NEET Physics Gravitation Questions
Chapter 3 Gravitation Short Answer Type Question And Answers
Question 1. Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between two small gold balls weighing 500 g and 2 kg kept on a horizontal table, with their centers 40 cm apart. Take G = 6.7 × 10-11 Nm2 kg2-2
Answer.
Given:
Two small gold balls weighing 500 g and 2 kg kept on a horizontal table, with their centres 40 cm apart.
Given: m1 = 500g = 0.5 kg
m2 = 2 kg
r = 40 cm = 0.40 m
and G = 6.7 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
By Newton’s law of gravitation,
F = \(\frac{G m_1 m_2}{r^2}\)
= \(6.7 \times 10^{-11} \frac{\mathrm{Nm}^2}{\mathrm{~kg}^2} \times \frac{0.5 \mathrm{~kg} \times 2 \mathrm{~kg}}{(0.4 \mathrm{~m})^2}\)
= \(6.7 \times 10^{-11} \times \frac{0.5 \times 2}{0.16} \mathrm{~N}\)
= \(6.7 \times 10^{-11} \times \frac{100}{16} \mathrm{~N}\)
∴ F = 4.1875 × 10-10 N
The gravitational force of attraction between two small gold balls = 4.1875 × 10-10 N
Question 2. With what force earth attracts moon? With what force moon attracts earth?
Answer.
Take ME = 6 × 1024 kg
Mm = 7.5 × 1022 kg
r = 3,80,000 km = 3.8 × 108 m
According to Newton’s law of gravitation,
F = \(\frac{G M_E M_m}{r^2}\)
= \(6.7 \times 10^{-12} \frac{\mathrm{Nm}^2}{\mathrm{~kg}^2} \times \frac{6 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg} \times 7.5 \times 10^{22} \mathrm{~kg}}{\left(3.8 \times 10^5 \mathrm{~m}\right)^2}\)
= \(\frac{6.7 \times 6 \times 7.5 \times 10^{35}}{3.8 \times 3.8 \times 10^{16}} \mathrm{~N}\)
Therefore, F = 20.9 × 1019 N
According to Newton’s III law, moon will also attract earth towards itself with the same force i.e., 20.9 × 1019 N.
Read And Learn More NEET Foundation Short Answer Questions
Question 3. A body is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 ms-1. Find
- how long it takes to reach the highest point
- maximum height attained by it.
Take g = 9.8 ms-1 and neglect air-friction.
Answer. Given: u = 49 ms-1
v = 0 (at the highest point)
a = −9.8 ms-2
t = ?
h = S = ?
(1) We know that
v = u + at
0 = 49 + (−9.8) × t
9.8 t = 49
∴ t = 49
9 8. = 5 s
5 s it will takes to reach the highest point
(2) ∵ v2 = u2 + 2ah
0 = (49)2 + 2 (−9.8) h
19.6 h = 49 × 49
∴ h = \(\frac{49 \times 49}{19.6}\)
∴ h = 122.5 m
Maximum height attained by it is 122.5 m
Question 4. A body is dropped from the top of a tower 200 m tall. Simultaneously, another body is thrown vertically upwards from its foot with a velocity of 100 ms-1. Find when and where they meet or cross each other.
Take g = 10 ms-2 and ignore air friction.
Answer.
Given:
A body is dropped from the top of a tower 200 m tall. Simultaneously, another body is thrown vertically upwards from its foot with a velocity of 100 ms-1.
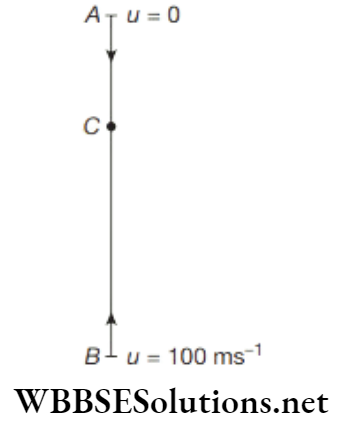
Suppose the two bodies meet at point C after ‘x’ seconds.
Consider downward motion AC of first body.
∵ S = \(u t+\frac{1}{2} g t^2\)
∴ AC = \(0+\frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times x^2\)
∴ AC = 5x2 (1)
Consider upward motion BC of second body.
∴ S = \(u t+\frac{1}{2} g t^2\)
∴ BC = \(100 x+\frac{1}{2}(-10) x^2\)
∴ BC = 100x − 5x2 (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), we get
AC + BC = 5x2 + 100x − 5x2
∴ AB = 100x
i.e., 200 = 100x
∴ x = \(\frac{200}{100}=2 s\)
Substituting x = 25 in equation (i) we get,
AC = 5x2 = 5 × 22 = 20 m
Therefore, the two bodies meet at a point 20 m below the top of the tower or (200 − 20) m = 180 m above the foot of the tower, 2 s after they embark on their journey.
Gravitation NEET Questions
Question 5. A girl weighing 40 kg is wearing pointed sandals having a total area of 2 × 10-4 m2. How much pressure she will exert on ground? In which case, the ground is more likely to be damaged? Explain. (Take g = 10 ms-2)
Answer.
Given:
A girl weighing 40 kg is wearing pointed sandals having a total area of 2 × 10-4 m2.
A boy of same weight wears shoe having area of 100 × 10-4 m.
Pressure Pg exerted by girl on the ground due to her weight is given by
Pg = \(\frac{\text { Force }}{\text { Area }}=\frac{\text { Weight }}{\text { Area }}=\frac{M g}{A}\)
= \(\frac{40 \times 10 \mathrm{~N}}{2 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}^2}\)
Pg = 2 × 106 Nm-2or Pa Similarly pressure exerted by the boy on the ground due to his weight
Pb = \(\frac{\mathrm{Mg}_g}{A}=\frac{40 \times 10 \mathrm{~N}}{100 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}^2}\)
Pb = 4 × 104 Nm-2 or Pa
Since Pg > Pb, the girl is more likely to damage the ground than the boy
NEET Foundation Physics Chapter 3
| Class 11 Physics | Class 12 Maths | Class 11 Chemistry |
| NEET Foundation | Class 12 Physics | NEET Physics |
Question 6. A tall cylinder contains water column of height 3 m. Calculate the pressure it exerts on the bottom of the cylinder. Take g = 10 ms-2. Density of water = 1000 kg.
Answer.
Given:
A tall cylinder contains water column of height 3 m.
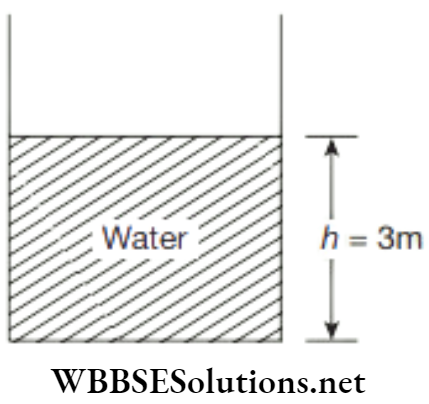
We know that, pressure exerted by a liquid column is given by,
P = h ρ g
= \(3 \mathrm{~m} \times 1000 \frac{\mathrm{kg}}{\mathrm{m}^3} \times 10 \frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{s}^2}\)
∴ P = 3 × 104 Nm2 or Pa
The pressure it exerts on the bottom of the cylinder = 3 × 104 Nm2 or Pa
Gravitation Short Answer Questions
Question 7. It is often said that atmospheric pressure is 76cm of mercury column. What does it mean? Express this pressure in Pascal.
Take ρmercury = 13.6 × 103 kgm-3 and g = 9.8 ms-2.
Answer.
The given statement means that the earth’s atmosphere exerts some pressure as exerted by a mercury column of height 76 cm.
∴ Atmospheric pressure = Pressure of 76 cm of mercury
= h ρ g
= 0.76 m × 13.6 × 103 kgm-3 × 9.8 ms-2
= 1.013 × 105 Pa
∴ Pressure in Pascal = 1.013 × 105 Pa
Physics Gravitation Practice Problems
Question 8. A ship having a total weight of 20,000 tonnes is floating on water. How much upthrust acts on the ship?
Take g = 10 ms-2
Answer.
Ship is in equilibrium (i.e., at rest)
So, Upward force acting on the ship = Downward force acting on the ship.
U = W
= Mg
= \(20,000 \text { tonnes } \times 10^s \frac{\mathrm{kg}}{\text { tonne }} \times 10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}\)
= 2 × 108 N
∴ Upthrust acts on the ship is 2 × 108 N
