NEET Foundation Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. Which of the following is true?
- ABA open stomata.
- ABA and cytokinin does not effect on stomata.
- ABA open, cytokinin close stomata.
- ABA close and cytokinin open the stomata.
Answer. 4. ABA close and cytokinin open the stomata.
Question 2. Gizzard of cockroach is a part of
- respiratory system
- digestive system
- immune system
- circulatory system
Answer. 2. digestive system
Question 3. Opening and closing of stomata is controlled by
- K+
- Mg2+
- Ca2+
- N
Answer. 1. K+
Question 4. In which of the following solution volume of a cell increases?
- Hypotonic
- Isotonic
- Hypertonic
- Supertonic
Answer. 1. Hypotonic
Question 5. Allele is
- isomer of a gene
- a chromosome
- chromatids
- alternate form of gene
Answer. 4. alternate form of gene
Question 6. Potato is the modification of
- stem
- root
- leaf
- flower
Answer. 1. stem
Question 7. Triticum aestivum is
- tetraploid
- hexaploid
- triploid
- pentaploid
Answer. 2. hexaploid
Question 8. Carrot is micropropagate through
- embryo
- embryoids
- shoot culture
- callus
Answer. 4. callus
Question 9. For self-pollination, flower must be
- unisexual
- bisexual
- monosexual
- asexual
Answer. 2. bisexual
Question 10. Electron microscope is discovered by
- Robert Hooke
- Knoll and Ruska
- Robert Brown
- Janssen
Answer. 2. Knoll and Ruska
Question 11. Which is common in respiration and photosynthesis?
- Oxidation
- Phytochrome
- Cytochrome
- Photosystem
Answer. 3. Cytochrome
Question 12. Treatment of seeds with low temperature is called
- vernalization
- phytochrome
- hybridization
- scarification
Answer. 1. vernalization
Question 13. C2 plant shows efficiency even in
- low CO2 concentration
- low temperature
- high O2 concentration
- at low water
Answer. 1. low CO2 concentration
Question 14. Oxidative phosphorylation occur in
- photosynthesis
- respiration
- NADH2 formation
- photolysis of water
Answer. 2. respiration
Question 15. Lactic acid converted into alcohol in process called
- fermentation
- aerobic respiration
- respiration
- photosynthesis
Answer. 1. fermentation
Question 16. Quantasome are present in
- stroma
- grana
- mitochondria
- golgi body
Answer. 2. grana
Question 17. Sunder ban contain mainly
- mangrove plant
- alpine tree
- tice forest
- grass
Answer. 1. mangrove plant
Question 18. Bhopal gas tragedy is due to
- benzyl isocyanide
- benzene cyanide
- methyl isocyanide
- methyl cyanide
Answer. 3. methyl isocyanide
Question 19. Ferrodoxin contain
- Mg
- Co
- iron
- nitrite
Answer. 3. iron
Question 20. The scientific study of inheritance of character to improve human race is
- genetics
- eugenics
- euthenic
- genealogy
Answer. 2. eugenics
Question 21. Modern system of classification classified organisms in _________ kingdom.
- one
- two
- four
- five
Answer. 4. five
Question 22. Middle lamella contain
- chitin
- lignin
- pectin
- cellulose
Answer. 3. pectin
Question 23. Root develop from any part of plant is
- tap root
- adventitious
- primary root
- secondary root
Answer. 2. adventitious
Question 24. Cork cambium is called
- phellem
- bast
- phellogen
- wood
Answer. 3. phellogen
Question 25. Guard cell lined
- stomata
- hydathode
- lenticel
- pneumatophore
Answer. 1. stomata
Question 26. Maximum water loss takes place through
- cuticle
- stomata
- hydathode
- lenticel
Answer. 2. stomata
Question 27. In succession complexities in structure
- drastically increasing
- slowly increasing
- does not increasing
- constant
Answer. 2. slowly increasing
Question 28. The part which is grafting on stalk of another tree is called
- graft
- bulbil
- bud
- scion
Answer. 4. scion
Question 29. Centrosome are present
- in plant cell only
- in animal cell
- in both plant and animal cell
- None of these
Answer. 2. in animal cell
Question 30. ER work for synthesis of
- carbohydrate
- protein
- photosystem
- ATP
Answer. 2. protein
Question 31. Lysosome contain
- hormone
- lytic enzyme
- hydrolytic enzyme
- useful material
Answer. 3. hydrolytic enzyme
Question 32. Development of fruit without fertilization is called
- parthenocarpy
- hybridizations
- tissue culture
- anther culture
Answer. 1. parthenocarpy
Question 33. Prokaryotic cell does not have
- nucleolus
- membrane bound organelles
- centrioles
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 34. Sea anemone belongs to the phylum
- porifera
- echinodermata
- coelenterata
- protista
Answer. 3. coelenterata
Question 35. Which is an indicator of air pollution?
- Lichens
- Mosses
- Algae
- Fungi
Answer. 1. Lichens
Question 36. The alcohol obtained on fat metabolism is
- methanol
- ethanol
- glycerol
- All of these
Answer. 3. glycerol
Question 37. Source of light in an electron microscope is
- infrared rays
- UV rays
- visible light
- electron beam
Answer. 4. electron beam
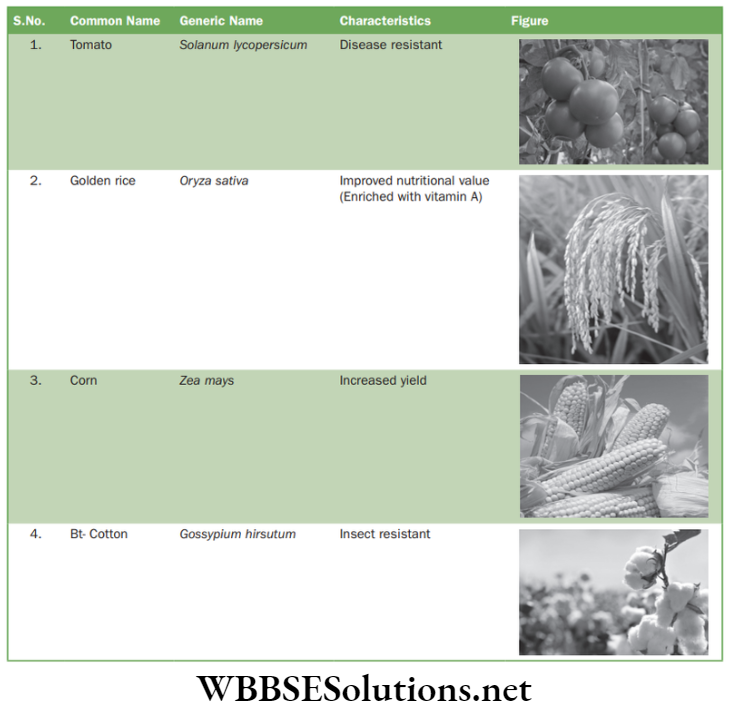
Question 38. Which of these is not correct regarding Bt cotton?
- It Is A Disease Or Resistant Plant.
- It Produces More Yield Of Cotton.
- It Has Been Obtained By Recombination.
- No Such Plant Is Heard Of.
Answer. 4. No Such Plant Is Heard Of.
Question 39. Green revolution was given by
- Darwin
- Wallace
- Norman Borlaug
- R. Mishra
Answer. 3. Norman Borlaug
Question 40. Which of these enzymes is maximum in chloroplast
- RUBP carboxylase
- PEP
- glucohexokinase
- isomerase
Answer. 1. RUBP carboxylase
Question 41. Vessels in xylem and companion cells in phloem are the characteristic features of
- angiosperm
- gymnosperm
- pteridophytes
- bryophytes
Answer. 1. angiosperm
Question 42. Edible part in Tomato is
- mesocarp
- thalamus
- pericarp
- endocarp, inflorescence
Answer. 3. pericarp
Question 43. Multinucleate aseptate hyphae present in Rhizopus are called
- homothallic
- heterothallic
- trichogone
- coenocyte
Answer. 4. coenocyte
Question 44. Stored food in green algae is
- starch
- cellulose
- fat
- glycogen
Answer. 1. starch
Question 45. Fat soluble vitamin is
- A
- B
- C
- B12
Answer. 1. A
Question 46. Clitellum in earthworm is responsible for
- respiration
- locomotion
- digestion
- cocoon formation
Answer. 4. cocoon formation
Question 47. Conglobate gland is present in
- male cockroach
- female cockroach
- earthworm
- Hydra
Answer. 1. male cockroach
Question 48. Conjoint, collateral, closed, scattered vascular bundles with sclerenchymatous sheath is observed in
- dicot stem
- monocot stem
- dicot root
- monocot root
Answer. 2. monocot stem
Question 49. Plants growing near seashores are expected to behave as
- hydrophytes
- xerophytes
- lithophytes
- halophytes
Answer. 4. halophytes
Question 50. The pyramid of biomass in a good ecosystem is
- always upright
- sometimes upright
- inverted
- upright and some times inverted
Answer. 3. inverted
Question 51. Which of these is incorrect in view of double fertilization?
- Given by Nawaschin in 1889
- It refers to the Fusion of Male and Female Gamete and Male Gamete with the Secondary Nuclei
- Endosperm Formed is Diploid
- Endosperm Formed Provides Nutrition to the Embryo
Answer. 3. Endosperm Formed is Diploid
Directions (52–64): In each of the following questions, a statement of assertion is given and a corresponding statement of reason is given just below it. Of the statements, mark the correct answer as:
- if both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- if both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- if A is true but R is false.
- both A and R are false.
Question 52. Assertion: Protists are similar to prokaryotes.
Reason: Protists do not possess membrane bound organelles.
Answer. 4. both A and R are false.
Question 53. Assertion: Diatoms are golden brown or yellow in colour.
Reason: Cell wall in diatoms in silicified.
Answer. 2. if both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 54. Assertion: Euglena is motile.
Reason: It shows pseudopodia locomotion.
Answer. 3. if A is true but R is false.
Question 55. Assertion: Diatoms are useful even after their death.
Reason: Dead bodies of diatoms made the ocean floor fertile for the growth of other organisms.
Answer. 3. if A is true but R is false.
Question 56. Assertion: Euglenophyta do not reproduce in unfavourable conditions.
Reason: Sexual reproduction do not take place in euglenophyta.
Answer. 1. if both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 57. Assertion: Protista is internally diverse group.
Reason: Plant like organisms and animal like organisms both are grouped under protista.
Answer. 1. if both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 58. Assertion: Diatoms are motile.
Reason: They lack any organelles of locomotion.
Answer. 2. if both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 59. Assertion: Salmonella typhi most commonly affects the lungs.
Reason: Salmonella typhi causes pneumonia.
Answer. 4. both A and R are false.
Question 60. Assertion: Gout is a communicable disease.
Reason: In gout body forms excess ammonia.
Answer. 4. both A and R are false.
Question 61. Assertion: AIDS is the starting stage of HIV infection.
Reason: In HIV infection, immune system is unaffected.
Answer. 4. both A and R are false.
Question 62. Assertion: Dengue is a viral disease.
Reason: Dengue is a viral disease.
Answer. 2. if both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 63. Assertion: Plague is a disease of rats caused by bacteria.
Reason: It is also called black death.
Answer. 2. if both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 64. Assertion: Sandfly transmits kala-azar.
Reason: In kala-azar, the parasite damages the brain.
Answer. 3. if A is true but R is false.
Question 65. Gymnosperms constitute dominant flora of
- tropical regions
- temperate regions
- both (1) and (2)
- none of these
Answer. 2. temperate regions
Question 66. Gymnosperms generally have
- tap roots
- adventitious roots
- small roots
- none of these
Answer. 1. tap roots
Question 67. Which plants act as connecting link between gymnosperms and angiosperms?
- Cycadales
- Ginkgoales
- Gnetales
- None of these
Answer. 3. Gnetales
Question 68. Vessels in xylem of gymnosperms are
- present
- absent
- absent except genetales
- present except genetales
Answer. 3. absent except genetales
Question 69. Pollination in gymnosperms occurs by
- wind
- insects
- water
- all of these
Answer. 1. wind
Question 70. Endosperm in gymnosperms is
- generally haploid
- always haploid
- triploid
- with different ploidy levels
Answer. 2. always haploid
Question 71. Ovule in gymnosperms in generally
- anatropous and bitegmic
- orthotropous and bitegmic
- orthotropous and unitegmic
- anatropous and unitegmic
Answer. 3. orthotropous and unitegmic
Question 72. Seeds in gymnosperms represent
- single generation
- 2 generations
- 3 generations
- none of these
Answer. 3. 3 generations
Question 73. Which is commonly known as ‘Living fossil’?
- ginkgo biloba
- thuja
- araucaria
- cupressus
Answer. 1. ginkgo biloba
Question 74. Which is the largest order of modern gymnosperms?
- Gnetales
- Cycadales
- Coniferales
- Ginkgoales
Answer. 3. Coniferales
Question 75. Gymnosperms differ from most of angiosperms
- in having seeds
- in being smaller in system
- in having naked ovules
- None of these
Answer. 3. in having naked ovules
Question 76. One of the main evolutionary features of alternation of generations from algae to flowering plant is
- gradual elaboration of sporophyte
- gradual elaboration of gametophyte
- gradual elaboration of gametophyte and sporophyte
- elimination of sporophyte
Answer. 1. gradual elaboration of sporophyte
Question 77. Phenomenon of ‘Sulphur shower’ is related with
- cycas
- pinus
- ginkgo
- none of these
Answer. 2. pinus
Question 78. Gymnosperm of medicinal use is
- ephedra
- pinus
- zamia
- cycas
Answer. 1. ephedra
Question 79. The characteristic of gymnosperm ovule is the presence of
- pollen chamber
- integument
- vascular supply
- nucellus
Answer. 1. pollen chamber
Question 80. Endosperm in gymnosperms develops from
- microspore
- megaspore
- secondary nucleus
- archegonium
Answer. 2. megaspore
Question 81. Megasporophylls of ferns of gymnosperms are comparable to which structure of angiosperms?
- Stamens
- Ovules
- Carpels
- Megasporophylls
Answer. 3. Carpels
Question 82. Birbal Sahni discovered a fossil plant from Rahmahal hills. It belongs to
- Angiosperms
- Gymnosperms
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
Answer. 2. Gymnosperms
Question 83. Largest ovules (or largest gametes or longest plants) are found among
- monocots
- dicots
- gymnosperms
- angiosperms
Answer. 3. gymnosperms
Question 84. The explanation for occurrence of ciliated motile sperms in xerophytic Cycas is
- it is vestigial character indicating the periodophytic ancestry of Cycas
- it is a functional character, the pollen chamber of Cycas is filled with water and the sperms must be ciliated for swimming
- when the pollen grain and ovules of Cycas fall on the ground, the pollen germinates and sperms swim in rain water to reach the ovule
- the cilia are a zerophytic character like hair
Answer. 1. it is vestigial character indicating the periodophytic ancestry of Cycas
Question 85. Wood of Pinus is
- manoxylic and monoxylic
- pycnoxylic and monoxylic
- manoxylic and polyxylic
- pycnoxylic and polyxylic
Answer. 2. pycnoxylic and monoxylic
Question 86. Which gymnosperms is having ‘bitegmic ovules’?
- Cycas
- Ginkgo
- Gnetum
- Taxus
Answer. 3. Gnetum
Question 87. How much time is generally taken by the pine plant from pollination to fertilization?
- Four months
- Fifteen months
- Two years
- Four years
Answer. 2. Fifteen months
Question 88. Term ‘Alternation of generations’ was first used in plants by
- Amici
- Hofmeister
- Kolreuter
- None of these
Answer. 2. Hofmeister
Question 89. Foremost Indian embryologist was
- S.C. Maheswari
- P. Maheshwari
- H.Y. Mohan Ram
- None of these
Answer. 2. P. Maheshwari
Question 90. Single microsporangium per anther is found in
- Gossypium
- Hibiscus
- Arceuthobium
- Najas
Answer. 3. Arceuthobium
Question 91. ‘Callase’ enzyme that dissolves callose of pollen tetrads to separate four pollens is provided by
- pollens
- tapetum
- middle layers
- endothecium
Answer. 3. middle layers
Question 92. Compound pollens held together in small units are called
- pollinium
- massulae
- translator
- None of these
Answer. 2. massulae
Question 93. Ubisch bodies are provided by
- tapetum
- pollen kitt
- exine
- intine
Answer. 1. tapetum
Question 94. ‘Pollen grains embryo sacs’ were first observed in
- Hymenocallis
- Elodaea
- Hyacinthus
- None of these
Answer. 3. Hyacinthus
Question 95. Iatropalynology is
- medicinal aspects of pollen grains
- fossil pollen grains
- pollens in relation to honey
- None of these
Answer. 1. medicinal aspects of pollen grains
Question 96. Pollinia are characteristic of
- Asclepiadaceae
- Labiatae
- Compositae
- Aristolochiaceae
Answer. 1. Asclepiadaceae
Question 97. Pollen grain is a
- megaspore
- microspore
- microsporophyll
- microsporangium
Answer. 2. microspore
Question 98. If the innermost layer of integument becomes specialized as a nutritive layer, it is
- tapetum
- endothecium
- endosperm
- endothelium
Answer. 4. endothelium
Question 99. Pollenkitt is present in pollens of
- anemophilous flowers
- entomophilous flowers
- zoophilous flowers
- malacophilous flowers
Answer. 2. entomophilous flowers
Question 100. The stamens represent
- microsporangia
- megasporangia
- megasporophylls
- microsporophylls
Answer. 4. microsporophylls
Question 101. Division of cytoplasm after meiotic division in pollen mother cell is called
- cytokinesis
- cytomixis
- amphimixis
- apomixis
Answer. 1. cytokinesis
Question 102. Which one of the following produces both enzymes and hormone?
- endothecium
- middle layer
- epidermis
- tapetum
Answer. 4. tapetum
Question 103. Normal type of sexual reproduction is
- apomixis
- amphimixis
- pseudogamy
- None of these
Answer. 2. amphimixis
Question 104. Tapetum and endothecium in anther are derived from
- primary sporogenous cell
- primary parietal cell
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer. 2. primary parietal cell
Question 105. In a pollen grain, larger nucleus is
- generative nucleus
- vegetative nucleus
- polar nucleus
- None of these
Answer. 2. vegetative nucleus
Question 106. The fibrous thickenings of endothecium are mainly made of
- Cellulose
- Pectin
- Lignin
- None of these
Answer. 1. Cellulose
Question 107. Which is the most common type of tapetum in angiosperms?
- Amoeboid
- Secretory or glandular
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer. 2. Secretory or glandular
Question 108. Vascular tissue is derived from
- the ectoderm
- all the germ layers
- the epithelium
- the mesoderm
Answer. 4. the mesoderm
Question 109. The connective tissues, which from the frame work of organs such as lymph nodes, bone marrow and liver are
- reticular
- areolar
- adipose
- None of these
Answer. 1. reticular
Question 110. Term ecology was given by
- Reiter
- Cuvier
- Haeckel
- Malthus
Answer. 3. Haeckel
Question 111. Leaf abscission, fruit fall, and bud dormancy occur by which phytohormone?
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Gibberellins
- Abscisic acid
Answer. 4. Abscisic acid
Question 112. Number of segments found in the body of cockroach are
- 8
- 10
- 12
- 15
Answer. 2. 10
Question 113. Which of the following is not an insectivorous plant?
- Drosera
- Nepenthes
- Monotrapa
- Utricularia
Answer. 3. Monotrapa
Question 114. Which branch study about remains of plant life?
- Palaentology
- Palaeobotany
- Eugenics
- Palynology
Answer. 2. Palaeobotany
Question 115. If water enters in a cell, the pressure exerted by its swollen protoplast is
- turgor pressure
- DPD
- osmotic pressure
- imbibition
Answer. 1. turgor pressure
Question 116. How many molecules of glycine is required to release one CO2 molecule in photorespiration?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer. 2. Two
Question 117. Wilting occurs when
- rate of transpiration is higher than absorption
- rate of absorption is higher than transpiration
- excess root pressure
- high relative humidity in air
Answer. 1. rate of transpiration is higher than absorption
Question 118. Longest animal with one nostril is
- whale
- tortoise
- shark
- python
Answer. 1. whale
Question 119. Bacterial flagella is made up of
- protein
- amines
- lipids
- carbohydrates
Answer. 4. carbohydrates
Question 120. Pollution of SO2 destroy
- Lichen
- Fungi
- Algae
- Fishes
Answer. 1. Lichen
Question 121. Seaweeds are important source of
- chlorine
- fluorine
- iodine
- bromine
Answer. 1. chlorine
Question 122. Agar agar is obtained from
- green algae
- red algae
- brown algae
- blue green algae
Answer. 2. red algae
Question 123. Basic structure of protein was given by
- Stanley
- Nicholson
- Watson
- Singer
Answer. 1. Stanley
Question 124. Nucleus pulposus is found in
- brain
- nucleus
- intervertebral disc
- liver
Answer. 3. intervertebral disc
Question 125. Animal that excrete urea produced during metabolism of amino acid is
- ureotelism
- uricotelism
- ammonotelism
- aminotelism
Answer. 1. ureotelism
Question 126. In frogs, oviduct is formed by
- wolffian duct
- mesonephric duct
- mullerian duct
- bidder’s canal
Answer. 3. mullerian duct
Question 127. Which of the following nephridia is not found in earthworm?
- Septal nephridia
- Macro nephridia
- Integumentary nephridia
- Pharyngeal nephridia
Answer. 2. Macro nephridia
Question 128. Which of the following is a neem product and used as insect repellent?
- Azadirachtin
- Rotenon
- Parathion
- Endrin
Answer. 1. Azadirachtin
Question 129. Which of the following sugar is found in nucleic acid?
- Dextrose
- Glucose
- Levulose
- Deoxyribose
Answer. 4. Deoxyribose
Question 130. Cellulose is a polymer of
- α-glucose
- β-glucose
- α-fructose
- β-fructose
Answer. 2. β-glucose
Question 131. Broad leaved forest oak are found in
- tropical deciduous forest
- tropical ever green forest
- temperate deciduous forest
- north coniferous forest
Answer. 3. temperate deciduous forest
Question 132. The sum total of all population of the same kind of organisms constitute
- cline
- genus
- community
- species
Answer. 4. species
Question 133. Competition for food, light and space is most severe between two
- closely related species growing in the same area
- closely related species growing in different habitats
- distantly related species growing in different habitats
- distantly related species growing in same area
Answer. 1. closely related species growing in the same area
Question 134. Amphids found upon lips of Ascaris
- are organ of smell and chemoreception
- secrete saliva
- are adhesive organs
- secrete proteolytic enzymes
Answer. 1. are organ of smell and chemoreception
Question 135. In sex linkage, the speciality is
- atavism
- reversion
- gene flow
- criss-cross inheritance
Answer. 4. criss-cross inheritance
Question 136. By which of the following food is captured in sponges?
- Porocytes
- Pinacocytes
- Choanocytes
- Trophocytes
Answer. 3. Choanocytes
Question 137. The flight muscles of birds are attached to
- coracoid
- scapula
- keel of sternum
- clavicle
Answer. 3. keel of sternum
Question 138. Which one of the following shows a taxonomically closely-related group?
- Earthworm, ringworm, tapeworm
- Silverfish, cuttlefish, starfish
- Housefly, dragonfly, butterfly
- Sea horse, sea anemone, sea urchin
Answer. 3. Housefly, dragonfly, butterfly
Question 139. Ephyra is the larva of
- Sea anemone
- Obelia
- Aurelia
- Physalia
Answer. 3. Aurelia
Question 140. Gymnospermous plants lack fruit because
- fertilization does not occur in them
- they lack pollination
- they lack ovary
- All of these
Answer. 3. they lack ovary
Question 141. In lichens, the term ascomata is applied to
- ascocarp
- ascus mother cell
- ascogenous hyphae
- None of these
Answer. 1. ascocarp
Question 142. The characteristics that define a family are more general than those that define a
- genus
- class
- phylum
- cohort
Answer. 4. cohort
Question 143. Which one of the following is responsible for healing the wounds in plants?
- Intercalary meristem
- Promeristem
- Lateral meristem
- Secondary meristem
Answer. 4. Secondary meristem
Question 144. In which of the following, amphivasal vascular bundles are reported?
- Dracaena
- Salvia
- Mangifera indica
- both (1) and (3)
Answer. 1. Dracaena
Question 145. Which one of the following is seedless vascular plant?
- Ferns
- Horse tails
- Club mosses
- All of these
Answer. 4. All of these
Question 146. Sedimentation, a process that has been going since the earth was formed, can take place
- on land
- in water bodies
- Both (1) and (2)
- in deserts
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 147. Stomatal pores bounded by a single ring-shaped guard cells are found in
- capsule of Funaria
- pinnule of Cycas
- leaf of Dryopteris
- None of these
Answer. 1. capsule of Funaria
Question 148. Cohesive-adhesive theory of water molecules explains that
- water ascends in the plant due to transpiration pull
- column of water remains continuous due to cohesive force of water molecules
- Both (1) and (2)
- water does not ascend in plant due to transpiration pull
Answer. 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 149. The arrangement of leaves in a pattern that minimizes overlapping or shading but maximizes leaf exposure to light is called
- etiolation
- leaf mosaic
- introrse condition
- glossopodium
Answer. 2. leaf mosaic
Question 150. In Selaginella, the adaxial outgrowth from the base of the leaf is called
- velum
- glossopodium
- ligule
- rhizophore
Answer. 3. ligule
Question 151. Under which condition, transpiration from plants would be must rapid?
- When there is lot of humidity in the atmosphere
- When the air is still (immovable)
- When environmental conditions are dry
- All of these
Answer. 3. When environmental conditions are dry
Question 152. Presence of ciliated anterozoids in Dryopteris indicates
- terrestrial habit
- aquatic ancestry
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer. 2. aquatic ancestry
Question 153. Mesophyll is differentiated into palisade and spongy tissue in
- hydrophytic leaf
- monocot leaf
- dicot leaf
- xerophytic leaf
Answer. 3. dicot leaf
Question 154. The rate at which the energy is stored by photosynthetic and chemosynthetic activity of producers, is called
- secondary productivity
- net productivity
- Both (1) and (2)
- primary productivity
Answer. 4. primary productivity
Question 155. The ascomycetes growing under soil level are termed as
- hypogean
- lignicolous
- terricolous
- coprophilous
Answer. 1. hypogean
Question 156. The biomass of each succeeding trophic level is
- equal to the next trophic level
- more than one proceeding it
- constantly fixed
- less than the one proceeding it
Answer. 4. less than the one proceeding it
Question 157. Lignin is component of the secondary cell walls of
- parenchyma
- sclerenchyma
- collenchyma
- epidermis
Answer. 2. sclerenchyma
Question 158. Plasmodesmata allow direct exchange of materials
- within the cells
- between neighbour cells
- between two distant cells
- None of the above
Answer. 2. between neighbour cells
Question 159. Gaseous exchange in the submerged hydrophytes occurs through
- stomata
- hydathodes
- lenticels
- general body surface of plants
Answer. 4. general body surface of plants
Question 160. Exarch and polyarch vascular bundles occur in
- monocot stem
- monocot root
- dicot stem
- dicot root
Answer. 2. monocot root
Question 161. Which of the following terms represents a pair of contrasting characters?
- Alleles
- Genotypes
- Phenotypes
- Homozygous
Answer. 1. Alleles
Question 162. Which type of fruit the Betel nut is?
- Nut
- Sorosis
- Drupe
- Berry
Answer. 4. Berry
Question 163. In which of the following plants, there is no differentiation of bark, heartwood and sapwood?
- Date palm
- Ashok
- Mango
- All of these
Answer. 1. Date palm
Question 164. Which of the following tissues is present in periderm?
- Phellem
- Xylem
- Duramen
- Bast
Answer. 1. Phellem
Question 165. Which one of the following is the characteristic of photosynthesis?
- Formation of starch from formaldehyde.
- Oxidation of chlorophyll occurs.
- There occurs formation of chlorophyll pigment from inorganic salts.
- Light energy is converted into chemical energy.
Answer. 4. Light energy is converted into chemical energy.
Question 166. Bicollateral vascular bundle is a characteristic feature of family
- cruciferae
- solanaceae
- cucurbitaceae
- All of these
Answer. 3. cucurbitaceae
Question 167. The old leguminous roots turn green because
- leghaemoglobin changes into chlorophyll-c
- leghaemoglobin is broken down
- leghaemoglobin changes into chlorophyll-b
- leghaemoglobin changes into chlorophyll-a
Answer. 2. leghaemoglobin is broken down
Question 168. In which of the following fruits dispersal takes place by grazing animals such as goat and cow?
- Coconut
- Xanthium
- Mangifera indica
- Cactus
Answer. 2. Xanthium
Question 169. The family leguminosae is divided into three subfamilies on the basis of
- gynoecium only
- corolla
- aestivation of calyx and corolla
- corolla and androecium
Answer. 4. corolla and androecium
Question 170. Fern and Cycas are similar in having
- ciliated gametes
- seeds
- trachea
- cambium
Answer. 1. ciliated gametes
Question 171. Third generation pesticide is
- juvenile hormone analogue
- pheromone
- sterilogastrone
- weedicide
Answer. 1. juvenile hormone analogue
Question 172. Formation of coal from plant material by the process of diagenesis and metamorphism is known as
- coal gasification
- plant ash
- coalification
- fossilization
Answer. 3. coalification
Question 173. Which one of the following oils is produced by Linum usitatissimum in India?
- Linseed oil
- Sunflower oil
- Groundnut oil
- Palm oil
Answer. 1. Linseed oil
Question 174. A plant completing its life cycle before the onset of dry condition is said to be
- short day plant
- long day plant
- drought escaping
- amphibious
Answer. 3. drought escaping
Question 175. Dumb-bell shaped guard cells are seen in
- dicot leaves
- monocot leaves
- seeds
- fruits
Answer. 2. monocot leaves
Question 176. Fat globules are present in
- areolar tissue
- fibres
- adipose tissue
- blood tissue
Answer. 3. adipose tissue
Question 177. Experiment to prove necessity of CO2 for photosynthesis is
- Hills experiment
- Mohl’s experiment
- Calvins experiment
- Arnon’s experiment
Answer. 2. Mohl’s experiment
Question 178. A hypothetical substance involved in flowering is
- auxin
- kinetin
- GA
- florigen
Answer. 1. auxin