Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Discuss the state reorganisation in India from 1947-50. OR, Discuss the political structure of India during the period of 1947-50.
Answer:
The state reorganisation in India from 1947-50
The former country of India was divided into two separate countries—India and Pakistan on 15 August 1947. At that time, independent India possessed 9 Governor ruled states, 4 chief commissioners ruled states and 562 independent native states.
During 1948-49, the native states were included within the state of India under the leadership of Sardar Vallabbhai Patel. Some of them were added to the Governor ruled states while some were converted to princely states. On 26 January 1950, India was declared as a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic. The Constitution of India was formed.
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Read and Learn Also WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography and Environment
During this time the states of India were divided into four categories—
| Part A (Governor Ruled States] | West Bengal, Assam, Bihar, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Bombay, Madras and Punjab (Total 9 states) |
| Part B [Former Princely States] | Hyderabad, Madhya Bharat, Mysore, Patiala and East Punjab State Union (PEPSU), Jammu and Kashmir, Rajasthan, Saurashtra and Travancore (Cochin) (Total 8 states) |
| Part C [Chief Commissioner Ruled States] | Ajmer, Bhopal, Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh, Kachchh, Coorg, Delhi, Manipur, Tripura and Vindhya Pradesh (a Total of 10 states) |
| Part D [Central Ruled State] | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
Question 2. Discuss the reorganisation of states from 1956 till date.
Answer:
State reorganisation in 1956: The State Reorganisation Commission (SRC) was formed in 1953, under whose recommendations India was reorganised into 14 states and 6 Union Territories on 1 November 1956 The main basis of this reorganisation was language.
States: Pradesh, Kerala, Jammu and Kashmir, West Bengal, Punjab, Bihar, Bombay, Madhya Pradesh, Mysore, Madras and Rajasthan.
Union Territories: Tripura, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Delhi, Lakshadweep, Manipur and Himachal Pradesh.
State reorganisation during other periods: After the reorganisation of the states in 1956, many
States were further reorganised during different periods. In this course, several states were renamed, e.g.—Madras was renamed as Tamil Nadu, Orissa as Odisha, Mysore as Karnataka, Rajputana as Rajasthan, etc. State reorganisation during other periods is listed below—
| Date | State Reorganisation |
| 19 August 1947 | The formation of the state of Orissa (now Odisha) was completed, |
| 1 May 1960 | The former state of Bombay was divided to form the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. |
| 1 December 1963 | Nagaland was given the status of an independent state. |
| 1 November 1966 | The former state of Punjab was divided to form the states of Punjab and Haryana and the Union Territory of Chandigarh. |
| 20 February 1970 | The former NEFA (North-East Frontier Agency) was renamed Arunachal Pradesh. |
| 25 January 1971 | Himachal Pradesh was converted from a Union Territory to a State. |
| 1 November 1973 | The former state of Mysore came to be known as Karnataka. |
| 26 April 1975 | Sikkim was included as the 22nd state of India (Formerly it was ruled by Chogyal monarchs). |
| 20 February 1987 | The Union Territories of Mi Oram and Arunachal Pradesh were included as the 23rd and 24th states of India |
| 30 May 1987 | Goa was included as the 25th state of India. |
| 1993 | The capital of India, Delhi, was declared as the ‘National Capital Region. |
| 1 November 2000 | The state of Madhya Pradesh was divided to form the 26th state of India, Chhattisgarh. |
| 9 November 2000 | The state of Uttar Pradesh was divided to form Uttarakhand, the 27th state of India |
| 15 November 2000 | Jharkhand was formed from the former state of Bihar, forming the 28th state of India. |
| 2 June 2014 | The 29th state of India, Telangana was formed from the former state of Andhra Pradesh. |
| 31 October 2019 | The state of Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two Union Territories, Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir. |
| 26 January 2020 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu were formed after the merger of the former Union Territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. |
“WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 notes”
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Short Explanatory Answer Type Questions
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 1. Why is India regarded as a ‘miniature world’?
Answer:
India is a peninsular country in south Asia. It is bordered by oceans on three sides and the lofty Himalayan mountains on the northern side. It lies in the northeastern hemisphere and the Tropic of Cancer passes almost through the middle of the country.
Different kinds of physio-graphic features like mountains, plateaus, and plains are present here. Deserts, different types of soils, vegetation, climatic conditions and availability of mineral resources make the country a land of variety. Different species of animals and plants are present here.
Apart from these, different types of languages, cultures, religions, castes and creeds are found here. All these make India a representation of a miniature world.
Question 2. State the location of India according to – ciX latitudinal and longitudinal extent.
Answer:
Latitudinal extent: Latitudinally India lies in the northern hemisphere. The mainland of India extends from 8°4’N in the south (Kerala) to 37°6’N in the north (Jammu and Kashmir).
The southernmost point of India including the islands lies at 6°45’N (Indira Point or Pygmalion point of Great Nicobar Island).
Longitudinal extent: India lies between 68°7’E (Gujarat) and 97°25’E (Arunachal Pradesh) longitudes.
Question 3. State the boundary of India.
Answer:
The boundary of India on all sides are as follows—
1. North: The northern side of India is marked by the Himalayan mountains, China, Nepal and Bhutan.
2. West: India is bounded by Pakistan and the Arabian Sea on the west.
3. East: The eastern side of India is bounded by Myanmar, Bangladesh and the Bay of Bengal.
4. South: The peninsular region of India in the south is bounded by the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. The island country of Sri Lanka lies south of India, separated by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar. The Maldives lie to the southwest of India.
“Location of India in geography Class 10”
Question 4. Mention the location of India with respect to the distance from the sea.
Answer:
Location of India with respect to the distance from the sea
India lies in south Asia. It is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. Hence, it is called a peninsula. Being surrounded by the seas on three sides, no place in India is farther than 1700 km from the coast.
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 5. Name the neighbouring countries of India.
Answer:
The neighbouring countries of India
The neighbouring countries of India are— China, Nepal and Bhutan in the north, Pakistan in the west, Afghanistan in the north-west, Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east and Sri Lanka in the south (separated from India by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar). The island of Maldives lies to the southwest of India.
Question 6. Discuss the importance of the geographical location of India.
Answer:
The importance of the geographical location of India
India lies in south Asia. The geographical location of the country influences its economy, security and livelihood of people.
1. The presence of seas on three sides of India provides access to international waterways and promotes foreign trade. The seas also act as a natural barrier and safeguard the security of the
mainland.
2. The mighty Himalayas in the north and the desert in the west also act as natural barriers and protect the country from foreign invasions. The mountain passes help in foreign trade.
3. The presence of seas on three sides of the country promotes fishing and related activities. It also influences the social life, food habits and economic status of the people.
4. The Himalayan region in the north encourages tourism and supplies raw materials for several industries like fruit processing, furniture making, paper, tea and construction.
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 7. Mention the extent and population of India.
Answer:
Extent: The north-south extent of India is 3214 km and the east-west extent of India is 2933 km.
Area: Total area of India is about 32 lacks 87 thousand 263 sq. km. Of this, about 43 thousand sq. km. of area is occupied by China and Pakistan. According to size, India is the seventh largest country in the world (after Russia, Canada, China, USA, Brazil and Australia).
Population: India is the second most populated country in the world (after China). According to the 2011 census, the total population of India was 121 crores 1 lakh 93 thousand 422.
Question 8. Mention the importance of the peninsular location of India on the livelihood of people
Answer:
The importance of the peninsular location of India on the livelihood of people is—
- The peninsular location of India promotes international trade through waterways from all three directions (east, west, and south).
- The presence of seas on three sides of the country promotes activities like navigation and fishing.
- The seas act as a natural barrier and protect the country from foreign invasions.
- The northern part of India is connected to mainland of Asia. This helps in maintaining trade
“Administrative divisions of India WBBSE Class 10”
Question 9. Name the administrative divisions presently found in India.
Answer:
Presently, India is divided into types of administrative divisions- states and union territories. There are 28 states and 8 union territories in India.
| State | Capital |
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | Hyderabad |
| 2. Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 3. Assam | Dispur |
| 4. Bihar | Patna |
| 5. Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| 6. Goa | Panaji |
| 7. Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| 8. Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 9. Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 10. Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| 11. Karnataka | Bengaluru |
| 12. Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 13. Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| 14. Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| 15. Manipur | Imphal |
| 16. Meghalaya | Shillong |
| 17. Mizoram | Aizawl |
| 18. Nagaland | Kohima |
| 19.0disha | Bhubaneswar |
| 20. Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 21. Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| 22. Sikkim | Gangtok |
| 23. Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 24. Tripura | Agartala |
| 25. Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| 26. Uttarakhand | Dehradun |
| 27. West Bengal | Kolkata |
| 28. Telangana | Hyderabad |
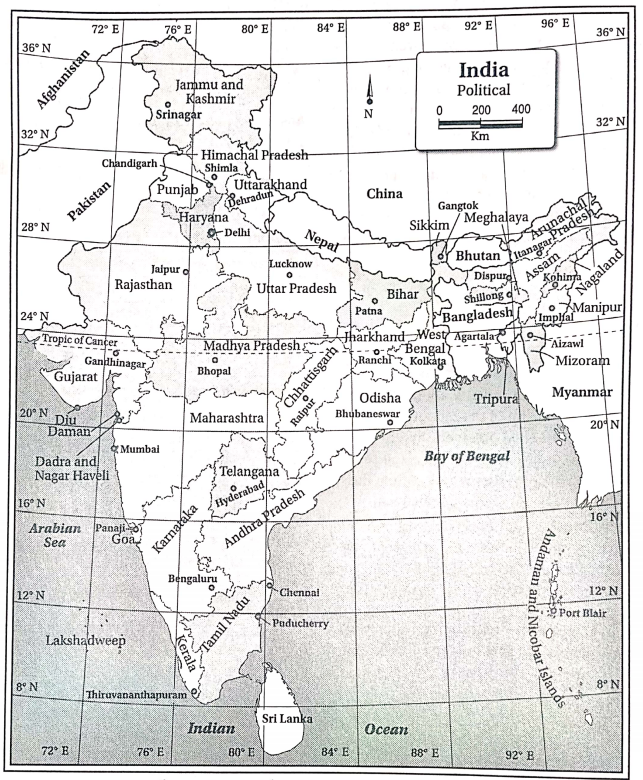
| Union Territories | Capital |
| 1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair |
| 2. Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 4. Delhi | Delhi |
| 5. Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| 6. Puducherry (formerly known as Pondicherry) | Puducherry |
| 7. Ladakh | Leh-Kargil |
| 8. Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (May-October) Jammu (November-April) |
Question 10. Discuss the standard meridian and standard time of India. OR, How does the longitudinal extent of India influence the standard time of the country?
Answer:
The standard meridian and standard time of India
India lies between the longitudes 68°7’E and 97°25’E. Therefore, the longitudinal extent is 97°25’E – 68°7’E = 29°18′ Each longitude or meridian has a different local time.
So, for ease of administration and time calculation, the meridian that passes through the centre of the country is chosen as the standard meridian, whose local time is considered the standard time of the country.
The 82°86’E meridian passes exactly through the centre of India. But for ease of calculation, the 82°30’E meridian is chosen as the standard meridian of India (passes through Allahabad). The local time of this standard meridian is considered as the standard time all over India.
Question 11. Why are Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya called so?
Answer:
The easternmost state of India was formerly known as the NEFA (North-East Frontier Agency). Being located at the eastern border, the first rays of sunlight could be seen from this region first in India as a whole. Hence, it was renamed Arunachal Pradesh.
The hilly regions of Khasi, Jaintia and Garo hills were included in the Union Territory of Meghalaya on 2 April 1970. The geographical location of the place influenced the weather conditions and generally kept the sky overcast with clouds.
Hence, it was named ‘Meghalaya'(the abode of clouds) by the famous geographer Dr S.P. Chatterjee. Later, on 21 January 1972, Meghalaya was given the status of a state.
“India’s physical environment Class 10 geography guide”
Question 12. What do you mean by ‘India subcontinent’?
Answer:
‘India subcontinent’:
The countries of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Maldives, Nepal, Bhutan and Sri Lanka together are known as the ‘Indian subcontinent’. These neighbouring countries have physical, geographical and cultural similarities. India is the largest country among them with respect to size and population.
It lies in the centre surrounded by the other five countries. Due to its size and location, India is the most influential country among them. Hence, the whole region is called the ‘Indian subcontinent’. Name the newly formed states of India and their capitals
authenticated by the Indian Constitution, more than 160 languages are spoken in the country. Language is a very important factor that influences the administration.
Thus, it plays an important role in state reorganisation. India was reorganised into 14 states and 6 Union Territories in 1956 based on the language popularly spoken over a large region.
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Short Answer Type Questions
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 1. Name the most and least populated states of India.
Answer:
According to the 2011 census, the most populated state of India is Uttar Pradesh (19.98 crores) and the least populated state of India is Sikkim (6.12 lakh).
Question 2. Presently, how many states and Union Territories are there in India?
Answer:
Presently, there are 29 states (including the newly formed states of Uttarakhand, Jharkhand and Telangana) and 7 Union Territories in India.
Question 3. Name the largest state and smallest state of India.
Answer:
The largest state of India is Rajasthan and the smallest state of India is Goa.
Question 4. Mention the latitudinal extent of the Indian mainland.
Answer:
The Indian mainland extends from 8°4’N in the south to 37°6’N in the north.
Question 5. Mention the longitudinal extent of India.
Answer:
The longitudinal extent of India is from 68°7’E in the west to 97°25’E in the east.
Question 6. From which erstwhile states the newly formed states of Uttarakhand and Chhattisgarh have been separated?
Answer:
Uttarakhand has been separated from the former state of Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh has been separated from the former state of Madhya Pradesh.
Question 7. Mention the east-west and north-south extent of India.
Answer:
The east-west extent of India is 2933 km and the north-south extent of India is 3214 km.
Question 8. What are the length of India’s border and its coastline?
Answer:
The length of the border of India along all sides is about 15107 km. The length of the coastline of India including the mainland, Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar Islands is about 7517 km.
Question 9. Name the largest and smallest Union Territory of India.
Answer:
The largest Union Territory of India in Jammu and Kashmir and the smallest one is Lakshadweep.
Question 10. Name the Union Territories of India.
Answer:
The Union Territories of India
The Union Territories of India are Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Delhi, Lakshadweep and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman, and Diu.
Question 11. Name the largest and smallest neighboring countries of India.
Answer:
The largest neighboring country of India is China and the smallest one is the Maldives.
Question 12. Which factors were given importance while state reorganization in India? OR, Mention two main bases of state reorganization of India?
Answer:
Different bases have been given importance during the time of state reorganization. Although the main basis of reorganization in 1956 was language, the other bases considered at different times are— culture, administrative advantage and skill, physical and geographical similarity, and economic stability.
Question 13. What are ‘The McMahon line’ and ‘Raddiffe line’?
Answer:
- McMahon Line: The Indo-China border running from the eastern side of Bhutan to Arunachal Pradesh is known as the McMahon line.
- Radcliffe Line: The Indo-Pakistan border in the northwestern part of India is known as the Radcliffe line.
“Geography chapter on India’s location and divisions WBBSE”
Question 14. Name two neighboring countries of India lying on the western side.
Answer:
Pakistan and Afghanistan are the two neighboring countries of India lying on the western side.
Question 15. Which Union Territory is recognized as the capital of two states of India?
Answer:
The Union Territory of Chandigarh is the capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana.
Question 16. What do you mean by SAARC?
Answer:
SAARC:
SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) is an organization formed for the political, economic, educational, cultural, scientific and technological, and recreational welfare of the member countries.
It was formed on 8 December 1985. Its headquarters is in Kathmandu, Nepal. The member countries are—India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and Afghanistan.
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India If The Statement Is True,
Write True And If False Write False Against The Following
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 1. The state reorganization in India occurred in the year 1950, on the basis of language.
Answer: False
Question 2. Rajasthan is the largest state in India.
Answer: True
Question 3. Jharkhand is the newest state in India.
Answer: False
Question 4. The Amindivi island lies within the Lakshadweep islands.
Answer: True
Question 5. The east-west extent of India is 2933 km.
Answer: True
Question 6. The north-south extent of India is lesser than the east-west extent.
Answer: False
Question 7. The Minicoy island is situated in the Manas Sarovar.
Answer: False
Question 8. The difference between the easternmost and westernmost longitudes of India is almost 29°18
Answer: True
Question 9. The local time of Allahabad is considered the standard time of India.
Answer: True
Question 10. The southernmost point of India is Kanyakumari.
Answer: False
Question 11. India was declared a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic on 15 August 1947.
Answer: False
Question 12. The Tropic of Cancer passes through Bihar.
Answer: False
Question 13. NEFA has been renamed Mizoram.
Answer: False
Question 14. Jharkhand was given the status of a different state on the basis of regional cultural differences.
Answer: True
Question 15. India is the largest peninsular country in the world.
Answer: True
Question16. Goa is the smallest state in India.
Answer: True
Question 17. Sikkim was included as an Indian state in 1975.
Answer: False
Question 18. Goa was given the status of a state in 1989.
Answer: False
Question 19. ‘Meghalaya’ was named by Dr. S. P. Chatterjee.
Answer: True
Question 20. The newest state of India is Telangana.
Answer: True
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Fill In The Blanks With Suitable Words
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
Question 1. India was declared a sovereign democratic republic in the year_______
Answer: 1950
Question 2. The State Reorganisation Commission was formed in_______
Answer: 1953
Question 3. The the_______islands lie on the Bay of Bengal.
Answer: Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Question 4. India is separated from Sri Lanka by the_______
Answer: Palk Strait
Question 5. The local time of_______ is considered the standard time of India.
Answer: Allahabad
Question 6. Presently, there are _______ Union Territories in India.
Answer: 8
Question 7. Rajasthan was previously known as _______
Answer: Rajputana
Question 8. Chennai was previously known as _______
Answer: Madras
Question 9. India is surrounded by oceans on _______ sides.
Answer: Three
Question 10. The Darjeeling Gorkhaland Territorial Administration is an _______body that looks after the administration of the hills of the Darjeeling district.
Answer: Autonomous
Question 11. The capital of Tripura is _______
Answer: Agartala
Question 12. The chief language spoken in Karnataka is_______
Answer: Kannada
Question 13. Indira point is also known as the _______
Answer: Pygmalion point
Question 14. _______ is considered the standard meridian of India.
Answer: 82°30’E
Question 15. _______ is the capital of both Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Answer: Hyderabad
Question 16. Kerala was given the status of a state in _______
Answer: 1956
Question 17. Delhi was declared as a Union Territory of India in _______
Answer: 1956
Question 18. The chief languages spoken in Telangana are_______ and _______
Answer: Telugu and Urdu
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Answer In One Or Two Words
Question 1. When has India declared a sovereign, socialistic, secular democratic republic?
Answer: 26 January 1950.
Question 2. Which state’s capital is Bengaluru?
Answer: Karnataka.
Question 3. Which is the largest neighbouring country of India?
Answer: China.
Question 4. Name the capital of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
Answer: Daman.
Question 5. Name the capital of Chattisgarh.
Answer: Raipur.
Question 6. Where is the headquarters of SAARt located?
Answer: Kathmandu in Nepal.
Question 7. Name the smallest neighbouring country of India.
Answer: Maldives.
Question 8. When was Telangana given the status of a separate state?
Answer: 2 June 2014.
Question 9. What was Karnataka previously known as?
Answer: Mysore.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 10. Which former state was broken into Gujarat and Maharashtra?
Answer: Bombay (presently known as Mumbai).
Question 11. Which languages are popularly used in Tripura apart from Bengali?
Answer: Kokborok and Manipuri.
Question 12. What is the India-Pakistan border popularly known as?
Answer: Radcliffe Line.
Question 13. Name the smallest Union Territory of India.
Answer: Lakshadweep.
Question 14. Which state was broken to form Uttarakhand?
Answer: Uttar Pradesh.
Question 15. How many languages have been accepted by the Constitution of India, to be spoken here?
Answer: 22.
Question 16. Name the capital of Uttarakhand.
Answer: Dehradun.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Chapter 5 India Physical Environment Topic 1 Location And Administrative Divisions Of India Match The Left column With The Right Column
1.
| LeftColumn | Right Column |
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | A. Malayalam |
| 2. Tamil Nadu | B. Kannada |
| 3. Goa | C. Tamil |
| 4. Karnataka | D. Telugu |
| 5. Kerala | E. Konkani |
Answer: 1-D,2-C,3-E,4-B,5-A
2.
| Left Column | Right Column |
| 1. Telangana | A. Kohima |
| 2. Jharkhand | B. Ranchi |
| 3. Tripura | C. Dehradun |
| 4. Uttarakhand | D Hyderabad |
| 5. Nagaland | E. Agartala |
Answer: 1-D,2-B,3-E,4-C,5-A
3.
| Left Column | Right Column |
| 1. Himachal Pradesh | A. 2000 |
| 2. Chhattisgarh | B. 2014 |
| 3. Goa | C. 1971 |
| 4. Telangana | D. 1963 |
| 5. Nagaland | E. 1987 |
Answer: 1-C,2-E,3-E,4-B,5-D
