WBBSE Class 6 Geography WBBSE Chapter 2 Is the Earth Round Topic B Geoid Analytical Type Questions
Question 1. The shape of the Earth is unlike any object found on Earth. That is why the shape of the Earth is like the Earth itself. Prove the truth of this statement.
Answer:
The shape of the Earth is unlike any object found on Earth. That is why the shape of the Earth is like the Earth itself.
Scientists believe that the Earth was a perfect sphere at the time of its origin.
But in the process of becoming solid and cold from a hot mass of swirling gases and vapors, there was a tendency of matter in the middle to fly outwards while it was spinning.
At this point, the Earth became compressed at the Poles and bulged out slightly in the middle.
As time passed, this idea also changed. Space research has shown that the Earth is shaped like the Earth itself. This unique shape of the Earth has been given a new name—geoid.
The Greek word ‘Geo’ means ‘the Earth’ and ‘Eidos’ means ‘to see’. So, geoid means—looking like the Earth.

WBBSE Class 6 Geoid Explanation
Uneven surface: As proof, it can be said that on the Earth, there is a mountain peak named Mount Everest, which is 8,848 metres high above sea level and there is also a trench known as the Mariana Trench,
which is 10,915metres deep from the Pacific Ocean Plane. The difference in elevation between the highest & the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface is about 20,000m or 20km.
Satellite imagery: The images received from the artificial satellite has proven the Earth’s unique shape. It is flat at the Poles and bulges out in the middle.
Thus, the difference between the equatorial diameter and polar diameter is 42km. So, the unique shape of the Earth is called Geoid.
Read And Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 Geography
Class 6 Geography WBBSE

Question 2. Give proof of the oblate spheroid shape of the earth
Answer:
Proof of the oblate spheroid shape of the earth:
The Earth is not a perfect sphere—it is categorised as an oblate spheroid. Some facts that give proof of the oblate spheroid shape of the Earth are as follows:
The Earth’s equatorial diameter is less than its polar diameter: The Earth’s equatorial diameter is 12,756km while its polar diameter is 12,714 km. This shows that the Earth is not a perfect sphere.
The difference in weight: We know that the closer an object is to the centre of the Earth, the greater the gravitational force acting on it and the greater its weight.
Any object weighs more at the Poles than at the Equator. If the Earth were perfectly spherical, all objects would weigh the same at all points on the Earth.
Jean Richard’s experiment: In 1671, Jean Richard, a French astronomer of South America, while living at Cayenne Island in Guyana (5°N latitude) noticed that every day his clock was losing two and a half minutes.
Yet his clock used to run perfectly on time in Paris (56°N latitude). To keep the time intact, Richard cut off 1/2 inch of his pendulum.
This difference in time was because of the effect of differential gravitational force on the pendulum. The places nearer to the Equator experience higher gravity and so the speed of the pendulum is higher.
The Earth’s rotation: When an object revolves on its axis, the middle tends to bulge out and the two Poles become flattened. As the Earth has been revolving since its origin, it is an oblate spheroid.
Class 6 Geography WBBSE
Question 3. Is the earth a perfect sphere? Answer with proof.
Answer:
Ancient Indian scientist, Aryabhatta, believed that the Earth was a sphere.
English mathematician and physicist, Sir Isaac Newton, thought that the Earth was not a perfect sphere; rather it was shaped like an orange.
When Yuri Gagarin, the first man in space, looked at the Earth from his spacecraft (12 April 1961 AD), the Earth looked like a sphere to him.
Some experiments prove that the Earth is not an exact sphere.
Experiment 1: Let us suppose we have taken a lump of soft clay and then inserted a stick through its centre. Then this lump of clay is spun from west to east.
After some time, when the lump comes to rest, we will see that it has bulged out at the middle and become flattened at the top and bottom.
Thus, the Earth is not perfectly round as it is in constant motion.

Experiment 2: If we take a laddu, we notice that it is well-rounded. But when we keep it on the ground and spin it, its top portion becomes flattened and its middle bulges out, which means its spherical shape gets distorted.
Some other proofs show that the Earth is not a perfect sphere. These are:
- The Earth has high mountains and plateaus as well as deep ravines and gorges. Thus the Earth is not a perfect sphere.
- Photographs taken from outer space by artificial satellites show that the Earth’s surface is irregular.
Thus, the Earth is not perfectly round as it is in constant motion.
Question 4. What is meant by the terms ‘polar diameter’ and ‘equatorial diameter’?
Answer:
‘Polar diameter’ and ‘equatorial diameter’:
The imaginary line joining the North and South Poles is called the polar diameter. The length of the polar diameter is 12,714 kilometres.
The imaginary line extending through the centre of the Earth in the east-west direction is called the equatorial diameter.
The length of the equatorial diameter is 12,756 kilometres. The difference between the Earth’s equatorial diameter and its polar diameter is almost 42 kilometres (12,756 km-12,714 km).

Question 5. Why is the Earth called an oblate spheroid instead of a sphere?
Answer:
Earth called an oblate spheroid instead of a sphere:
An oblate spheroid is an object that is flattened at the top and bottom and bulging out in the middle—not quite a sphere.
Since the Earth is flattened at the Poles, it is an oblate spheroid in shape and not a sphere.

The shape of the Earth is also often compared to the shape of an orange. Both, have a spherical shape with a flattened top and bottom. However, they bulge around their centre.
Conceptual Questions on Earth’s Shape and Geoid
Question 6. Why the Earth Is flattened at the Poles and bulged at the middle?
Answer:
The Earth Is flattened at the Poles and bulged at the middle:
When a top spins, its north and south portions appear flat and the middle portion appears to bulge out.
If an iron rod is inserted into a sphere of clay or earth and spun, we will be able to understand this phenomenon better.
The Earth’s rotation produces centrifugal force and as a result, particles of matter show a tendency to fly out from the centre.
Because of this, there is more matter near the equatorial region. On the other hand, the centripetal force produced at the Poles causes them to be compressed towards the centre.
That is why, the Earth is flattened at the Poles and bulged in the middle.
Question 7. The weight of an object is more at the Poles than at the Equator on the surface of the Earth. Why does this happen? Has this got anything to do with the shape of the Earth?
Answer:
The weight of an object is more at the Poles than at the Equator on the surface of the Earth:
The Earth is not perfectly spherical in shape—
it is actually an oblate spheroid. It is flat at the Poles and bulging out in the middle.
While the Earth’s polar diameter is 12,714km, the equatorial diameter is 12,756km—meaning there is a difference of almost 42km.
The Earth’s gravitational force and its density affect each other. The surface at the equator is further away from the centre of the Earth than that of the Poles.
According to Newton’s laws, gravitational force decreases with the distance from the centre of the Earth and density increases.
That’s why objects weigh more at the Poles than at the Equator.
Practical Examples of Geoid Applications
Question 8. Why don’t we fall off the spherical earth?
Answer:
We Dontfall off the spherical earth:
The Earth is spherical and in constant motion as well. The Earth revolves around the Sun while rotating on its own axis.
This means we are standing on an object that is rotating as well as revolving continuously.
But still, we don’t fall off because of the gravitational force of the Earth. The Earth pulls all objects on its surface towards its centre.
That is why even though the Earth is a sphere that is in constant motion and we are on its surface, we remain stable.
Question 9. What is the altitudinal difference between the highest point and the lowest point on the Earth?
Answer:
The altitudinal difference between the highest point and the lowest point on the Earth:
The highest point on the Earth’s surface is MountEverestwhichis8,848m above sea level and the lowest point on the Earth’s surface is Mariana Trench which is 10,915m deep.
So the difference between the two points is 8,848m + 10,915m = 19,763m or 20,000m (approx) or 20km.

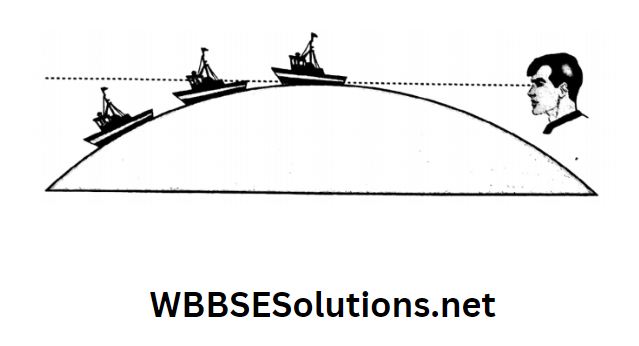
Question 10. Look at the four arcs. Arc 1 has the smallest radius and arc 4 has the largest. Observe the highlighted parts of each arc. Can you say which one has the maximum curvature? Which one is the most straightened?
Answer:
Observing the arcs it is evident that arc 1 has the smallest radius and the radius of arc 4 is the largest. The greater the length of the radius of a circle, the lesser its curvature.
The Earth is round-shaped and has an average radius of 6400 km. Standing on a circle of such a large radius, only a very small part of it catches our eyes.
So the surface of the Earth seems to be flat, as in the case of arc 4. Therefore, arc 4 is the most straightened and arc 1 has the maximum curvature.

Aesthetics and Creativity: This segment will check the aesthetic and creativity of the students.
Importance of Geoid in Geography
Question 11. Tie one end of a string to a pencil. Measure 5cm, 15cm and 30cm intercepts with the string and draw arcs with each as radius. You will get to know why we do not perceive the curvature of the Earth.
Answer:
After drawing arcs of 5 cm, 15 cm and 30 cm radius respectively, it is found that the curvature of the 5 cm radius arc is the highest and the curvature of the 30 cm radius arc is the lowest.
This proves that the curvature of the arc with a radius of a large length is less than the arc with a radius of a smaller length.
That is why we do not generally understand the curvature of the spherical earth with a radius of about 6400 km. So the surface of the Earth seems to be flat.

Question 12. Fill in the knowledge hive with information on the Earth’s oblate spheroid shape

Answer:
1. Polar diameter is 12;714km and equatorial diameter is 12,756km.
2. Objects weigh more at the Poles than at the Equator.
3. The pressure varies with the varying circumference of the Earth.
Question 13. Crossword

Clues:__________
Down:
1. A part of the circumference of a circle.
2. The boundary between the Earth’s surface and the sky.
4. This word means Earthlike or Earth-shaped.
5. This Portuguese explorer set off in 1519 with a fleet of 5 ships to circumnavigate the Earth.
Across: 3. At this time, the Sun is always overhead.
6. This is the shape of the Earth’s orbit.
7. This level experiment was done to prove that The Earth is round.
8. He was the first Indian scientist to say that The Earth is round and that it is in constant motion.
Answer: Down 1. Arc, 2. Horizon, 4. Geoid, 5.Magellan
Across: 3. Noon, 6. Elliptical, 7.Bedford, 8. Aryabhatta
WBBSE Chapter 2 Is the Earth Round Topic B Geoid Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What do you understand by a geoid?
Answer:
Geoid:
Geoid is a Greek word derived from ‘Geo’ meaning earth and ‘eidos’ meaning ‘to see’. The combination of these words means earth shaped. The most accurate word to describe the shape of the Earth is ‘geoid’.
Question 2. What is the actual shape of the Earth?
Answer:
Actual shape of the Earth:
The actual shape of the Earth is like the Earth itself (geoid or earth-shaped) because the Earth’s shape is not similar to any object found on Earth.
Geoid vs. Ellipsoid Explained
Question 3. Why is the Earth’s shape compared to that of an orange?
Answer:
Earth’s shape compared to that of an orange:
The Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is slightly flattened at the Poles. This gives it a similarity to the shape of an orange.
Question 4. What is an oblate spheroid?
Answer:
Oblate spheroid:
The spherical objects that are a little flattened at the top and the bottom i.e. North and South Poles and a little bulge in the middle are called an oblate spheroid.
For example, the shape of the Earth is closely comparable to an oblate spheroid.
Question 5. What is meant by the Earth’s radius?
Answer:
Earth’s radius:
Half the length of the Earth’s diameter with which if we draw an arc, we can measure the circumference of the Earth. This half-length of the Earth’s diameter is called the earth’s radius.
Question 6. What is meant by equatorial diameter?
Answer:
Equatorial diameter:
The diameter of the Earth which is calculated along with the Equator, is called the equatorial diameter. The length of the equatorial diameter is 12,756km.
Question 7. What is meant by the axis of the Earth?
Answer:
Axis of the Earth:
The imaginary spine of the Earth which passes through its centre and reaches the Poles and around which the Earth spins from west to east is called the axis of the Earth.
Question 8. What is the average diameter of the Earth?
Answer:
The average diameter of the Earth:
The average diameter of the Earth is— Equatorial diameter 12,756 km Polar diameter +12,714 km 25,470 km + 2 The average diameter of the Earth 12,735 km
Question 9. Why is the same object heavier at the Poles than at the Equator?
Answer:
The same object heavier at the Poles than at the Equator:
As the Earth is a little flattened at the Poles, the distance from the centre of the Earth to the Poles is less than that to the Equator.
Class 6 Geography Question Answer WBBSE
Thus, the gravitational force exerted at the Poles is more and so, the same object is heavier at the Poles.
Question 10. What is Mount Everest?
Answer:
Mount Everest:
Mount Everest is the highest peak in the Himalayan mountain range. It is 8,848 metres high above sea level and is the highest point on the Earth.
Question 11. What is the Mariana Trench?
Answer:
Mariana Trench:
The Mariana Trench is a long, narrow, deep depression in the Pacific Ocean bed which contains the Challenger Deep—
- The deepest known point on the Earth.
- The Mariana Trench is about 10,915m deep.
Question 12. The Earth’s surface has its highest point at Mount Everest (8,848 m up from sea level) and its lowest point at Mariana Trench (10,915 m down from sea level). Is the shape of the Earth affected by such massive undulations?
Answer:
Yes, the shape of the Earth is affected by such massive undulations. That is why, the shape of the Earth is like its own—that is called ‘geoid’.
WBBSE Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Is The Earth Round Topic B Geoid Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is the meaning of the word ‘geoid’?
Answer: ‘Earth-shaped’ or ‘like the Earth’.
Question 2. What is the length of the circumference of the Earth?
Answer: 40,000km (approx).
Question 3. What is the surface area of the Earth?
Answer: 515.4 million square km.
Question 4. How much greater is the Earth’s size than India’s?
Answer: 160 times.
Question 5. Is the weight of an object heavier or lighter at the Poles than it is at the Equator?
Answer: Heavier.
Question 6. Spherical: Oblate spheroid: Geoid: Orange
Answer: Orange (not a geographical term used to describe the shape of the Earth)
Question 7. Newton: Aryabhatta: Eratosthenes: Magellan
Answer: Newton (didn’t give any information about the Earth’s shape)
Question 8. Pole Star: Rohini: Venus: Evening St
Answer: Rohini (not a celestial body)
Question 9. In 200 BC, Magellan first said that the Earth is round.
Answer: Eratosthenes
Question 10. The horizon always appears as plane.
Answer: 42km
Question 11. Aryabhatta first deduced that the Earth was round after observing the Earth’s shadow on the Moon during an eclipse.
Answer: Spherical
Question 12. The difference between the earth’s equatorial diameter and its Polar diameter is about 67km.
Answer: 42km
WB Class 6 Geography Question Answer
Question 13. The deepest known point on earth is Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench in the Indian Ocean.
Answer: pacific ocean
Question 14. I am the Portuguese explorer who set sail with a fleet of 5 ships to circumnavigate the Earth in 1519. Who am I?
Answer: Magellan
Question 15. I look like a bright, blue ball to astronauts. Who am I?
Answer: Earth
Question 16. During an eclipse, the Earth’s circular shadow falls on me. Who am I?
Answer: Moon
Question 17. I am 6,400km long and with my length, you can draw the shape of the Earth. Who am I?
Answer: Earth’s radius
Question 18. I am the vertical distance of 12,714km between the Earth’s Poles. Who am I?
Answer: Polar Diameter
Question 19. I am the highest point on Earth and the highest peak in the Himalayas. Who am I?
Answer: Mount Everest
Question 20. I am the deepest point in the Pacific Ocean and also on Earth. Who am I?
Answer: Mariana Trench
WBBSE Chapter 2 Is The Earth Round Topic B Geoid Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The Earth is actually____________shaped.
Answer: Earth
Question 2. The outer surface of the Earth is made of solid ____________ materials.
Answer: Rocky
Question 3. The Earth is bulging out at the centre, but at the Poles, it is ____________
Answer: Flattened
Question 4. The imaginary line drawn around the middle of the Earth is called the ____________
Answer: Equator
Question 5. The Earth’s equatorial diameter is ____________ km.
Answer: 12,756
Question 6. The difference between the Earth’s equatorial diameter and its polar diameter is ____________ km.
Answer: 42
Question 7. Any object’s weight is at the Equator ____________
Answer: Least
Question 8. The deepest point on the Earth is ____________
Answer: Mariana trench
Question 9. The Mariana Trench is in the ____________ Ocean.
Answer: Pacific
Question 10. The altitude of the highest point on Earth is ____________ metres.
Answer: 8,848
Question 11. Mount Everest is the highest peak in the ____________ mountain range.
Answer: Himalayan
WBBSE Chapter 2 Is The Earth Round Topic B Geoid Write True Or False
Question 1. The mean diameter of the Earth is 12,756 km.
Answer: False
Question 2. The Earth’s equatorial diameter is less than its polar diameter.
Answer: False
Question 3. Mount Everest is in India.
Answer: False
Question 4. The height of Mount Everest is 10,915m.
Answer: False
Question 5. Mariana Tr.ench is in the Atlantic Ocean.
Answer: False
WBBSE Chapter 2 Is The Earth Round Topic B Geoid Match The Columns
Question 1.

Answer: 1-E,2-A,3-D,4-B,5-C