Arithmetic Chapter 4 Square Root Of Fraction Exercise 4 Solved Example Problems
Introduction
You have learnt the method of finding the square root of the perfect square integers in the previous class. Here, you will be able to learn the method of finding the square root of fractions and decimals.
As in our practical life we have to deal not only with integers but also with fractions and decimals so it is necessary to know the method of finding the square root of fractions and decimals as well.
The square roots of fractions and decimals are calculated in a similar way as that of integers but here the method is slightly complicated.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 7 Maths
Square root of decimal fraction
If a decimal fraction is multiplied by itself then the product is called the square of the decimal fraction and the original decimal fraction is called the square root of the product.
Example:
Square of 0.2 0.2 0.2 = 0.04; the therefore square root of 0.04 = √0.04= 0.2.
Square of 0.7 0.7 x 0.7 = 0.49; therefore square root of 0.49 = √0.49 = 0.7.
Similarly, (0.12)2= 0.12 x 0.12 = 0.0144, hence √0.0144 = 0.12
(0.24)2 = 0.24 x 0.24 = 0.0576, hence √0.0576 = 0.24

Rule:
1. Mark pair of digits, for an integral part, starting from the digit in the units’ place (i.e., from the digit immediately before the decimal point), towards the left in a similar way as you have done in the case of integers.
Then, similarly, mark the digits immediately after the decimal point in pairs towards the right.
2. If the decimal fraction do not contain any integral part then perform marking the pairs after the decimal point.
3. If the given decimal fraction has an odd number of decimal places, put a zero at the end to make the number of digits after decimal point even.
4. The decimal point should be put in the square root immediately when the pair of digits from the decimal part is brought down at the end of an integral part.
WBBSE Class 7 Arithmetic Square Root Examples
Example: Find the square root of: 150.0625

∴ The required square root is 12.25.
Example: (0.1)2 = 0.01; Here, 0.01 < 0.1
And (1.5)2 = 2.25; here 2.25 > 1.5
The square root of a vulgar fraction
If a vulgar fraction is multiplied by itself then the product is called the square of that vulgar fraction and the original vulgar fraction is called the square root of the product.
Example: Square of \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
therefore square root of \(\frac{1}{2}\) = ![]() = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)

Arithmetic Chapter 4 Square Root Of Fraction Exercise 4 Some Problems On Square Root Of Decimal Fractions
Example 1. The area of a square is 32.49 sq cm. What is the length of one side of the square?
Solution:
Given:
The area of a square is 32.49 sq cm.
The length of the side of the square = √32.49 cm = 5.7 cm.
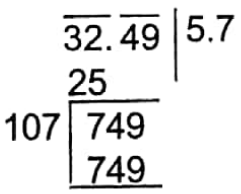
∴ 5.7 cm
The length of one side of the square 5.7 cm.
Example 2. What least number must be subtracted from 0.0582 so that the result of subtraction be a perfect square decimal number?
Solution:
Given:
0.0582
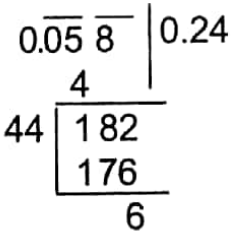
Hence, it is found that the number 0.0582 exceeds the square of 0.24 by 0.0006.
Hence, at least 0.0006 should be subtracted from 0.0582 so that the result of subtraction will be a perfect square decimal number.
∴ At least 0.0006 should be subtracted.
Example 3. Find the length of one side of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of two rectangles whose areas are 2.1214 sq m and 2.9411 sq m.
Solution:
Given:
2.1214 sq m And 2.9411 sq m
Total area of the two rectangles = (2.1214+2.9411) sq m = 5.0625 sq m
∴ Area of the square = 5.0625 sq m
∴ Length of the side of the square = √5.0625 m = 2.25 m
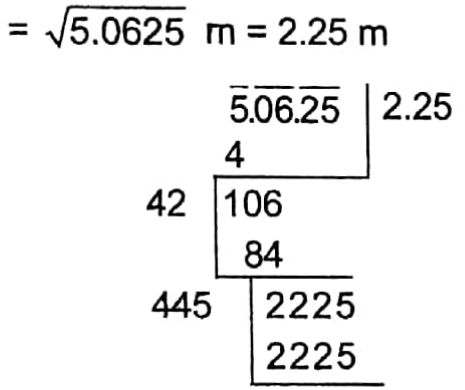
∴ 2.25 m
Length of the side of the square 2.25 m
Example 5. What must be added with 0.28 so that the square root of 1?
Solution:
Given:
0.28
Since, square root of the sum is 1 therefore, sum is also 1.
Number to be added = (1-0.28) = 0.72 = 0.72
∴ 0.72
Solved Problems for Class 7 Square Roots of Fractions
Example 6. Find the square root of the product of 0.032 and 0.2.
Solution:
Given:
0.032 And 0.2
The required square root
= √0.032×0.2= √0.0064=0.08
= 0.08
The square root of the product 0.08
Example 7. Find the value of √240.25 + √2.4025 + √0.024025
Solution:
Given:
√240.25 + √2.4025 + √0.024025
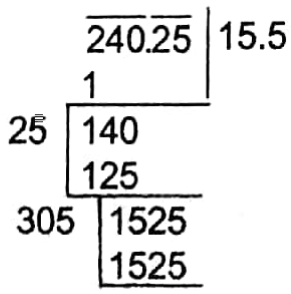
∴ √240.25 = 15.5
Similarly, √240.25 = 1.55 and,
√0.024025 = 0.155
∴ The required sum = 15.5 + 1.55 + 0.155 = 17.205
∴ 17.205
The value of √240.25 + √2.4025 + √0.024025 = 17.205
Class 7 Maths Exercise 4 Solutions on Square Roots
Example 8. Which number should be subtracted from 48.03 so that the square root of the difference is 5.7?
Solution:
Since, the square root of the difference is 5.7 therefore, the difference = (5.7)2 = 32.49.
Hence, the number to the subtracted = 48.03 – 32.49 = 15.54
Example 9. Find the decimal number which when multiplied by itself gives 1.1025 as the product.
Solution: The required number will be the square root of 1.1025 = √1.1025 = 1.05
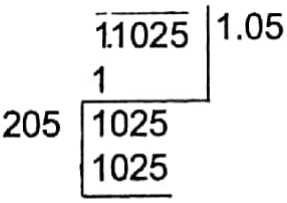
∴ 1.05
Example 10. Find the square root of 2 upto 3 places of decimals.
Solution:
Given:
Here, although 2 is an integer it is not a perfect square number.
Hence, the square root of 2 must be a decimal fraction.
Also, we may consider 2 as 2.000000…
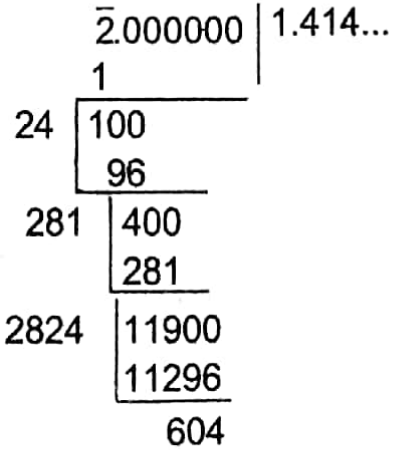
∴ The required square root = 1.414.
Example 11. Which decimal number is to be added with 0.75 so that square root of the sum will be 2?
Solution:
Since, the square root of the sum will be 2 therefore the sum will be 4.
∴ Number to be added = 4-0.75 = 3.25
∴ 3.25.
Example 12. Find the square root of 5.842 up to 3 places of decimals.
Solution:
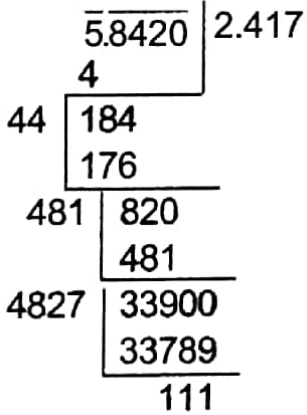
∴ The required square root is 2.417.
Example 13. Find the approximate value of √15 upto 2 decimal places. Find how greater or less than 15 is the square of this approximate value.
Solution:
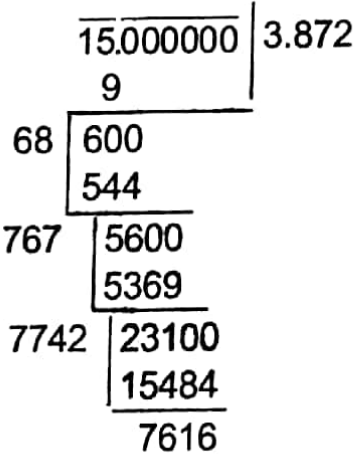
Therefore, the approximate value of upto 2 decimals places is 3.87.
Now, square of 3.87 = (3.87)2 = 14.9769.
Therefore, the square is less than 15 by (15-14.9769)=0.0231.
∴ 3.87, 0.0231 less.
Example 14. Find the square root of 52.983841 correct upto two places of decimals
Solution:

Hence, the square root of 52.983841 correct up to two places of decimals is 7.28
Example 15. Find the value of √0.5 correct up to three decimal places.
Solution:
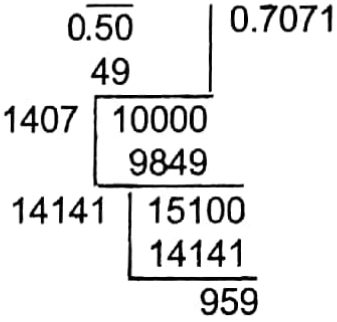
∴ The value of √0.5 correct up to three decimal places is 0.707.
Example 16. Which decimal fraction multiplied by itself will give a product 7.5625?
Solution: The required decimal fraction will be the square root of 7.5625
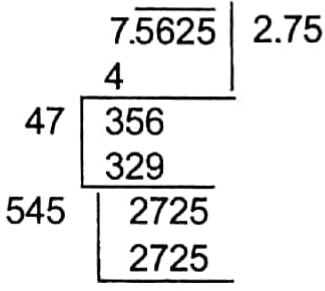
∴ 2.75
West Bengal Board Class 7 Square Root Assistance
Example 17. Find the least number which when added to 31.69 will make it a perfect square having 4 places after the decimal.
Solution:
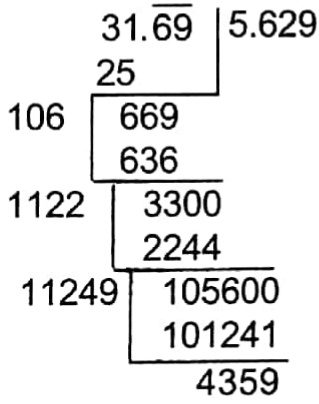
Example 18. Find the difference of the lengths of the sides The area of the new square of the squares whose areas are 1.4641 sq m and 1.0609 sq m.
Solution:
The length of side of the first square. Each side of the new square = √14641 m = 1.21 m.
The length of side of the second square = √1.0609 m = 1.03 m
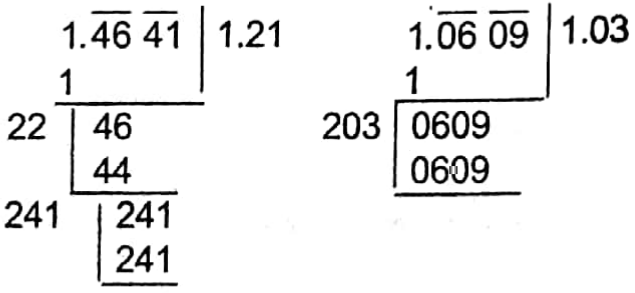
Example 19. Find the length of the side of the square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of two rectangles having areas 3.24 sq m and 2.52 sq m.
Solution:
The sum of the areas of two rectangles (3.24 + 2.52) sq m = 5.76 sq m.
∴ Length of the side of the square = √5.76 m = 2.4 m
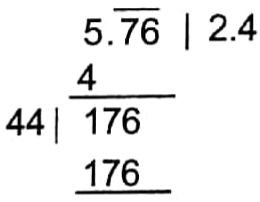
∴ The length of the side of the square is 2.4 m.
Example 20. The sides of two squares are 16.5 and 22 metres respectively. Find the side of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of the two squares.
Solution:
Area of the first square = (16.5)2 sq m = 272.25 sq m
Area of the second square = (22)2 sq m = 484 sq m
The area of the new sqaure = (272.25 + 484) sq m = 756.25 sq m
∴ Each side of the new square = √756.25 m = 27.5 m
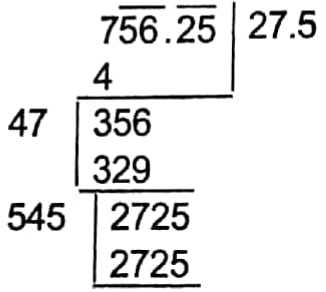
∴ 27.5 meters.
Example 21. A man spent ₹ 506.25 and each day he spent as many rupees as the number of days in which the money was spent. How much did he spend each day?
Solution:
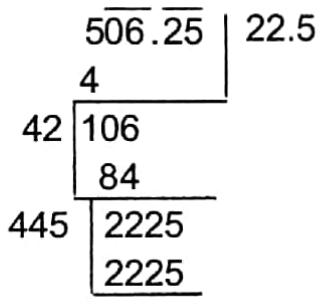
Since the number of days and the number of rupees spent each day are equal, therefore the product of two equal numbers = 506.25
∴ Each number = √506.25 = 22.5
Example 22. A ladder 36 metres long, stands against a wall so that its bottom is 21.6 metres away from the wall. How high is its top on the wall?
Solution:
Let Bc = 36 metres be the ladder and AB = 21.6 metres.
Let AC = h metres.
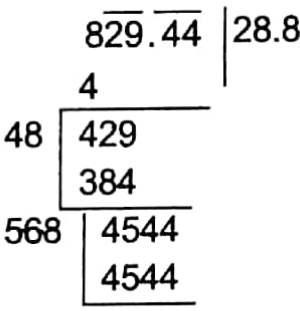
Now h2+ (21.6)2 = (36)2
or, h = (36)2 – (21.6)2
= 1296 – 466.56 = 829.44
or, h =√829.44 = 28.8
Arithmetic Chapter 4 Square Root Of Fraction Exercise 4 Some Problems On Square Root Of Vulgar Fractions
Example 1. Find the square root of \(\frac{324}{625}\)
Solution:
Square root of
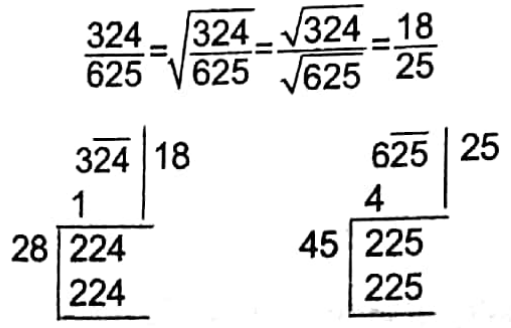
∴ \(\frac{18}{25}\)
WBBSE Class 7 Chapter 4 Square Roots Guide
Example 2. The area of a square is \(\frac{1089}{825}\) sq. cm.What is 825 the length of one side of the square?
Solution:
Length of the side of the square
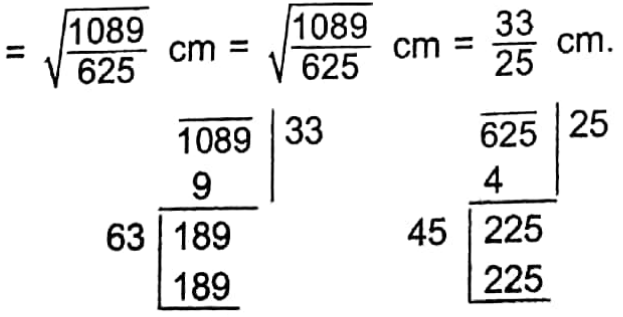
∴ Length of one side of the square is \(\frac{33}{25}\) cm.
Example 3. A vulgar fraction multiplied by itself gives the product \(\frac{841}{2025}\) Find the fraction.
Solution:
Here the required vulgar fraction is the Square root of \(\frac{841}{2025}\)
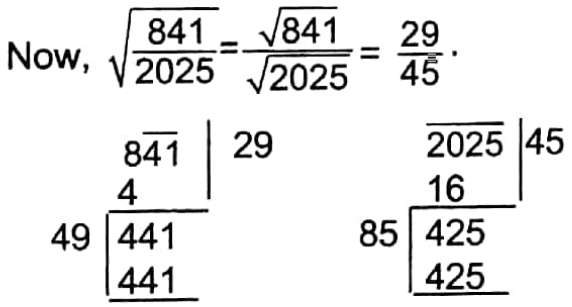
∴ \(\frac{29}{45}\)
Example 4. Find the square root of 6 \(\frac{433}{676}\)
Solution:
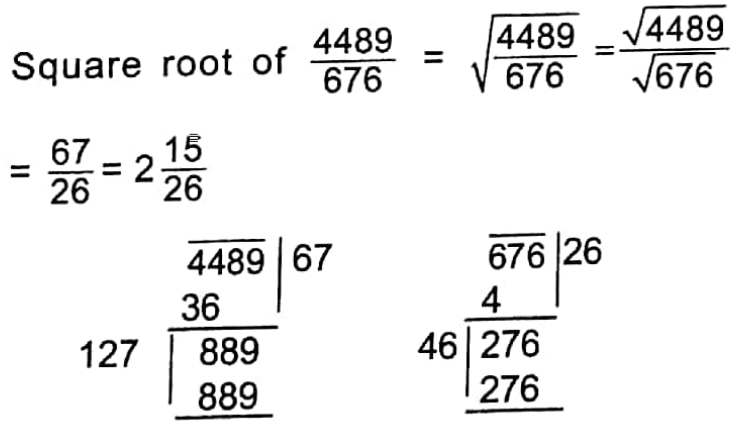
∴ The required square root = 2 \(\frac{15}{26}\)
Example 5. Extract the square root of \(\frac{2}{5}\) to two places of decimals.
Solution:
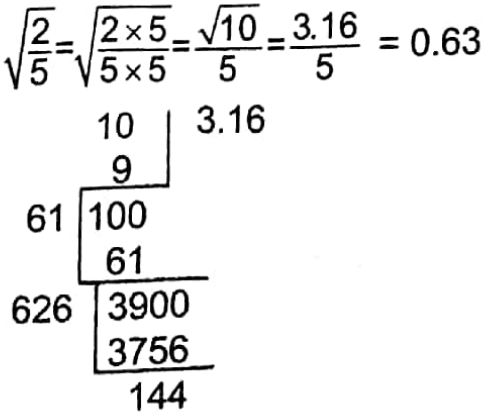
∴ 0.63
Understanding Square Roots of Fractions for Class 7
Example 6. By what should the square root of \(\frac{121}{169}\) be multiplied so that the product will be 1?
Solution: Square root of
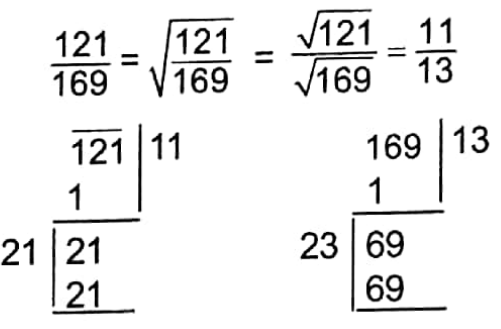
Now, \(\frac{11}{13}\) should be multiplied by \(\frac{13}{11}\) so that the product will be 1.
∴ To be multiplied by \(\frac{13}{11}\)
Example 7. The product of two numbers is \(\frac{75}{121}\) and one of them is threice the other. Find the numbers
Solution:
Greater number x smaller number = \(\frac{75}{121}\)
or, 3 x smaller x smaller number = \(\frac{75}{121}\)
or,(smaller number)2 = \(\frac{75}{3 x 121}\) = \(\frac{25}{121}\)
or, smaller number = ![]()
∴ greater number = 2 x \(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{4}\)
∴ The two numbers are \(\frac{7}{4}\) and \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Example 9. Find the smallest whole number by which \(\frac{64}{125}\) should be multiplied so that the product will be a fraction which is a perfect square.
Solution:
\(\frac{64}{125}\) = \(\frac{8 x 8}{5 x 5 x 5}\)
Clearly, it should be multiplied at least by 5 so that the product will be a fraction which is a perfect square.
∴ 5
Example 10. Find a fraction, which when multiplied by itself gives 6 \(\frac{145}{256}\)
Solution:
6 \(\frac{145}{256}\) = \(\frac{1681}{256}\)
The required fraction will be the sqaure root of \(\frac{1681}{256}\)
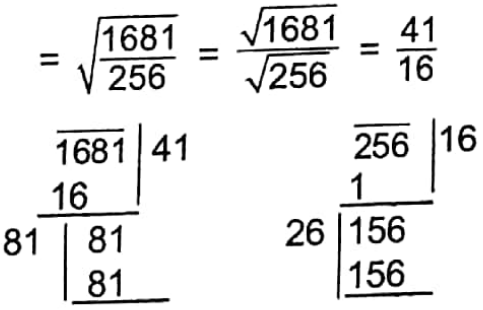
∴ The required fraction = \(\frac{41}{61}\)
Class 7 Maths Exercise 4 Solved Examples
Example 11. Find the square root of ![]()
Solution:
![]()
= \(\frac{9}{25}\) + \(\frac{16}{25}\) = \(\frac{9 + 16}{25}\) = \(\frac{25}{25}\) = 1
the square root of 1 is 1
Question 12. By which fraction should \(\frac{49}{91}\) be multiplied so that the square root of the product is 1?
Solution:
Square root of the product will be 1. Therefore, product will also be 1.
\(\frac{49}{91}\) should be multiplied by \(\frac{91}{49}\) sp, that the product is 1.
∴To be multiplied by \(\frac{91}{49}\)
Example 13. ![]() =what?
=what?
Solution:
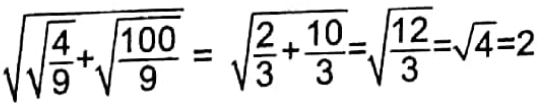
∴ 2
Example 14. By which fraction should \(\frac{35}{42}\) be multiplied so that the square root of the product is 2?
Solution:
\(\frac{35}{42}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\)
If the square root of the product is 2 then the product is 4.
∴ The required number = 4 ÷ \(\frac{5}{6}\)
= 4 x \(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{24}{5}\) = 4 \(\frac{4}{5}\)
∴ To multiplied by 4 \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Step-by-Step Solutions for Class 7 Square Root Problems
Example 15. By what number should the square root of \(\frac{625}{144}\) be multiplied nso that the product will be 1?
Solution:
Square root of
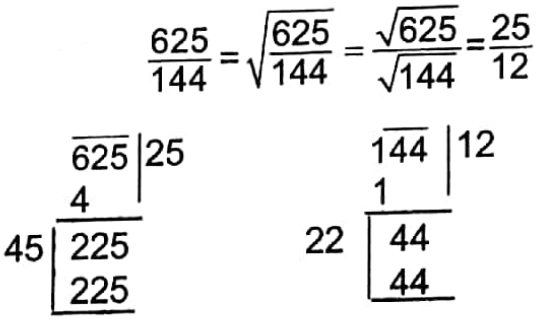
Now, the number by which \(\frac{25}{12}\) should be multiplied so that the product will be 1 is \(\frac{12}{25}\)
∴ \(\frac{12}{25}\)
Example 16. Find the least positive integer by which \(\frac{9}{50}\) should be multiplied so that the product will be a perfect square.
Answer:
\(\frac{9}{50}\) = \(\frac{3 X 3}{5 X 5 X 2}\)
Therefore, it should be multiplied at least by 2, so that the product will be a perfect sqaure.
∴ To be multiplied by 2.
Example 17. One number is thrice the other, If the product of the two numbers be 15\(\frac{3}{16}\) then what are the numbers?
Solution:
The greater number x smaller number = 15 \(\frac{3}{16}\)
or, 3x smaller number x smaller number= \(\frac{243}{16}\)
or, (smaller number)2 = \(\frac{243}{16 X 3}\) = \(\frac{81}{16}\)
or, smaller number = ![]()
∴ greater number = 3 x \(\frac{9}{4}\) = \(\frac{27}{4}\) = 6 \(\frac{3}{4}\)
∴ The numbers are 2 \(\frac{1}{4}\) and 6 \(\frac{3}{}\)
Example 18. The product of two positive numbers is \(\frac{14}{15}\) and their quotient is \(\frac{35}{24}\). Find the numbers.
Solution:
Let the two numbers be x and y.
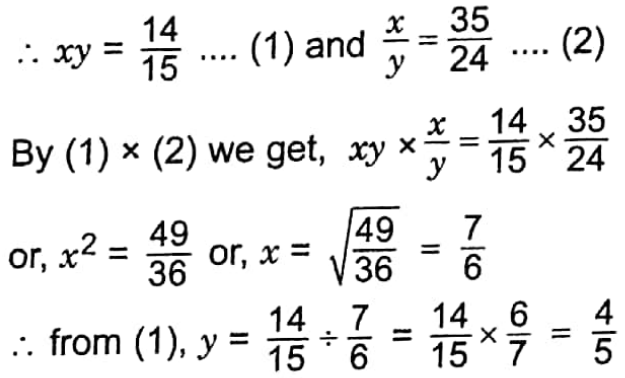
∴ The two numbers are \(\frac{7}{6}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Example 19. Out of the three numbers, the product of the first and the second number is 3, that of the second and the third number is 8 \(\frac{2}{5}\) and that of the third and the first number is 4 \(\frac{3}{8}\). Find the three numbers.
Solution:
First number x second number=3…………..(1)
Second number x third number = \(\frac{42}{5}\) …..(2)
Third number x first number = \(\frac{35}{8}\) ……(3)
By (1) x (2) x (3) we get,
(First number x second numnber x third number)2
= 3 x \(\frac{42}{5}\) x \(\frac{35}{8}\) = \(\frac{21 X 21}{4}\)
∴ First number x second number x third number = ![]() = \(\frac{21}{2}\)
= \(\frac{21}{2}\)
By (4) ÷ (1) we get, the third number
= \(\frac{21}{2}\) x \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{7}{2}\) = 3 \(\frac{1}{2}\)
By (4) ÷ (2) we get, first number
= \(\frac{21}{2}\) x \(\frac{5}{42}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\) = 1 \(\frac{1}{4}\)
By (4) ÷ (3) we get, second number
= \(\frac{21}{2}\) x \(\frac{8}{35}\) = \(\frac{12}{5}\) = 2 \(\frac{2}{5}\)
∴ The numbers are 1 \(\frac{1}{4}\), 2 \(\frac{2}{5}\), 3 \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Example 20. Find by what magnitude is (√25+ √81) more than (√16 + √36).
Solution:
√16+ √36=4+6=10
√25+√815+9=14
Now, 14-10=4
∴ Is more by 4.
Example 21. The area of a square is 4225 sq metres. If it is divided into 9 equal parts then each part becomes a square. What is the length of each side of such a square?
Solution:
If a square of area 4225 sq metres is divided into 9 equal parts then area of each part becomes \(\frac{4225}{9}\) sq metres.
If these parts are squares, then length of each side of such a square= ![]() meters =
meters =
= \(\frac{65}{3}\) metres = 21 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
∴ 21 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Example 22. Find the value of ![]()
Solution:
![]()
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) – \(\frac{1}{4}\) – \(\frac{1}{5}\)
⇒ 2 x 3 x 10 = 60
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\)) – (\(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{5}\))
= \(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{9}{20}\) = \(\frac{50- 27}{60}\) = \(\frac{23}{60}\)
∴ \(\frac{23}{60}\)
Example 23. Area of the square ‘A’ is \(\frac{225}{289}\)th of the area of the square ‘B’. What fraction of the side of ‘B’ is the side of ‘A’?
Solution:
Area of the square ‘A’ = Area of the square ‘B’ x \(\frac{225}{289}\)
∴ Length of the side of ‘A’ = Length of the side of ‘B’ x ![]()
∴ Length of the side of ‘A’ = Length of the side of ‘B’ x \(\frac{15}{17}\)
Hence, length of the side of the square ‘A’ is \(\frac{15}{17}\) th part of the length of the side of the square ‘B’.
∴ \(\frac{15}{17}\)
Example 24. Arrange the following in the descending order of their magnitude: ![]()
Solution:
![]()
∴ In descending order of magnitude the numbers are:
![]()
Example 25. The areas of two rectangles are \(\frac{24}{25}\) sq metres and \(\frac{12}{25}\) sq metres respectively, Find the length of each side of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of these two rectangles.
Solution:
Given:
The areas of two rectangles are \(\frac{24}{25}\) sq metres and \(\frac{12}{25}\) sq metres respectively
The sum of the areas of the two rectangles = (\(\frac{24}{25}\) + \(\frac{12}{25}\)) sq metres = \(\frac{36}{25}\) sq meters.
Hence, the area of the square = \(\frac{35}{25}\) sq metres.
Hence, the length of each side of the square
= ![]() metres
metres
= \(\frac{6}{5}\) metres = 1 \(\frac{1}{5}\) metres.
∴ 1 \(\frac{1}{5}\) metres.
Example 26. 308 square stones are required to pave a square of area 1925 square metres. Find the length of each side of such a stone.
Solution:
Given:
308 square stones are required to pave a square of area 1925 square metres.
By 308 stones 1925 sq metres is paved
By 1 stones \(\frac{1925}{308}\) sq metres is paved
= \(\frac{25}{4}\) sq metres is paved
Therefore, area ofeach stone = \(\frac{25}{4}\) sq metres.
∴ Length of each side of a stone = ![]() metres =\(\frac{5}{2}\) metres = 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) metres.
metres =\(\frac{5}{2}\) metres = 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) metres.
∴ 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) metres.
Example 27. The sides of two squares are \(\frac{12}{5}\) metres. metres and \(\frac{9}{5}\) metres.respectively. Find the side of a a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of the two squares.
Solution:
Given:
The sides of two squares are \(\frac{12}{5}\) metres. metres and \(\frac{9}{5}\) metres.respectively.
The area of the first square = (\(\frac{1}{2}\))2 sq metres
= \(\frac{144}{25}\) = sq metres
∴ The area of the second square = (\(\frac{9}{5}\))2
= \(\frac{81}{25}\) sq metres.
∴ Area of the new square
=(\(\frac{144}{25}\) + \(\frac{81}{25}\))
= \(\frac{225}{25}\) sq metres = 9 sq metres.
∴ Each side of the new square=√9 metres = 3 metres
∴ 3 metres.
The side of a a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of the two squares is 3 metres.
