Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Descriptive Questions
Question 1. Trace the evolution of trade and commerce in India from the 6th century BC to the 6th century AD.
Answer:
The evolution of trade and commerce in India from the 6th century BC to the 6th century AD:
From the 6th century BC to the 6th century AD there were gradual changes in trade and commerce in India.
1 Age of sixteen mahajanapadas:
During this age trade and commerce was important occupation. In the beginning, trade was carried through land routes. Later on, rivers and seas were also used for trading purposes.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 History
2 Mauryan age:
During the Mauryan age, India exported spices, muslin, pearls, etc. and imported items like fruits, wines, and silver vessels. Royal officers were appointed to supervise the work of the merchants.
3 Kushana age:
In the Kushana period, both internal and external trade expanded. In the international markets, there were a demand for Indian muslin and other textiles, pearl, diamond, lapis lazuli and spices. Chinese silk and glass items were imported.
WBBSE Class 6 History Chapter 7 Question Answer
4. Gupta and Post-Gupta period:
During the Gupta and Post-Gupta period, there was a trade relationship between India and other parts of Asia. But there was a slump in foreign trade due to the Huna invasion.
Trade with Rome was hampered. Two important parts of this time were Tamralipta and Kaveripattinam.
Question 2. What were the similarities and dissimilarities between the Mauryan and Gupta administration.
Answer:
The similarities and dissimilarities between the Mauryan and Gupta administration:
There were some similarities and dissimilarities between the Mauryan and Gupta administrations.
Similarities
- In the Mauryan administration, absolute power rested with the emperor. In the Gupta administration also the emperor was absolute.
- The Mauryan emperors used to rule with the help of the royal officials known as Amatyas. Gupta royal officials also assisted the emperor in administration. Amatya or ‘Sachiv’ was the most important official.
- Like the Mauryan empire, the Gupta empire was also divided into a number of provinces.
- In the Mauryan age, below the provincial administration, there was a district administration known as Aahar. In the Gupta administration also there were districts known as Vishaya.
Dissimilarities
- The Mauryan emperors did not perform any sacrifices to claim their power. But the Gupta emperors performed yajnas or sacrifices to demonstrate their might.
- The Mauryan rulers favoured and promoted non-Hindu religions. Here mention may be made of Ashoka’s adoption of Buddhism. But the Gupta rulers followed and promoted Hinduism. During the Gupta period, there is no such instance of the rulers promoting non-Hindu religions like Buddhism.
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Objective Type Questions
Strike the odd one out
Question 1. War, conflict, fight, treaty.
Answer: Treaty
Question 2. Janapada, Mahajanapada, village, city.
Answer: City
Question 3. Rupak, dinar, karshapana, guild.
Answer: Guild
Question 4. Kushanas, Satavahanas, Guptas, Agrahara.
Answer: Agrahara
WBBSE Class 6 History Chapter 7 Question Answer
Question 5. Brahmanas, Vaishyas, Sudras, traders.
Answer: Traders
Question 6. Megasthenes, Fa-Hien, Hieun-Tsang,Rudradaman.
Answer: Rudradaman
Question 7. Dholi, Chador, dupatta, cot.
Answer: Cot
Question 8. Ashoka, Chandragupta II, hudradaman, Vakataka.
Answer: Vakataka
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Match The Columns
1.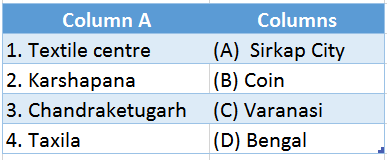
Answer: 1. (C), 2. (B), 3. (D), 4. (A)
2.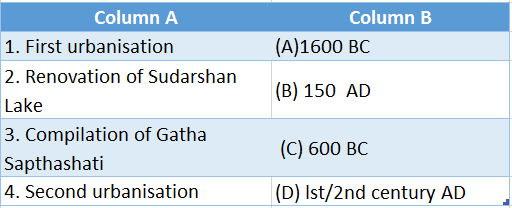
Answer: 1. (A), 2. (B), 3. (D), 4. (C)
3.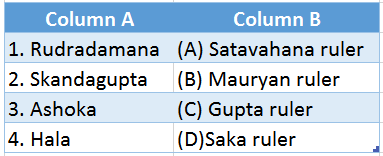
Answer: 1. (D), 2. (C), 3. (B), 4. (A)
4.
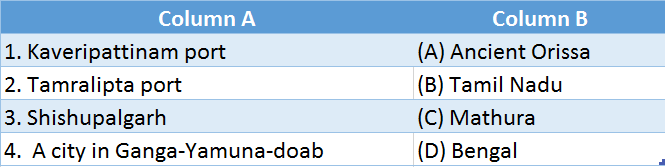
Answer: 1. (B), 2. (D), 3. (A), 4. (C)
WBBSE Class 6 History Chapter 7 Question Answer
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Exercise
Which of the options appears most suitable to the following statements
Question 1. Many guilds had emerged in the Post-Mauryan age.
1. Kings had created guilds to expand trade and commerce.
2. Craftsmen and merchants had formed guilds.
3. Common people had formed guilds to deposit money and for cash transactions.
Answer: 2. Craftsmen and merchants had formed guilds.
Question 2. Cotton cultivation was good in the Deccan.
1. The black soil of the Deccan was suitable for cotton cultivation.
2. All the cultivators of the Deccan used to cultivate only cotton.
3. No other crop was grown in the Deccan.
Answer: 1. The black soil of the Deccan was suitable for cotton cultivation.
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Fill In The Blanks With The Correct Word
Question 1. Janapada was a/an _______ (agricultural/craft based /labour based) area.
Answer: Agricultural
Question 2. In the Mauryan Age, the economy was mainly dependent on _________ (crafts/agriculture/ trade and commerce).
Answer: Agriculture
Question 3. During the Gupta and Post-Gupta age, the system of donating land for religious purposes was known as _______ (Samanta/Begar/Agrahara) system.
Answer: Agrahara
History Class 6 Chapter 7 Question Answer WBBSE
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Write In Your Own Words
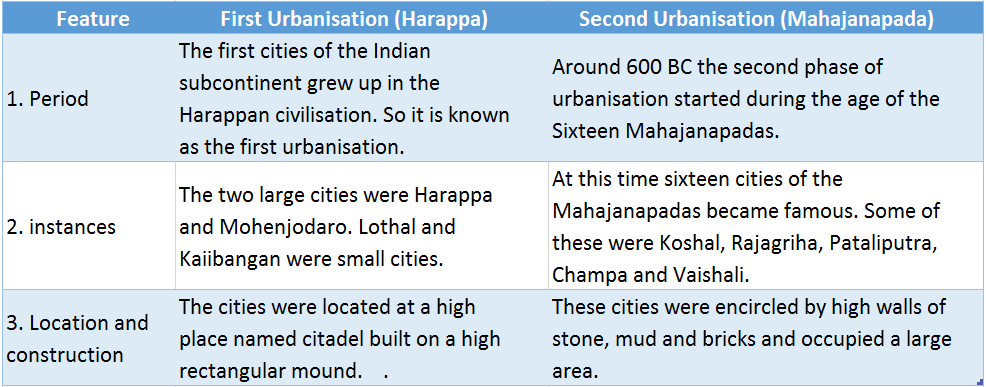
Question 1. Do you notice any difference between the first urbanisation (Harappa) and the second urbanisation (Mahajanapada)?
Answer:
Question 2. Why did the irrigation system develop in ancient India? Do you notice any difference between the irrigation system of these times and that of the present?
Answer:
Reason for the development of the irrigation system:
Agriculture was the basis of the economy in ancient India. So it was necessary to build up an efficient irrigation system for greater development in the field of agriculture.
History Class 6 Chapter 7 Question Answer WBBSE
Comparison with modern irrigation system:
In the ancient period, arrangements were made to supply river water to the fields through irrigation. Nowadays irrigation is done by constructing artificial reservoirs, wells and tanks.
In the earlier days, well water was drawn out for irrigation with the help of a wheel-like structure. Today irrigation implements have been considerably improved with the help of mechanical and electrical technology.
Question 3. What differences can be noticed in the patterns of cultivation and the crops cultivated in the northern and southern parts of the Indian subcontinent in the period between the 6th century BC and the 6th century AD?
Answer:

Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Hands-On
Question 1. Make a list of the different occupations of the people from the 6th century BC to the 6th century AD. Which of these occupations are prevalent in present times? What were the points of similarity and dissimilarity between the occupations of Vedic age and this particular period?
History Class 6 Chapter 7 Question Answer WBBSE
Answer: Various professionals from the 6th century BC to the 6th century AD.
- Philosopher
- Farmer
- Cattle breeder and hunter
- Artisan and trader
- Soldier
- Spy
- Blacksmith
- Jeweller
- Goldsmith
- Tanner
- Potter
- Bamboo craftsman
- Florist and gardener
- Perfume maker
- Dyer
Vedic professions which are still prevalent:
The different professions existing since 6th century BC till 6th century AD such as soldier and spy have become permanent jobs today. Cattle rearing is no more an important occupation. Hunting has been legally prohibited.
Some professions have been modified today. Those of blacksmiths, tanner, and potters are no more personal occupations but have become a collective profession.
Similarities and dissimilarities between Vedic professions and modern professions:
In spite of a considerable modification the Vedic occupations like blacksmith, jeweller, goldsmith and tanner are still prevalent. However, there is a collective venture in place of individual effort.
Many new employment avenues have been created due to various technological developments in the present age and these professions bear no similarity to the Vedic professions.
History Class 6 Chapter 7 WBBSE
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Food For Thought
Question 1. What are the points of similarity and dissimilarity between the society of Mauryan times and that of Vedic soci- ety?
Answer:
The points of similarity and dissimilarity between the society of Mauryan times and that of Vedic soci- ety:
The following are some of the similarities and dissimilarities between the society of Mauryan times and that of Vedic society.
Similarities:
- Agriculture was the main occupation of the people of both the Vedic and Mauryan periods.
- Women enjoyed high status in both societies. Women were treated with dignity and honour in the Vedic and Mauryan times.
- The caste system was prevalent in both the Vedic and Mauryan periods.
- Both the Vedic and Mauryan societies were patriarchal.
Dissimilarities:
- In both the Vedic and Mauryan periods caste system was prevalent. Megasthenes states that in the Mauryan period, the caste system was not based on birth as was prevalent in Vedic society. The caste system in the Mauryan period was rather based on occupation.
- In the Vedic period, there was the system of Chaturashrama or the four stages of life. But in the Mauryan period, we do not come to know of the Chaturashrama.
- Slavery was not prevalent in the Vedic society but slavery is believed to be prevalent in the Mauryan period.
- In the Mauryan period, Buddhist monasteries were developed as important educational institutions but in the Vedic period, there was no existence of monasteries.
Question 2. Make a list of the food items of those times. Simultaneously prepare a list of food items that you consume at present. Compare the lists.
Answer:
A comparison of the list of food items of ancient India and present-day India is given below

Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Formative
Excerpt from the text:
During Gautama Buddha’s time, much advancement was made in the art of making a particular kind of earthenware pottery. Archaeologists have identified these as Northern Black Polished Ware.
These were even more advanced than the Painted Grey Ware pottery of the preceding times. These vessels were made of very good quality clay. Due to the widespread use of the potter’s wheel, it had become easy to make these vessels.
History Class 6 Chapter 7 WBBSE
The main characteristic of these vessels was that these were as shiny as mirrors. Earthen wares were well-fired in ovens to make them black. The vessels were then polished.
As specimens of these earthen-ware vessels, plates and bowls of different kinds have been discovered. Sample questions related to the above passage are given below for Formative evaluation.
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Questioning And Experimentation
Question 1. How were clay vessels made with the help of potter’s wheel?
Answer:
A potter’s wheel is like a spinning round table. There is a pan that goes around the wheel to catch water and clay as it spins. For this, a potter has to learn with patience how to make clay vessels with the help of a potter’s wheel.
Question 2. How are the vessels, which are found in the modern days’ made?
Answer:
At present, along with clay vessels, different types of plastic vessels are also available. They are made in factories with the help of machines. As these are machine-made, a huge number of vessels are produced within a short time.
If these questions are asked to the learner, the learner will enquire and find out how the clay vessels were made and also will try to know how the different vessels are made nowadays. In this way the learner will develop a sense of questioning and experimentation.
History Class 6 Chapter 7 WBBSE
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Interpretation And Application
Question 1. Why this type of vessel came into use in northern India?
With the passage of time, there were changes in the everyday life of man. In the changing circumstances, to suit the needs of the people, better vessels than before came into use.
From the above question or similar type of questions, the learner from their own experience can make some inferences. As a result their potentiality of interpretation and application will develop.
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Aesthetics And Creative Expression
With the help of pictures compare the clay vessels of ancient India and present-day India.


The above pictures will create the sense of creativity in the mind of the learner and the learner will be able to go deep into the subject matter.
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1. The second phase of urbanisation took place in
- 500 BC
- 600 BC
- 700 BC
- 800 BC
Answer: 2. 600 BC
Question 2. India has been referred to as In-Tu by
- Xuanzang
- It-Sing
- Faxian
- Lao Tzu
Answer: 1. Xuanzang
Question 3. The Gatha Saptashati was compiled by
- Rudradamana
- Hala
- Satakarni
- Samudragupta
Answer: 2. Hala
History Class 6 Chapter 7 WBBSE
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. _______ (Agra/Varanasi/Magadha) was famous as a textile centre.
Answer: Varanasi
Question 2. Silver currency was introduced for the first time during the reign of _______ (Ashoka/Chandragupta II/ Shasanka).
Answer: Chandragupta II
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous State Whether The Following Statements Are True Or False
Question 1. Megasthenes was aware of the four varnas of Indian society.
Answer: False
Question 2. In the Mauryan period, the economy was mainly dependent on trade.
Answer: False
Question 3. In the Kushana age, Varanasi and Mathura were famous for manufacturing glass items.
Answer: False
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Write In A Complete Sentence
Question 1. Name one famous port of Tamil Nadu in the Gupta period.
Answer: One famous port of Tamil Nadu in the Gupta period was Kaveripattinam.
Question 2. What is Karshapan?
Answer: Karshapan was a kind of currency used during the period of the Sixteen Mahajanapadas.
Class 6 History Chapter 7 WBBSE
Chapter 7 Economy And Society Topic C Miscellaneous Answer The Following Questions
Question 1. How was the communication system in the Mauryan period?
Answer:
In the Mauryan period, the communication system between the capital and other regions of the empire was developed. To supervise the roads royal officers were appointed.
Question 2. What was the impact of Agrahara?
Answer:
In the Gupta and Post-Gupta period sometimes lands were donated to the Brahmins or Buddhist viharas. This system of land donation is known as agrahara.
The impact of the agrahara system were as follows:
- Due to land donation ownership over land increased.
- Cultivation started in many uncultivated lands and thus agricultural production increased.
- Agricultural labourers were employed to make uncultivable lands cultivable.
- There was increased agricultural activity over land.
Question 3. Trace the evolution of trade and commerce in India from the 6th century BC to 6th century AD.
Answer:
From 6th century BC to 6th century AD there were gradual changes in trade and commerce in India.
1. Age of sixteen mahajanapadas:
During this age trade and commerce was important occupation. In the beginning, trade was carried through land routes. Later on rivers and seas were also used for trading purposes.
Class 6 History Chapter 7 WBBSE
2. Mauryan age:
During the Mauryan age, India exported spices, muslin, pearls, etc. and imported items like fruits, wines, and silver vessels. Royal officers were appointed to supervise the work of the merchants.
3. Kushana age:
In the Kushana period, both internal and external trade expanded. In the international markets, there were a demand for Indian muslin and other textiles, pearl, diamond, lapis lazuli and spices. Chinese silk and glass items were imported.
4. Gupta and Post-Gupta period:
During the Gupta and Post-Gupta period, there was a trade relationship between India and other parts of Asia. But there was a slump in foreign trade due to the Huna invasion.
Trade with Rome was hampered. Two important ports of this time were Tamralipta and Kaveripattinam.


Very helpful. Thanks a lot. We need more