Chapter 6 Improvement In Food Resources Short Answer Type Question And Answers
Question 1. What are the advantages of organic farming?
Answer.
Advantages of organic farming:
- There is no use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides in organic farming.
- Organic farm wastes can be recycled in the form of manure.
- It also maintains the soil fertility.
- It controls the attack of pests and the growth of weeds through a cropping system.
- There is no toxicity released during organic farming which can harm our environment.
Read And Learn More NEET Foundation Short Answer Questions
Question 2. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Answer.
Method of crop production:
The one method used for crop production which ensures high yield is plant breeding. It is the science involved in improving the varieties of crops by breeding plants. The plants from different areas/places is picked up with desired traits and then hybridization or cross-breeding of these varieties is done to obtain a plant/crop of desired characteristic.
The high yielding crop variety shows the following characteristics, namely high yield, early maturation, less water for irrigation, better quality seeds are produced, less fertilizers required and adapts itself to the environmental conditions.

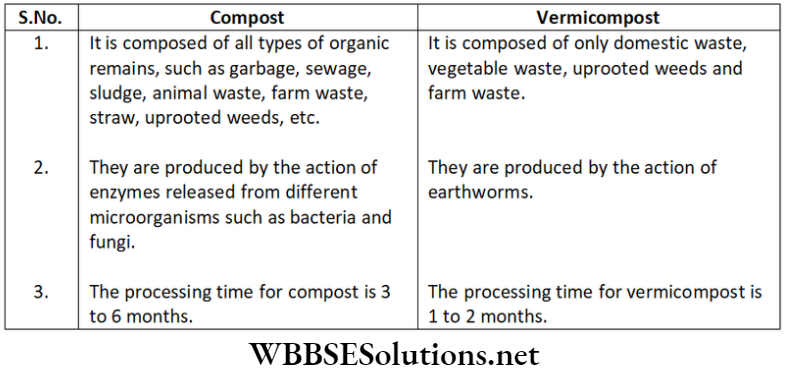
Question 3. Discuss the differences between compost and vermicompost.
Answer.
The differences between compost and vermicompost:
Question 4. Discuss the different types of biofertilizers with their examples.
Answer.
The different types of biofertilizers with their examples:
- Nitrogenous fertilizers are those organisms that provide nitrogen to the plants.
Example: Rhizobium, Azotobacter, BGA (blue-green algae). - Phosphate solubilizing microbes provides phosphorous to the plants.
Example: Azospirilium, Acetobacter and Azotobacter. - Mycorrhizal fungi lives in symbiotic relationship with a plant and increases the nutrient and water uptake of the plant, making it disease and drought resistant.
Question 5. What do you understand by water management?
Answer.
Water management:
The arrangement and supply of required water to the crop plants without disturbing the water table and soil aeration and causing soil salinity and water logging problem is defined as water management.
Improvement In Food Resources
Question 6. What are the irrigation system?
Answer.
Irrigation system:
- The irrigation system provides fresh water to crop plants that are enriched in hydrogen and oxygen. Hence, it provides two important elements to crops that are essential for their growth and development.
- Irrigation provides sufficient water and minerals dissolved in the water to the crop plants and hence, a number of aerial branches increases in the crop plants leading to an increase in the crop yield.
- Irrigation water from river basins even carries slit with them which are nutrient rich thereby, improving soil fertility and crop yields.
- Irrigation allows the cultivation of crops throughout the year rather than being restricted to a specific season.
Question 7. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture?
Answer.
Difference between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture
- Capture fishing: It is the fishing in which fishes are captured from natural resources like pond, sea water and estuaries.
- Mariculture: It is the culture of fish in marine water. Varieties like prawns’, oysters, bhetki and mullets are cultured for fishing.
- Aquaculture: It is done both in fresh water and in marine water.
Question 8. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and beekeeping?
Answer.
Through cross-breeding, the production of poultry, fisheries and beekeeping can be increased.
Question 9. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Answer:
The factors responsible for loss of grains, during storage and production are as follows.
- Biotic factors like rodents, pests, insects, etc.
- Abiotic factors like temperature, humidity, moisture, etc. Combination of both biotic and abiotic factors are responsible for the following parameters.
-
- Infestation of insects
- Weight loss
- Poor germination ability
- Degradation in quality
- Discolouration
- Poor market price
| Class 11 Physics | Class 12 Maths | Class 11 Chemistry |
| NEET Foundation | Class 12 Physics | NEET Physics |
Question 10. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
The desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements are as follows.
- Tallness and profuse branching are the desirable characters for fodder crops.
- Dwarfness is desired in cereals, so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Answer: Diseases in plants are caused by pathogens. To get rid of pathogens, some preventive measures and biological control methods are used as they are simple, economic and minimize pollution without affecting the soil quality.
Question 11. What is genetic engineering?
Answer:
Genetic Engineering:
Introduction of desired gene with specific characteristics in the genome of a plant also produces improved quality of crop. Such crops are known as genetically modified crops (GMO) and the technique employed is known as genetic engineering.
Question 12. What is hybridization?
Answer:
Hybridization:
Hybridization is a process of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants that result in the production of a new variety.
Question 13. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Answer:
The factors responsible for losses of grains during storage are as follows.
- Abiotic factors like moisture (present in food grains), humidity (of air) and temperature.
- Biotic factors like insects, rodents, birds, mites, bacteria and fungi.
Question 14. What is nutrient management?
Answer:
Nutrient Management:
The selection of time, nutrient and amount of nutrient is controlled under the system called nutrient management.
Question 15. What do you understand by farm yard manure?
Answer:
Farm Yard Manure:
It is the oldest manure composed of the decomposed mixture of dung, urine of farm animals, remains of roughages or fodder fed to the cattle.
Question 16. What are macronutrients and why are they called macronutrients?
Answer:
Macronutrients:
Macronutrients are the essential elements which are utilized by plants in large quantities. Many macronutrients are required by the plants for the following functions.
- As the constituent of protoplasm.
- N, P and S are present in proteins.
- Ca is present in cell wall.
- Mg is the important constituent of chlorophyll.
Question 17. How do plants get nutrients?
Answer:
Plants get nutrients as follows
Plants get nutrients from air, water and soil. There are sixteen nutrients essential for the growth of plants. Carbon and oxygen are supplied by water. The remaining thirteen nutrients are supplied by soil.
Question 18. Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Answer:
The effects of using manures on soil quality are as follows.
- The manures enrich the soil with nutrients.
- They provide a lot of organic matter (humus) to the soil and thus, it restores the water retention capacity of sandy soils and drainage in clayey soil.
- The addition of manures reduces soil erosion.
- They provide food for soil organisms like soil-friendly bacteria.
The effects of using fertilizers on soil quality are as follows.
- By the continuous use of fertilizers, the soil becomes powdery, dry and the rate of soil erosion increases.
- Using fertilizers, the organic matter decreases which further decreases the porosity of soil and the plant roots do not get oxygen properly.
- The nature of soil changes to acidic or basic.
Question 19. Discuss how fertilizers can be classified.
Answer:
classification of fertilizers
They are classified into four groups based on their nutrient content.
- Nitrogenous fertilizers: They provide nitrogen (macronutrient).
- Phosphorous fertilizers: They provide phosphorous (macronutrient).
- Potassic fertilizers: They provide potassium (essential micronutrient).
- Complex fertilizers: They provide two or more than two nutrients (N2, P2O4 and K2O).
Question 20. What are biofertilizers?
Answer:
Biofertilizers:
Some living microorganisms are also used as fertilizers, which provide nutrient to the plants and such fertilizers are known as biofertilizers.
Question 21. What is irrigation?
Answer:
Irrigation:
The process of supplying water artificially through water reservoirs and tube wells to the agricultural field where crop plants are grown is known as irrigation.
Question 22. What do you understand by the term water augmentation?
Answer:
Water Augmentation:
Augmentation is a process of using existing water to carry out new work.
Question 23. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
- Farmers use high-quality seeds and do not adopt irrigation or use fertilizer.
- Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Answer: In this, (2) farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Use of any quality seeds is not sufficient until they are properly irrigated, enriched with fertilizers and protected from biotic factors. Hence, option (2) will give the most benefits.
Question 23. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
- Farmers use high-quality seeds, do not adopt irrigation or use fertilizer.
- Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Answer: In this, (2) farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures. Use of any quality seeds is not sufficient until they are properly irrigated, enriched with fertilizers and protected from biotic factors. Hence, option (2) will give the most benefits.
Question 24. What are the pathogens?
Answer:
Pathogen:
Pathogens are microorganisms that cause diseases to the crop plants whereas it may be a bacteria, fungus or virus. They are present in the soil, air and water, it becomes virulent in favourable conditions.
Question 25. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops?
Answer:
Diseases in plants are caused by pathogens. To get rid of pathogens, some preventive measures and biological control methods are used as they are simple, economic and minimize pollution without affecting the soil quality.
Question 26. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Answer:
The factors responsible for losses of grains during storage are as follows.
- Abiotic factors like moisture (present in food grains), humidity (of air) and temperature.
- Biotic factors like insects, rodents, birds, mites, bacteria and fungi.
Question 27. What are weeds?
Answer:
Weeds:
The unwanted plants that grow with main crop plants utilize the nutrient of the soil in large amount and hence, they reduce the growth of the crop and such plants are known as weeds.
Question 28. What is intercropping?
Answer:
Intercropping:
When two or more than two crops are grown simultaneously in the same crop field, but in a definite pattern to increase the productivity of farm per unit area, then it is called intercropping.
