Class 9 History WBBSE Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Topic A The Russian Revolution Long Answer Questions
Question 1. What was the Narodnik Movement? What was the aim of the movement? Was the movement a failure?
Answer:
Narodnik Movement:-
The most important movement in Russia in the 60s of the 19th century was the Narodnik movement. The Russian word ‘Narod’ means the ‘people’. One who sought to help the people (peasants i.e. narod) take the path of revolutionary struggle for a just life was known as Narodnik.
The aim of the Narodnik movement was
[1] Overthrow the rule of the autocratic Czars in Russia.
[2] Destruction of the prevalent social structure.
[3] Agrarian socialist society to be established.
The Narodniks failed to motivate the peasants with their ideology. Their movement, though a failure, made the doctrine of socialism known to the people. People were trained for future révolution.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Class 9 History Long Answer Questions
Question 2. What were the causes of the Russian Revolution?
Answer:
Russian Revolution:-
The Russian Revolution of 1917 is a very important event in world history. It brought an end to Czarist autocracy and established socialist Russia.
Class 9 History WBBSE
The causes of the Russian Revolution are as follows:
[1] The Czars were corrupt. There was absolutely no progress in any aspect of the life of the common Russians. Though the life of the people was miserable, no effort was made to remove their grievances. Naturally, the Russians desired the fall of Czarist rule.

[2] The intellectual ground for the outbreak of the revolution was prepared by writers like Gorky, Turgenev, Dostoevsky, Leo Tolstoy and others.

[3] The Russian army was inefficient. Russia was defeated in the Crimean War (1854- 66) and the Russo-Japanese War (1905). This exposed the weakness of the Czarist rule.
Class 9 History WBBSE
[4] Russian society was divided into the ‘Haves’ and the ‘Have-nots’. The ‘Haves’ were those who were very rich. The ‘Have nots’ were poor farmers and labourers. This created a feeling of class struggle among the people.

[5] The Industrial Revolution was another factor contributing to the outbreak of the Russian Revolution. Owing to the use of machines the labourers were thrown out of employment and were forced to live in miserable conditions.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
[6] The bureaucracy of Russia was also responsible for the outbreak of the Russian revolution. Most of the high officers belonged to rich families. They had no sympathy for the common people and always exploited them. The people of Russia were thus firmly determined to bring about a thorough change in the system of administration. Thus the Russian Revolution broke out.
Question 3. What was Lenin’s ‘April Thesis’?
Answer:
April Thesis:-
Lenin, the leader of the Bolshevik party in Russia, was the pioneer of the October Revolution. The Menshevik thesis was rejected by Lenin. The people were attracted to the Bolsheviks when they promised bread to the workers, peace to the army and land to the peasants. Yet the people could not decide their future plans. In early April 1917, Lenin returned from his exile in Switzerland and announced his famous ‘April thesis’ titled “What is to be done”.

In his thesis he said:
[1] History has given a very opportune time to the Bolsheviks.
[2] The provisional republic is yet out of roots. Once it wins a general election it will be impossible for the Bolsheviks to overthrow it. So Lenin put forward his idea of ‘Now or Never’.

[3] Since the Bolsheviks were the architects of the 1917 revolution they have every right to hold a government lawfully.
[4] The bourgeoisie and the proletarian revolution-both will happen simultaneously and the proletarian will overthrow the bourgeoise system.
[5] The Russian workers, peasants and soldiers will offer their allegiance to the Soviets only and those who will not do so will be punished.
[6] In the villages and towns workers’ Soviets will capture the power and they will defy the provisional republican government.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
[7] The war with Germany launched by the Provisional Government was an imperialist war-the Russian people had no sympathy for it.
Question 4. Discuss Lenin’s New Economic Policy.
Answer:
New Economic Policy:-
The Civil War in Russia that had begun in 1918 and continued till 1921 was a crucial time of the newly founded Bolshevik government. During this time, the Bolshevik government faced a financial crisis. The situation in Russia was saved by Lenin, the Bolshevik leader who introduced the ‘New Economic Policy’ (NEP).
The chief features of the NEP were:
[1] The farmers were allowed to sell their produce in the open market.
[2] Private enterprise was allowed on a small scale.
[3] Nationalisation was applied only to big industries.
[4] The workers were allowed to enjoy suitable wages.
[5] Heavy industries like iron, coal, and railways were kept under state control.
[6] There was an acute scarcity of capital in Russia. So, profit-sharing concessions were allowed to foreign capitalists for large-scale agricultural and engineering projects.
[7] Power was allocated between the central and constituent republics.
The New Economic Policy of Lenin stimulated production and thus the condition of agriculture and industries was immensely improved. Though the introduction of NEP led to the re-establishment of capitalism to a great extent, the Russian government still maintained control over some important aspects of the economic life of the country such as foreign trade, railways and big industries.
Class 9 History Question Answers WBBSE Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Topic B The First World War and Aftermath Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Describe the major events of the First World War.
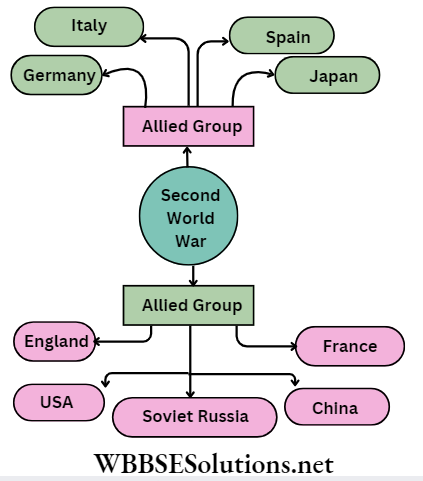
Answer: The First World War broke out in 1914 and ended in 1918. The war was waged between the Allied powers (comprising Britain, France, Russia and Serbia) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria, Hungary and Turkey).

[1] On 28 June 1914 Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the Austrian throne, was assassinated at Sarajevo. Austria held Serbia responsible for the murder. England declared war on Serbia. Russia joined hands with Serbia. It declared war on France and Russia invaded Belgium to reach France. France was helped by Britain.
[2] Japan attacked Germany in order to get control of her colonies in the Far East. Turkey and Bulgaria sided with Germany.
[3] Italy joined France and England. The German army marched towards Paris but were stopped near the river Marne. The German army was defeated in the Battles of Marne and Somme.
[4] The United States of America joined the war in 1917 when the British ship Lusitania carrying American passengers was sunk by a German U-Boat. At first, the Germans were winning. They used U-boats to sink enemy ships as well as ships of neutral countries going to Britain.
Class 9 History Question Answers WBBSE
[5] In 1917 the new communist government under the leadership of Lenin was established. In 1918 Russia signed the treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Germany and withdrew from the war.
[6] Germany mounted violent attacks on France and Belgium.
[7] America entered the war and the Germans started losing. The allies started counterattacks forcing the Germans back. Germany was devastated and emperor William II fled.
[8] The Central Powers surrendered and accepted an armistice in 1918. Shortly thereafter, the 1919 Treaty of Versailles ended World War I.
Question 2. What were the effects of the First World War?
Answer: The outbreak of the First World War on July 28, 1914, is the most outstanding event of the early 19th century.
The effects of the First World War are as follows:
[1] About one crore thirty lakh soldiers died during the First World War. The death rate of the civilians was much more. About 28 thousand crore dollars were spent during the war. After the war there was acute financial crisis.
[2] Severe economic difficulties created by the war and the demand for reparation caused despair and hardship which ensured an uncertain future for Germany.
[3] The Great War sounded the death knell for monarchies in Germany and Russia which became republics.
[4] The Ottoman empire and Austria-Hungary completely collapsed.
[5] The USA emerged from the war clearly as the greatest power as well as the creditor nation of the world.
[6] In Russia, the war led to the Russian Revolution and a civil war broke out in Russia which continued for three years beyond World War I.
[7] World War I was also the cause for a rise in nationalistic tendencies leading to the demand for independence in many British colonies outside Europe.
[8] On most countries after the Great War, monarchy came to an end and democratic governments were established.
[9] After the Great War the prices of articles went up.
Class 9 History Question Answers WBBSE
[10] Almost all the countries were so heavily burdened that for years together their path of progress remained impeded.
[11] With men having joined the war, the women of most took over business and establishment.
[12] One distinct positive outcome of World War I was the boost received by research and technology. Rail and automobile transport, radio and wireless communications, and research and development of weapons and arms including nuclear research boomed.
[13] To curb the wars and maintain global peace the League of Nations was established in 1919 due to the persistent efforts of Woodrow Wilson.
Question 3. What were Wilson’s ‘Fourteen Points’?
Answer: With the surrender of Germany in 1918, the First World War came to an end. As an answer to all European problems the President of America Woodrow Wilson came up with peace proposals known as the ‘Fourteen Points’.
It said that:
[1] There would be no secret treaties among different countries. All terms will be openly discussed and agreed upon.
[2] The seas should be free in peace and in war to ships of all nations.
[3] The American Doctrine of ‘Open Door’ in China i.e. right of all nations to enjoy equal rights of trade in China will be implemented.
[4] Colonial questions to be settled peacefully.
[5] Russia should be allowed to choose whatever form of government it wanted.
[6] Germany shall restore genuine French territories to France.
[7] The barriers to trade between countries such as customs duties should be removed (free trade).
[8] The Habsburg and the Turkish Empires would be reorganised and reconstructed according to the doctrine of ‘one nation one state’.
[9] All countries should reduce their armed forces to the lowest possible levels.
[10] Poland should be constituted as an independent sovereign and united country.
[11] The national groups in Europe should, wherever possible, be given their independence.
[12] Russian territories may be restored to Russia.
[13] Readjustments of the frontiers of Italy to be made.
[14] The League of Nations would be formed for the prevention of war and for the peaceful settlement of international disputes.
Class 9 History Question Answers WBBSE
Question 4. What were the treaties signed in the Paris Peace Conference (1919)?
Answer: The First World War came to an end in 1918 with the surrender of Germany.
In the Paris Peace Conference (1919) the following peace treaties were concluded:
[1] The Treaty of Versailles:
The Treaty of Versailles was concluded in 1919 between the victorious allies (comprising Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia) and defeated Germany after World War I.
[1] ‘Germany lost Alsace-Lorraine to France, Upen, Malmedy, Moresnet to Belgium, Memel to the Allies, west Prússia and most of Posen to Poland. She handed over the province of Schleswig to Denmark.
[2] Danzig was made a free port.
[3] The Saar Valley was put under an international commission for 15 years.
[4] Germany was required to surrender her colonies, navy and coal mines.
[5] Germany had to pay heavy war reparations.
[2] The Treaty of Saint Germain:
This treaty was signed between the victorious Allies and defeated Austria in 1919. By this treaty
[1] The old House of Hapsburg was abolished.
[2] Austria had to accept the true existence of Hungary, Poland and Czechoslovakia.
[3] The Treaty of Neuilly:
This treaty was signed between the victorious allies and Bulgaria in 1919. According to this treaty
[1] Four provinces of Western Bulgaria were given to Yugoslavia;
[2] The strength of the Bulgarian army was reduced to ten thousand.
[4] The Treaty of Trianon:
The Allied powers concluded this treaty with Hungary in 1920. By this treaty
[1] Large portion of the territory was taken away from Hungary;
[2] The strength of the Hungarian army was reduced.
[5] The Treaty of Sevres:
The victorious Allies concluded this treaty with Turkey in 1920. By this treaty
[1] The Turkish empire was abolished
[2] Turkey had to give up her rights over Egypt, Cyprus, Morocco, Palestine, Arabia and Mesopotamia. Turkey’s army was also reduced.
Question 5. Criticise the treaty of Versailles. Or, The Treaty of Versailles contained the seeds of the Second World War-Discuss.
Answer:
[1] The Treaty of Versailles has been called ‘a dictated treaty’ which was imposed powers. The delegates of Germany were not upon by defeated Germany by the Allied invited to the Paris Peace Conference (1919) Treaty did not adhere to the principle of self and the treaty was a vengeful treaty.
[2] The determination. The right of self-determination transferred to Czechoslovakia. It led to a loss of was not applied for Sudetenland which was a balance of power in Europe.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
[3] While England’s colonies were confiscated in the name of goods and France increased their colonies, the German government.
[4] Germany was saddled with a was impossible for her to pay.
[5] According to the huge reparation amount by the Treaty which Wilson’s Fourteen Points, it was decided that all the states would reduce their war armaments. But this clause was only applied to Germany.
Humiliated Germany was looking forward to another war as an opportunity to avenge his Versailles contained the seeds of the Second defeat. It is thus said that the Treaty of World War.
Question 6. How was the League of Nations founded? Or, What was the role of Woodrow Wilson in the foundation of the League of Nations?
Answer: The terrible effects of the First World War (1914-18) had stunning effects on the minds of the people. It made the people cry for peace. At Paris in 1919 a peace conference was convened in order to solve the problems of the countries to conclude a treaty with the vanquished.
The meeting was called to find out a way to maintain peace and order in the world in future on a permanent basis. Wilson had also come to attend the conference. He put before the Allies his ‘Fourteen Points’ for consideration. The Allies agreed to work according to these points.
The last point of Wilson was directly related to the formation of the League of Nations. The Allies agreed that this organisation should be formed and its constitution should be prepared separately. Wilson suggested that the constitution of the League of Nations should be included in the Treaty of Paris.
Ultimately the Allies accepted the demand of Wilson. A document called Covenant was drafted at the Paris Peace Conference which led to the foundation of the League of Nations.
Question 7. What do you mean by Great Economic Depression? What were the causes of the economic depression of 1929?
Answer: The Great Economic Depression was a severe worldwide economic crisis in the decade preceding World War II that affected most of the developed world except Soviet Union throughout 1930.
The causes of the Great Depression in America or the world economic crisis were as follows:
[1] After the First World War, there was an overproduction of industrial goods in America. The surplus goods could not be sold in the domestic market or across the Atlantic.
[2] After the First World War, different European countries increased their industrial production. As a result demand for American goods dropped leading to an economic crisis.
[3] During the First World War farmers produced far more food than the population consumed. Farmers expanded their production to aid the war effort. After the war as demand dropped with increasing supply, the prices of products fell and farmers suffered. They fall into debt.
[4] On 24 October 1929, the American share market crashed. As the shareholders were panicked millions of shares had been sold on this fateful day.
[5] America imposed a high rate of tariff on goods imported from different European countries. The European countries also adopted the same policy. As surplus goods could not be sold in the market America’s foreign trade suffered. Many industries were closed and people became jobless.
Question 8. Write a note on Hoover’s Moratorium.
Answer: Herbert Hoover became the President of the USA in 1929. He said, “We in America are nearer to the final triumph over poverty than ever before in the history of any land”. But very soon came the economic crash of 1929.
Total industrial production fell by 48 per cent, the result being a rapid growth of unemployment. The business houses faced a great deal of losses. In order to speed up an economic revival, Hoover proposed an international moratorium from mid-1931 to mid-1932.
To meet rising unemployment, the government allotted large sums for the construction of public buildings and highways. The threatened insolvency of many banks and many railways forced the government to underwrite the credit structure. A Reconstruction Finance Corporation was created which was authorised to lend money for three years for financing commerce, industry and agriculture and for the exportation of agricultural and other products.
All these measures to solve the economic depression of the country failed. By 1932 over five thousand banks collapsed and the number of unemployed people rose to over 12 million. The Americans turned with hope to the new leadership of Franklin Roosevelt.

Question 9. What is ‘New Deal’ of Roosevelt?
Answer: When Franklin Delano Roosevelt became the President of the USA in 1933 the country was on the verge of complete collapse. He prophesied that the USA would ‘revive and prosper’ and he promised a New Deal for the American people.
The New Deal was a series of domestic programmes enacted in the United States between 1933 and 1938 and a few came later. They included both laws passed by Congress as well as presidential executive orders during the first term (1933-37) of President Roosevelt. The programme were in response to the Great Depression and focussed on what historians call the 3R’s-‘Relief, Recovery, Reform’, that is Relief for the unemployed and poor, Recovery of the economy to a normal level and Reform of the finances.
In the realm of ‘Relief,’ the government gave federal loans to rich businesses. It inaugurated a programme of public works in order to stimulate business and provide employment. It set up an elaborate system of conservation of natural resources. The New Deal reopened banks under strict supervision of the government. It controlled the selling of stocks and bonds and other securities. The New Deal paid particular attention to agriculture, labour and social security.
Class 9 History Solutions WBBSE
Question 10. What were the reasons that led to the USA as substitution of Europe by the USA as the power centre of the world?
Answer: In the beginning of the 20th century the centre of power of the world was shifted from Europe to, the USA.
Due to the following reasons:
[1] With the entry of the USA into the First World War in 1917 a new chapter opened in world history. Her participation changed the course of the war and enabled Britain and France to win the war.
[2] At the Paris Peace Conference (1919) President Wilson was one of the Big Four who laid the foundation of the world. peace organisation, the League of Nations USA’s prestige was raised and she became a prominent power in the world.
[3] USA’s emergence as a world power was also caused by her economic prosperity. The economic depression of 1929-33 affected not only the USA but also other countries of the world. President Roosevelt of the USA helped other countries to tide over this economic crisis and USA’s prestige was raised as a first-class world power.
[4] The USA rendered military and material help to the allies and totally changed the course of the war. The USA forced Japan to surrender in 1945 and played a leading role in the Second World War. She made her the arbiter of international politics.
[5] USA’s advancement in science and technology especially in weapons of mass destruction raised her status. She was the first to invent an atom bomb and the successful dropping of it in Japan was made. her the most prominent power in the world.
[6] The USA took the lead to counteract Russia’s influence. She took the initiative of extending economic assistance to Europe, especially through the Marshall Plan. The USA helped to restore all economies and modernise the armed forces of western Europe and became the centre of world politics.
[7] The Second World War (1939-45) weakened Britain and France. Britain’s economic crisis after the war was relieved to some extent by loan from the USA which heightened the prestige of the USA.
Chapter 5 Europe In The Twentieth Century Topic C
Aggressive Nationalism: Rise of Nazism and Fascism Long Answer Questions
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
Question 1. What was the programme of Hitler and the Nazi Party?
Answer: At the end of the First World War (1914- 18) Germany was left in a state of confusion and anarchy. People were not satisfied with the republican government in Germany. There were some political groups in Germany who were opposed to the policy of the government Among those parties was the Nazi Party led by Adolf Hitler.
The Programme of Hitler and his Nazi Party were as follows:
[1] To support one man’s rule:
Hitler was a bitter opponent of the Weimer Republic and was a strong supporter of one man’s rule.
Formation of Greater Germany:
Hitler’s aim was to form Greater Germany which meant that the provinces of other European countries in which the German language was spoken should be merged in Germany.
[2] To oppose the Jews:
Hitler’s aim was to organise the Greater Germany on the basis of pure blood and expel the Jews whom he considered as the enemies of Aryan race.
[3] Responsibility of the First World War:
Hitler was never ready to accept that Germany was responsible for the beginning of the First World War and wanted that the blame should be removed at any cost.
[4] To oppose the Treaty of Versailles:
Hitler never accepted the harsh conditions of the Treaty of Versailles and included the opposition of the Treaty as an important element in his programme.
[5] To oppose the payment of war indemnity:
According to Hitler, it was an act of great humiliation to Germany to pay the war indemnity and therefore Germany should not pay the reparation.
[6] To oppose the policy of disarmament:
The allies compelled Germany to disarm herself. Hitler opposed this decision and wanted to increase the military power of his nation.
[7] Acquisition of old German colonies:
Hitler’s programme also included the acquisition of old German colonies which had been snatched away by the allies according to the Treaty of Versailles.
[8] To take revenge in France:
Hitler considered France as the greatest enemy of Germany and planned to avenge the defeat of Germany in the First World War.
Question 2. What were the fundamental principles of Fascism?
Answer: Fascism had been established in Italy after the First World War. The founder of Fascism was Benito Mussolini. The basic and fundamental principles of Fascism were as follows:
[1] Opposition to individualism:
The concept of Fascism was against individualism. Mussolini believed in the supremacy of the state and gave no importance to the interests of the people.
[2] Establishment of a totalitarian state:
Mussolini believed in one party and one leader for the welfare of the nation. He believed that the state was supreme to all and that opposition has no importance.
[3] Opposition to democracy:
Fascism is opposed to democracy. Mussolini had no faith in the majority and public opinion. The order of the leader was the supreme law of Fascism.
[4] Opposition to communism:
Communism believed that economic factor moulds the history of human development. On the contrary, Fascism believed that political history moulds the history of mankind. So Fascism had no similarity with the principles of communism.
[5] Opposition to peace:
Fascism was opposed to the policy of peace and supported war. Mussolini criticised the League of Nations and told that war was the only means to bring human power to success.
It is clear from the above that Fascism had some original principles which did good to the nation to a considerable extent.
Question 3. Write a note on the Spanish Civil War.
Answer: After the First World War the political, social and economic condition of Spain was not stable. In 1931 general elections were held in Spain in which the monarchists were defeated. established in Spain. But the newly established Democratic-Republican government was successful. General Franco attacked the republican government could not work. republican government and overthrew it. Thus a civil war broke out in Spain.
In this civil war Italy and Germany helped General Franco. The attitude of India was different. In the Faizpur session of the Indian National Congress (1936) Jawaharlal Nehru, a leader of the Indian freedom movement, in his presidential address said that the civil war in Spain was not simply a war between Franco and the republican government or a war between Fascism and democracy.
He called it a war between reactionary and progressive forces. He remarked, “The struggle today is fiercest and clearest in Spain and on the outcome of that depends on war or peace in the world in the near future.”
An association was established in London by the Indians in support of the republican government in Spain. This association also raised a fund to support the republican government in Spain in 1937. During the Spanish civil war Jawaharlal Nehru visited Spain in June 1938. In this year on 13 October, Mahatma Gandhi sent a message to the Prime Minister of Spain telling him that his full sympathy was with them.
Question 4. How was the dictatorship established in Spain by General Franco?
Answer: Dictatorship was established in Spain through different stages by General Franco.
[1] After the First World War, the political, and social opponents of the republican government took full advantage of the discontent in Spain. The banner of revolt was raised by the army of Spain in Morocco in 1936 under the leadership of General Francisco Franco. He attacked the Republican Government with his army and overthrew it. Thus a civil war broke out in Spain.
[2] But the newly established republican government could not work successfully. Political disturbances in many provinces’ attempt by the monarchists to capture power, the poor economic condition of the country, rise of socialism and the deficit budget were some of the problems which threatened the republican government.
[3] The opponents of the republican government took full advantage of the discontent in Spain. The banner of revolt was raised by the army of Spain in Morocco in 1936 under the leadership of General Franciso franco. He attacked the Republican Government with his army and overthrew it. Thus a civil War broke out in Spain.
[4] In this civil war, Italy and Germany helped General Franco, while Russia helped the Republicans. The Republicans were defeated in the civil war. In 1939 Barcelona fell into the hands of General Franco. Franco established his dictatorship in Spain.