Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life Plant Tissue And Its Distribution Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Mention the correlation amongst cells, tissues, organs and body.
Answer:
Cells are the structural and functional unit of a living body. Cells of the same origin and function having similar or dissimilar structures form a tissue. One or more types of tissue when unite to perform a specific function, form a tissue system. Several tissue systems constitute an organ and various organs form a body.
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system → Organism
2 What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer:
The different utility of tissues in multicellular organisms is as follows:
1. Tissue brings division of labour to increase efficiency.
2. Tissues become organised to form organs and organ systems.
3. It decreases the workload of individual cells.
4. Chances of survival of the organisms increase due to higher efficiency and better organisation.
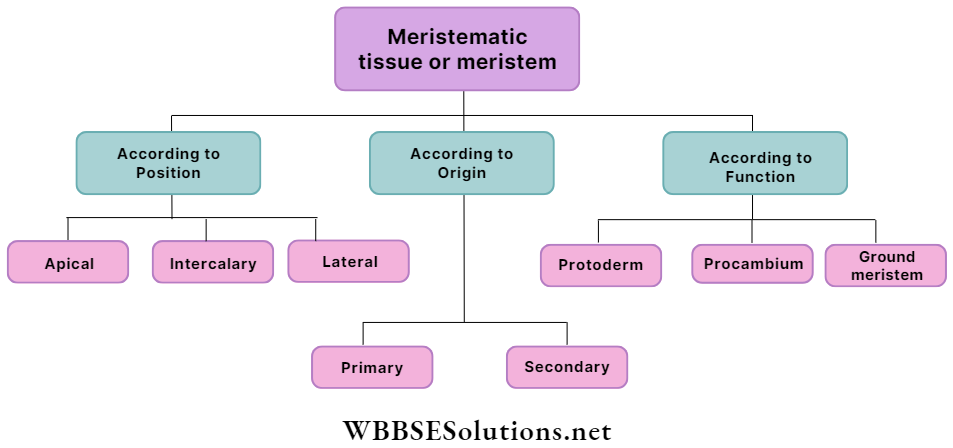
Question 3. Represent the classification of meristematic tissue based on position, origin and function in the form of a chart.
Answer:
We can classify meristematic tissue in the following way:
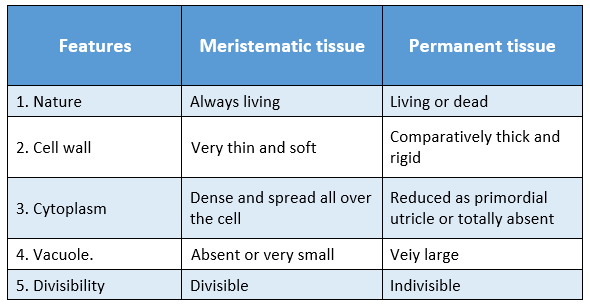
Question 4. Distinguish between meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between meristematic tissue and permanent tissue are:
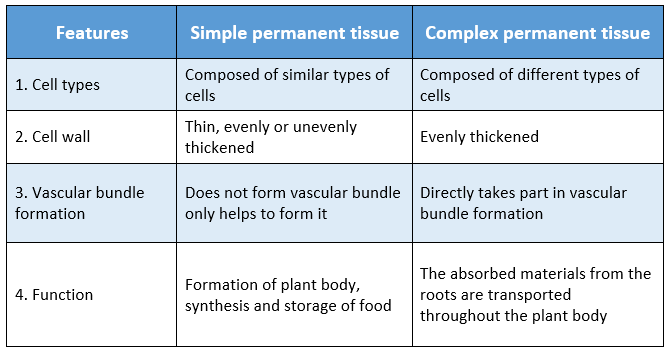
Question 5 Distinguish between simple permanent tissue and complex permanent tissue.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between simple permanent and complex permanent tissue are:
Question 6. Mention the occurrence of parenchyma cells.
Answer:
The occurrence of parenchyma tissue is as follows:
1. It is seen in the epidermis of all plant parts.
2. It is present in the ground tissue of plants including the cortex, medulla and medullary rays.
3. The mesophyll tissue of leaves is composed of parenchyma.
4. It occurs in the endosperm of seeds.
WBBSE Life Science And Environment Class 9 Solutions
Question 7. Where do you find collenchyma tissue?
Answer:
Collenchyma tissue is mainly found in the hypodermis of the stem. The Midrib and petiole of the leaves and peduncle of flowers are made up of collenchyma.
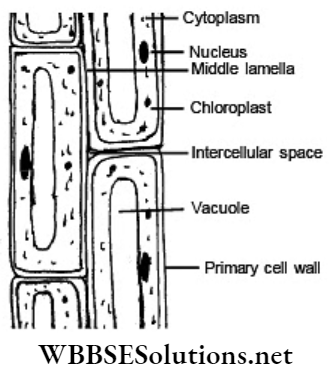
Question 8 Mention the different types of sclerenchyma, based on their features.
Answer:
Features of different types of sclerenchyma are as follows:
1. Sclerenchyma fibres are long and narrow cells with pointed ends.
2. Sclereids are broad with thick-walled cells which occur singly or in small groups.
Question 9. Where do you find sclerenchyma tissue in a plant?
Answer:
Components of sclerenchyma are found in the following parts of the plant:
1. Sclerenchyma fibres are present in the hypodermis, cortex, vascular bundles and pericycle.
2. Sclereids are found in seed coats.
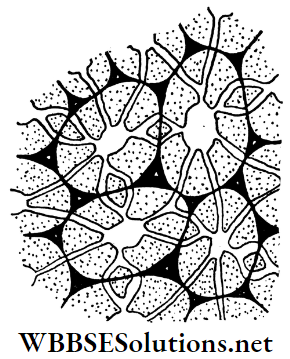
Question 10 Why are some specific types of sclereids called stone cells?
Answer:
The deposition of lignin, cutin and suberin on the cell wall of some short and oval or spherical-shaped sclereids, makes them hard, like stones. The lumen of such cells is almost squeezed due to the deposition.
That is why, these special types of sclereids are called stone cells. Stone cells are responsible for providing mechanical support to the plants.
WBBSE Life Science And Environment Class 9 Solutions
Question 11. Mention the functions of the cork cambium and vascular cambium.
Answer:
Functions of cork cambium:
It takes part in the growth of the outer part of the plant body beyond the vascular bundle, to produce cortex and bark to replace ruptured epidermis.
Functions of vascular cambium: It takes part in the formation of the xylem and phloem within the vascular bundle.
Question 12 Write down the functions of the xylem.
Answer:
The main functions of the xylem are the conduction of water and solutes from roots to the different parts of the plants, providing mechanical support to the plant and in some cases, helping in the storage of food materials.
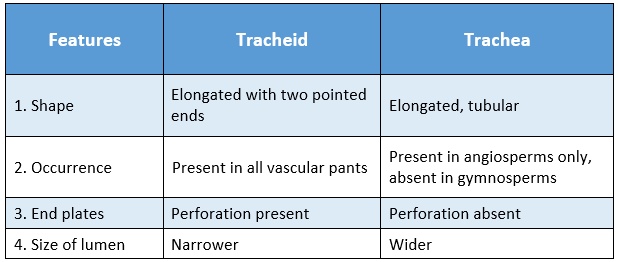
Question 13 Distinguish between tracheid and trachea.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between the tracheid and trachea are:
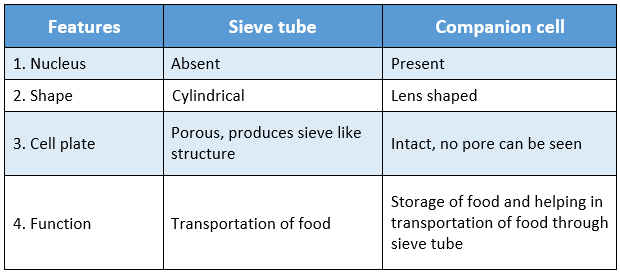
Question 14 Distinguish between the sieve tube and the companion cell.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between the sieve tube and the companion cell are
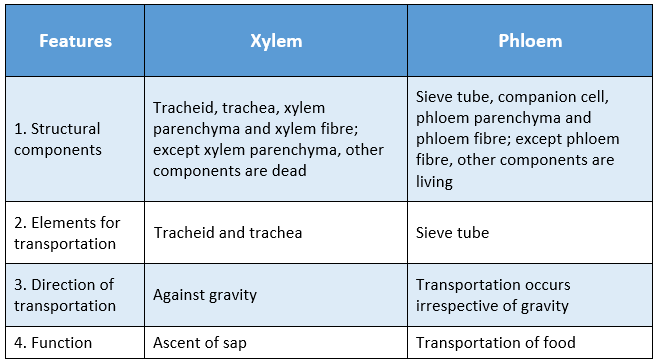
Question 15 Distinguish between xylem and phloem.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between the xylem and phloem are:
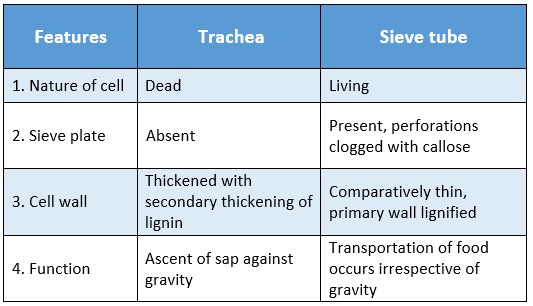
Question 16 Distinguish between the trachea and sieve tube.
Answer:
Distinguishing features between the trachea and sieve tube are:
Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life Plant Tissue And Its Distribution Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by epithelial tissue?
Answer:
Epithelial Tissue:-
The tissue, which typically covers the outer surface of the body as well as the inner and outer lining of internal organs, is known as epithelial tissue. It consists of one or more cell layers.
WBBSE Class 9 Life Science Question And Answer
Question 2 What is the basement membrane? What does it do?
Answer:
Basement membrane: The basement membrane is a typical acellular layer of epithelial tissue, composed of materials, somewhat similar to the matrix of connective tissue.
Function: The basement membrane holds the epithelial cells on it. It also helps the epithelium to remain attached to the surface of the connective tissue layer below it.
Question 3 Write the different types of epithelial tissue.
Answer:
It is of three types:
1. Surface protective epithelium,
2. Glandular epithelium,
3. Sensory or neurosensory epithelium.
The surface protective epithelium also has three types:
1. Simple
2. Stratified
3. Pseudostratified.
Question 4. Mention the types of simple epithelial tissues.
Answer:
Simple epithelial tissue is of different types:
These are:
1. Squamous epithelium
2. Cuboidal epithelium
3. Columnar epithelium
4. Ciliated epithelium.
Question 5. Mention the distribution of epithelial tissue.
Answer:
Distribution Of Epithelial Tissue:-
Epithelial tissue is present on the outer surface of the body (skin) and the inner lining of the oral cavity, intestine, blood vessels, nasal passage, respiratory tracts, alveoli, renal tubules, urinary bladder, uterus, fallopian tube and different glands.
WBBSE Class 9 Life Science Question And Answer
Question 6 Mention the two functions of simple epithelial tissue.
Answer:
Two functions of simple epithelial tissue are:
1. The tissue helps in the exchange of gaseous and liquid substances.
2. It protects the organs from friction.
Question 7. Mention the characteristics, distribution and function of simple squamous epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. Cells of the tissue are larger, flattened and elongated.
2. The nucleus is flattened and oval.
3. The cells remain arranged on the basement membrane.
Distribution: Present in alveoli, peritonium, pleura, loop of Henle and Bowman’s capsule of Kidney.
Function:
1. The tissue helps in the exchange of gaseous and liquid substances.
2. Helps in filtration.
3. Protects the body from microorganisms.
Question 8 Mention the characteristics, distribution and function of cuboidal epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. The cells of the tissues are equal in length and breadth.
2. the nucleus of the cell is oval-shaped.
3. The upper surface of the cell is polygonal.
Distribution: Present in the renal tubule, salivary glands, thyroid gland.
Function: Helps in secretion and defence.
Question 9 Mention the characteristics, distribution and function of columnar epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. The length of the cell is greater than the breadth.
2. Cells remain arranged on the basement membrane hence called columnar tissue.
3. The nucleus is oval and large in size.
4. Cytoplasm is reticular.
WBBSE Class 9 Life Science Question And Answer
Distribution: Present in the stomach, small intestine, large intestine and in certain glands.
Function:
1. Secretion and defence.
2. Protection.
Question 10 Mention the characteristics, distribution and function of ciliated epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. The cells of this tissue is somewhere columnar, somewhere cuboidal.
2. The cells of this tissue bear 28-30 hairlike appendages at their surface.
3. Cilia arise from the basal part.
Distribution: Present in alveoli and its’ adjacent part, uterus, oviduct, and ependymal cells (spinal cord).
Function:
1. Clears mucous, dust particles, and different types of microbes from the respiratory tract.
2. The cell helps to expel the ovum and spermatozoa.
Question 11 Mention the characteristics, distribution and function of the stratified or compound epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. The tissue is formed by 3 to 4 cell layers.
2. Cells of the upper layer are large, flattened and quadrangular.
3. Number of nucleus may be one or two.
Distribution: Present in the broadened part of the ureter, in the upper part of the urinary bladder and urinary duct.
Function:
1. Defence
2. Inhibit reabsorption of waste substances.
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
Question 12 Write the distribution of different types of stratified epithelial tissue.
Answer:
Stratified squamous epithelium:
1. Keratinised hair, nails, horns, and the epidermis of the skin.
2. Non-keratinised-Pharynx, oesophagus, vagina, mouth cavity.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium: Sweat gland, conjunctiva.
Stratified columnar epithelium: Glottis, epiglottis, rectum.
Question 13 Write the characteristics, distribution and function of the pseudostratified epithelium.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. This tissue though is made up of single-layered cells but the size of the cells is unequal hence it appears like a stratified layer.
2. Cells may be ciliated or non-ciliated.
3. The nucleus of the cells lies at a different plane.
Distribution: Present in the large duct of the salivary gland, urethra, etc.
Function: Protect associated organs and helps in the movement of some substances.
Question 14 What is meant by glandular epithelium?
Answer:
Glandular Epithelium:-
An epithelium, which has assumed secretory function is termed as glandular epithelium. It is present in all types of exocrine and endocrine gland and is associated with the secretion of various secretory substances.
Question 15 Write the distribution of sensory epithelium.
Answer:
Distribution Of Sensory Epithelium:-
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
The sensory epithelium is found in nasal passages and taste buds.
Question 16 Give two roles of glandular epithelium.
Answer:
Roles Of Glandular Epithelium:-
1. Glandular epithelium present in the inner lining of the gastrointestinal tract secretes various digestive enzymes.
2. In endocrine glands, glandular epithelium secretes hormones.
Image
Question 17 What is meant by connective tissue?
Answer:
Connective Tissue:-
The tissue of mesodermal origin, composed of less cells and more acellular matrix, connecting different tissues is known as connective tissue.
Question 18 Schematically represent different types of connective tissues.
Answer:
Schematic representation of different types of connective tissue is given below:
Question 19 Mention the characteristics and distribution of areolar tissue.
Answer:
Characteristics: Semidistinct, white, with wide intracellular space.
Distribution: This tissue binds the skin with the underlying part.
Question 20 Mention the characteristics and distribution of adipose tissue.
Answer:
Characteristics:
1. Cells are large, rounded and polygonal.
2. The nucleus lies at the periphery and fat remains deposited at the central portion of the cell.
Distribution: Found everywhere in the body but maximum below the skin, mesentery membrane and also in the adjacent area of the kidney.
Question 21 Write the functions of areolar tissue.
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
Answer:
Functions Of Areolar Tissue:-
1. provides strength and rigidity to the body.
2. Helps in bearing weight.
3. keep the organs in the proper place.
4. Helps to fill the intermediary place of tissue cells.
Question 22 Write the functions of adipose tissue.
Answer:
Functions Of Adipose Tissue:-
1. Resist the Injury.
2. To store fat in the body.
3. Conserve heat in the body.
Question 23 Define weight-bearing connective tissue. Classify it.
Answer:
Weight-Bearing Connective Tissue:-
The connective tissue which helps in bearing weight is called weight-bearing connective tissue or skeletal tissue. It is the hardest tissue.
They are of two types:
1. Cartilage,
2. Bone
Question 24 Write the functions of skeletal muscle.
Answer:
The functions of skeletal muscles are:
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
1. Helps in the movements of different body parts.
2. Protects many vital soft organs of the body.
Question 25 Connective tissue different types of what do mean by fluid connective tissue.
Answer:
It is a unique type of mobile connective tissue originating from embryonic mesoderm, transferred from one part of the body to another through the cardiovascular system.
Example: Blood.
Question 26 Why blood is called fluid connective tissue?
Answer:
Blood Is Called Fluid Connective Tissue:-
Blood is mesodermal in origin, has fewer cells and more matrix, and it maintains connection among various parts of the body. On the other hand, the matrix of blood, i.e., plasma, is fluid in nature. Therefore, blood is called fluid connective tissue.
Question 27 What is meant by muscular tissue?
Answer:
Muscular Tissue:-
The tissue, which has the ability to contract and relax and is associated with movement, is known as muscular tissue.
Question 28 Mention one function of the tendon and ligament those function of tendon and.
Answer:
The function of the tendon is to connect muscles to bones. The function of the ligament is to connect a bone to another bone.
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
Question 29 How many types of muscular tissues are found in higher animals?
Answer:
In higher animals three types of muscular tissues are found, these are:
1. voluntary or skeletal muscles,
2. smooth muscles and
3. cardiac muscles.
Question 30. Mention the distribution of muscular tissue.
Answer:
Distribution Of Muscular Tissue:-
1. Voluntary muscles are attached to bones.
2. Smooth involuntary muscles are present in the vital visceral organs, such as the oesophagus, intestine, urinary bladder, and stomach [3] Cardiac muscles are present in the heart.
Question 31 Write down the functions of different types of muscles.
Answer:
Functions Of Different Types Of Muscles:-
1. Skeletal muscles help in movement and locomotion.
2. Smooth muscles control the movement of the visceral organs like the stomach, intestine, urinary bladder, etc.
3. Cardiac muscles are responsible for rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Question 32 What do you mean by voluntary or skeletal muscle? Write its functions.
Answer:
Skeletal Muscle:-
Muscles which are normally attached to the bones are called skeletal muscle.
Functions:
1. Contraction of these muscles is under the voluntary control (controlled willingly) of the nervous system. Thus it helps to maintain posture and stabilize bones and joints.
2. Skeletal muscle is associated with reflex action.
3. These muscles can contract rapidly and are responsible for quick movements and thereby coordinates the entire body.
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
Question 33 Write the functions of unstriated muscles.
Answer:
Functions Of Unstriated Muscles:-
1. Unstriated muscle fibres present around the blood vessels, help to maintain blood pressure.
2. Unstriated muscle fibre in the digestive tract helps in the movement of food substances and thereby assists in digestion.
3. The presence of unstriated muscle in air passages regulates the inflow and outflow of air.
4. In the renal system unstriated muscle fibres propel the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Question 34 What do you mean by intercalated disc. State its significance.
Answer:
Intercalated Disc:-
Special fibrous discs are present at intervals of They are transmitting the signals of nerve cardiac muscle is known as the Intercalated disc. impulse between the cells of the heart.
Question 35 Define the haversian canal. Or, Write its distribution.
Answer:
Haversian Canal:-
Each osteon consists of a single central canal, known as a haversian canal, surrounded by concentric layers of calcified bone matrix. It allows the passage of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and never fibres.
Question 36 Name single-nucleated and multinucleated muscle cells.
Answer:
Single-Nucleated And Multinucleated Muscle Cells:-
WBBSE Class Nine Life Science
The single-nucleated muscle cell is an unstriated muscle cell, present in the visceral organ. The multinucleated muscle cell is a striated muscle cell, present in the hands and legs.
Question 37 What is nervous tissue?
Answer:
Nervous Tissue:-
The tissue, which is responsible for receiving and transmitting impulses and thereby coordinating different parts of the body, is known as nervous tissue.
Question 38 What are the cellular components of nervous tissue? Where do you find those components?
Answer:
Cellular components of nervous tissue: Neurone and neuroglia are the two cellular components of nerve tissue.
Distribution of neurone and neuroglia: Neurones are present in the brain, spinal cord, sense organs and nerves. Several neurones, surrounded by connective tissue, form a nerve. Neuroglia cells are found in the brain and spinal cord as packing material of neurones, providing them with necessary support and insulation.
Question 39 Write the functions of nervous tissue.
Answer:
Functions Of Nervous Tissue:-
1. Nerve tissue receives external and internal stimuli and responds to them.
2. It carries impulses and makes the body aware of the changes in the environment.
3. It helps to maintain coordination among all organs within the body.
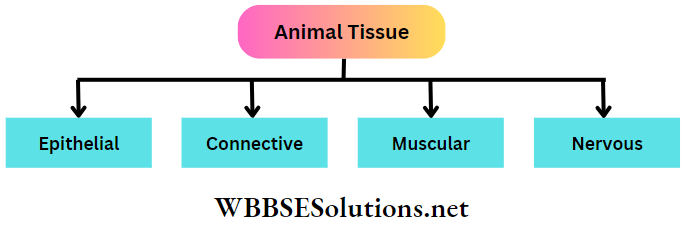
Question 40 Classify different types of animal tissue.
Answer:
Classification of animal tissue is given below:
Question 41 Define the term:
1. Axon-hillock
2. End brush.
WB Class 9 Life Science Question Answer
Answer:
1. Axon-hillock: The part of the cell body. from where the axon originates is called axon-hillock.
2. End brush: The terminal end of branches are nodular called terminal buttons or end brush. 45
Question 42 Write different membranes of the axon arranged in proper order.
Answer:
Neurilemma, myelin sheath and axolemma
Question 43 What are the nodes of Ranvier?
Answer:
Nodes Of Ranvier:-
The continuity of myelin sheath myelinated axon is interrupted by several constrictions. These are called nodes of Ranvier.
Question 44 What do you mean by synapse?
Answer:
Synapse:-
Synapse is the junctional region as anatomical border in nervous system where one neurone ends and the next neurone starts.
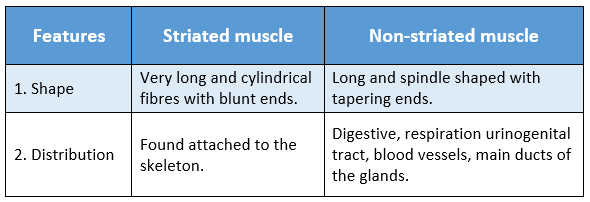
Question 45. Write the difference between striated and non-striated muscles.
Answer:
The differences between striated and non-striated muscles are:
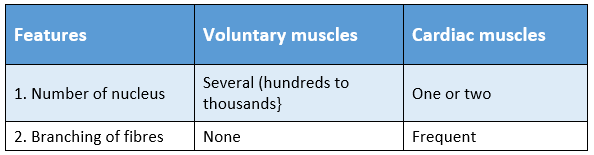
Question 46. Write the difference between voluntary muscle and cardiac muscle.
Answer:
The differences between voluntary muscle and cardiac muscle are: