five representatives to the session of the General Assembly. The total strength of the UN General Assembly is now 193.
Question 13. What is the composition of the Security education, and improvement of the standard of the Council of the United Nations Organisation? Or, Write a note on the membership of the Security Council.
Answer: The most important organ of the UNO is the Security Council. There are two types of members in Council-permanent and non-permanent. Five permanent members are the USA, USSR, UK, France and China. The ten non-permanent members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of two years.
Question 14. Name the permanent members of the Security Council of the UNO.
Answer:
The permanent members of the Security Council of the UNO are:
[1] America.
[2] England.
[3] France.
[4] Soviet Russia.
[5] China.

Question 15. What are the functions of UNESCO?
Answer:
Functions Of UNESCO:-
UNESCO deals with the issues of economic and social welfare and works for the preservation of human rights across the globe. This body fights against illiteracy and devotes itself to the protection of health, the spread of living of the people. The task before UNESCO includes education, social science, natural science, mass communication, cultural activities and relief services.
Question 16. What are the functions of WHO?
Answer:
Functions Of WHO:-
WHO (World Health Organisation) organises campaigns throughout the world against diseases such as pox, plague, smallpox, cholera and others. It undertakes medical research to find out the causes of diseases, improve vaccines and train medical research and aid workers.
Question 17. What are the functions of UNICEF?
Answer:
Functions Of UNICEF:-
The function of UNICEF is to help the establishment was to improve the condition of
member countries improve the health condition of their children and to save the lives of sick or starving children in the world who suffer from malnutrition, hunger and different kinds of diseases. It also looks after social welfare and vocational training of children. It also helps in the production of inexpensive books for children.
Question 18. What are the functions of the Security countries? An indirect function of the Trustee- Council of the UNO?
Answer:
The functions of the Security Council of the UNO are:
[1] To maintain international peace and security,
[2] To investigate all disputes and recommends ways and means for a peaceful settlement,
[3] To take action against a defaulting state and ask its members to send military forces in order to control a dangerous
situation.
Question 19. What are the functions of the Economic and Social Council?
Answer:
The functions of the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), a non-political organ of the UNO are:
[1] to promote the economic and social advancement of all people,
[2] planning of economic development, financial and technical assistance to underdeveloped countries, industrialisation of backward countries, improvement of education and aid to the world’s needy children,
[3] to appoint special committees from time to time to study specific problems.
Question 20. Write a short note on International Labour Organisation (ILO).
Answer:
International Labour Organisation (ILO):-
The headquarters of the International Labour Organisation was established at Geneva. All the member-states were also members of the International Labour Organisation. The main aim behind its establishment was to improve the condition of the labourers in different countries.
Question 21. Write a note on the function of the Trusteeship Council.
Answer:
Function Of The Trusteeship Council:-
After World War II, some underdeveloped countries were placed under the supervision of the Council. The primary task of the Council is to look after the economic, social, political and cultural development of these Countries. An Indirect function of the Trusteeship Council is to eliminate the possibility of rivalry among powerful nations of the world for the exploitation of underdeveloped nations.
Question 22. What is the function of the head of the Secretariat?
Answer:
Function Of The Head Of The Secretariat:-
The head of the Secretariat, the Secretary-General, prepares an annual progress report of the UNO and places it before the General Assembly. He has the right to draw the attention of the Security Council to any matter which in his opinion, may threaten international security.
Question 23. When was the Yalta Conference held? Name the countries which took part in the Yalta Conference.
Answer:
1. The Yalta Conference was held in 1945.
2. The countries which took part in the Yalta Conference were USA, Britain and Russia.
Question 24. When and where was the Atlantic Charter signed?
Answer:
Atlantic Charter:-
The Atlantic Charter was signed on 11 August 1941. Winston Churchill, the Prime Minister of Britain, and Franklin Roosevelt, President of the USA met together on a warship called the ‘Prince of Wales’ in the Atlantic Ocean near Newfoundland and signed the Atlantic Charter.
Question 25. What is the importance of the Atlantic Charter?
Answer:
Importance Of The Atlantic Charter:-
The Atlantic Charter is important because it contained the aims and fundamental principles for the reconstruction of the post-Second World War. An indication to set up a world organisation for the preservation of peace in the world was given in this Charter. In this Charter, the term ‘United Nations’ was first adopted.
Question 26. Mention two limitations of the UNO.
Answer:
Limitations Of The UNO:-
[1] The first limitation of the UNO is that the right of absolute veto has been given to each of the ‘Big Five (USA, UK, France, China and Russia). The Big Powers have always on several occasions misused this right in their self interest.
[2] UNO has not achieved success in gaining the cooperation of all the ‘Big Five’ at a time on the question of the enforcement of the decision of the Security Council with the help of an international army.

Question 27. Give an account of the success and failure of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Success And Failure Of The League Of Nations:-
The League of Nations utterly failed in its fundamental aim to prevent war and to maintain peace and order in the world on a permanent basis. The world had to witness again the Second World War in 1939 which proved the failure of the League.
On the other hand, if we evaluate the work of the League of Nations we find that the League tried its best to solve political disputes and the controversies which arose among different countries. In addition to this, the League acted also in the social and humanitarian fields for the benefit of mankind.

