Chapter 4 Work And Energy Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Direction: Choose the correct option for each questions. There is only one correct response for each question.
Question 1. We need ______ for other activities like playing, singing, reading, writing, thinking, jumping, cycling and running.
- Energy
- Work
- Motion
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Energy
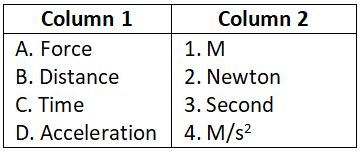
Question 2. What is the unit of work?
- Newton metre (Nm)
- Coulomb
- Ampere
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Newton metre (Nm)
Question 3. Which is the biggest natural source of energy to us?
- Moon
- Stars
- Sea
- Sun
Answer. 1. Moon
Question 4. On which factor the work done on an object does not depend?
- Displacement
- Force applied
- Angle between force and displacement
- Initial velocity of the object
Answer. 4. Initial velocity of the object
Question 5. Water stored in a dam possesses
- No energy
- Electrical energy
- Potential energy
- Kinetic energy
Answer. 4. Kinetic energy

Question 6. A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height h/2 , it will possess
- Only potential energy
- Only kinetic energy
- Half potential and half kinetic energy
- More kinetic and less potential energy
Answer. 3. Half potential and half kinetic energy
Question 7. How are Joule (J) and ergs (erg) related?
- J = 107 erg
- 1 erg = 10-7 J
- 1 J = 10-7 erg
- None of the above
Answer. 3. 1 J = 10-7 erg
Question 8. Work done = Force × ______.
- Displacement
- Acceleration
- Velocity
- Speed
Answer. 2. Acceleration
Question 9. 1 Joule = 1 ______.
- Nm2
- kg m/s2
- Nm
- N2m2
Answer. 1. Nm2
Question 10. Which form of energy does the flowing water possess?
- Gravitational
- Potential
- Kinetic
- electricity
Answer. 3. Kinetic
Question 11. 3730 watts = ______ h.p.
- 5
- 2
- 746
- 6
Answer. 3. 746
Question 12. The P.E. of a body at a certain height is 200 J. The kinetic energy possessed by it when it just touches the surface of the earth is
- > P.E.
- < P.E.
- = P.E.
- None of the above
Answer. 1. > P.E.
Question 13. Power is a measure of the
- Rate of change of momentum
- Force which produces motion
- Change of energy
- Rate of change of energy
Answer. 4. Rate of change of energy
Question 14. 1.5 kW = ______ watts.
- 150
- 15000
- 1500
- 15
Answer. 2. 15000
Question 15. What is the energy of the simple pendulum when it is at its mean position?
- Potential energy
- Kinetic energy
- Both (a) and (b)
- Sound energy
Answer. 3. Both (a) and (b)
Question 16. Name the physical quantity which is equal to the product of force and velocity.
- Work
- Power
- Energy
- Current
Answer. 2. Power
Question 17. What is the example of kinetic energy in the following options?
- A moving bus
- A moving particle in electric field
- A stretched rubber band just released
- All the above
Answer. 2. A moving particle in electric field
Question 18. A light and the heavy body have equal momenta, which one has greater kinetic energy?
- A light body
- A heavy body
- Both have same K.E
- None of the above
Answer. 4. Both have same K.E
Question 19. Sum of kinetic and potential energy is called
- Mechanical energy
- Chemical energy
- Electrical energy
- Magnetic energy
Answer. 1. Mechanical energy
Question 20. Kinetic energy is given by
- F × S
- \(\frac{1}{2} m V^2\)
- Mgh
- None of the above
Answer. 1. F × S
Question 21. 1 kJ equals to
- 100 J
- 10 J
- 1000 J
- None of the above
Answer. 2. 10 J
Question 22. Work done in raising an object from the ground to that point against gravity is called
- gravitational potential energy
- gravitational kinetic energy
- gravitational energy
- none of the above
Answer. 3. gravitational energy
| Class 11 Physics | Class 12 Maths | Class 11 Chemistry |
| NEET Foundation | Class 12 Physics | NEET Physics |
Question 23. The energy used in households, industries and commercial establishments are usually expressed in ______.
- kilowatt hour
- Joules
- kilo joule
- None of the above
Answer. 1. kilowatt hour
Question 24. Which is the formula of potential energy?
- Mgh
- \(\frac{1}{2} m V^2\)
- F × S
- None of the above
Answer. 1. Mgh
Question 25. What are the conditions needed for work to be done?
1. a force should act on an object and
2. the object must be displaced
3. there should be a chemical energy applied
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All the above
Answer. 1. 1 and 2
Question 26. Which of the following statements are true?
1. Work done by force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance moved in the direction of the force.
2. Work has only magnitude and no direction.
3. Here the unit of work is newton metre (N m) or joule (J)
4. There are two conditions need to be satisfied for work to be done
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 4
- 1, 2 and 3
- All the above
Answer. 1. 1 and 2
Question 27. What is the unit of work?
1. Newton metre
2. Joule
3. Ampere
4. Coulomb
- 1 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 28. Which statement is correct regarding energy?
1. The energy possessed by an object is measured in terms of its capacity of doing work.
2. The unit of energy is Joule.
3. 1 kJ equals 100 J.
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All the above
Answer. 3. 1 and 3
Question 29. Which of the following are the examples of kinetic energy?
1. A falling coconut
2. a speeding car
3. a rolling stone
4. a flying aircraft
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- All the above
Answer. 1. 1 and 2
Question 30. Which of the following are examples of potential energy?
1. Flowing water
2. Blowing wind
3. A coiled spring
4. Wheels on roller skates before someone skates
- 1 and 2
- 3 and 2
- 4 and 1
- 3 and 4
Answer. 1. 1 and 2
Question 31. Which statement is correct?
1. Power is defined as the rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of energy.
2. Power = work/time
3. The unit of power is watt
4. 1 W = 1 J s-1
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 1
- All the above
Answer. 4. All the above
Question 32. Work done in raising a box on a platform depends on
- how fast it is raised
- strength of the man
- negative work
- zero work
Answer. 4. zero work
Question 33. Work done upon a body is
- a vector quantity
- a scalar quantity
- always positive
- always negative
Answer. 3. always positive
Question 34. Kilowatt hour (kWh) represents the unit of
- power
- impulse
- momentum
- none of these
Answer. 2. impulse
Question 35. When two unequal masses possess the same momentum, then kinetic energy of the heavier mass is _______ kinetic energy of the lighter mass.
- same as
- greater than
- smaller than
- much greater than
Answer. 4. much greater than
Question 36. The number of joules contained in 1 kWh is
- 36 × 102
- 36 × 103
- 36 × 104
- 3.6 × 106
Answer. 3. 36 × 104
Question 37. A completely inelastic collision is one in which the two colliding particles
- are separated after the collision
- remain together after the collision
- split into small fragments flying in all directions
- none of the above
Answer. 4. none of the above
Question 38. A body moves through a distance of 3 m in the following different ways. In which case is the maximum work done?
- When pushed over an inclined plane
- When lifted vertically upward
- When pushed over smooth rollers
- When pushed on a plane horizontal surface
Answer. 2. When lifted vertically upward
Question 39. A truck and a car are moving on a smooth, level road such that the K.E. associated with them is same. Breakes are applied to both of them simultaneously. Which one will cover a greater distance before it stops?
- Car
- Truck
- Both will cover the same distance
- kinetic and potential energies
Answer. 2. Truck
Question 40. Two bullets P and Q, masses 10 and 20 g, are moving in the same direction towards a target with velocities of 20 and 10 m/s respectively. Which one of the bullets will pierce a greater distance through the target?
- P
- Q
- Both will cover the same distance
- Nothing can be decided
Answer. 3. Both will cover the same distance
Question 41. When the force applied and the displacement of the body are inclined at 90° with each other, then work done is
- infinite
- maximum
- zero
- unity
Answer. 1. infinite
Question 42. kg m2 s-2 represents the unit of
- kinetic energy
- work done
- potential energy
- all of these
Answer. 3. potential energy
Question 43. If sand drops vertically at the rate of 2 kg/sec on a conveyor belt moving horizontally with the velocity of 0.2 m/sec, then the extra force required to keep the belt moving is
- 0.04 N
- 0.08 N
- 0.4 N
- 0.2 N
Answer. 4. 0.2 N
Question 44. A body is dropped from a certain height to the ground. When it is halfway down, it possesses,
- only K.E.
- both K.E. and P.E.
- only P.E.
- zero energy
Answer. 3. only P.E.
Question 45. The energy required to raise a given volume of water from a well can be
- mega watts
- mega newton
- mega joules
- kilo watts
Answer. 2. mega newton
Question 46. If a force F is applied on a body and it moves with velocity v, then power will be
- F ×v
- \(\frac{F}{v^2}\)
- \(\frac{F}{v}\)
- F × v2
Answer. 3. \(\frac{F}{v}\)
Question 47. Which of the following graphs closely represents the P.E. (U) of a freely falling body and its height (h) above the ground?

Answer: 1
Question 48. The displacement x of a particle moving in one dimension, under the action of a constant force, is related to the time t by the equation, t x = + 3 where x is in metres and t in seconds. The displacement of the particle when its velocity is zero, is
- 0
- 6 m
- 12 m
- 18 m
Answer. 1. 0
Question 49. Asha lifts a doll from the floor and places it on a table. If the weight of the doll is known, what else does one need to know in order to calculate the work Asha has done on the doll?
- Time required
- Height of the table
- Mass of the ball
- Cost of the doll or the table
Answer. 1. Time required
Question 50. The work done in lifting a mass of 1 kg to a height of 9.8 m is
- 1 J
- (9.8)2 J
- 9.8 J
- None of these
Answer. 2. (9.8)2 J
Question 51. In which of the following cases, will the work done be maximum? The body is moved through a distances on the ground

Answer: 2
Question 52. Work done by a centripetal force
- increases by decreasing the radius of the circle
- decreases by increasing the radius of the circle
- increases by increasing the mass of the body
- is always zero
Answer. 2. decreases by increasing the radius of the circle
Question 53. Certain weight is attached with a spring. It is pulled down and then released. It oscillates up and down. Its K.E. will be
- maximum in the middle of the movement
- maximum at the bottom
- maximum just before it is released
- constant
Answer. 4. constant
Question 54. A 1 kg mass falls from a height of 10 m into a sand box. What is the speed of the mass just before hitting the sand box? If it travels a distance of 2 cm into the sand before coming to rest, what is the average retarding force?
- 12 m/sec and 3600 N
- 14 m/sec and 4900 N
- 16 m/sec and 6400 N
- 18 m/sec and 8100 N
Answer. 1. 12 m/sec and 3600 N
Question 55. If L, M denote the angular momentum and mass of a particle and p its linear momentum, which of the following can represent the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a circle of radius R?
- \(\frac{L^2}{2 M}\)
- \(\frac{p^2}{M}\)
- \(\frac{L^2}{2 M R^2}\)
- \(\frac{1}{2} M p\)
Answer. 2. \(\frac{p^2}{M}\)
Question 56. A particle of mass 4 m which is at rest and explodes into three fragments. Two of the fragments each of mass mare found to move with a speed v in mutually perpendicular directions. The total energy released in the explosion is
- 2mv2
- \(\frac{1}{2} m v^2\)
- mv2
- \(\frac{3}{2} m v^2\)
Answer. 3. mv2
Question 57. kWh represents the unit for
- force
- power
- time
- energy
Answer. 4. energy
Question 58. Energy cannot be measured in
- Js
- Ws
- kWh
- erg
Answer. 4. erg
Question 59. A steam engine converts
- heat energy into sound energy
- heat energy into mechanical energy
- mechanical energy into heat energy
- electrical energy into sound energy
Answer. 1. heat energy into sound energy
Question 60. A man throws bricks to the height of 12 m where they reach with a speed of 12 m/s. If he throws the bricks such that they just reach this height, then what percentage of energy will he save?
- 19%
- 38%
- 57%
- 76%
Answer. 2. 38%
Question 61. Two bodies with masses MA and MB are moving with equal kinetic energy. Their linear momenta are numerically in a ratio |PA| : |PB|, the ratio of their masses will be
- MB : MA
- MA : MB
- \(\sqrt{M_A}: \sqrt{M_B}\)
- \(M_{\mathrm{A}}^2: M_{\mathrm{B}}^2\)
Answer. 2. MA : MB
Question 62. Mechanical work done is equal to (symbols have their usual meanings)
- W = F/S
- W = FS
- W = F + S
- W = F – S
Answer. 3. W = F + S
Question 63. Which of the following graphs best represents the graphical relation between momentum (P) and kinetic energy (K) for a body in motion?

Answer: 2
Question 64. An elevator is designed to lift a load of 1000 kg through 6 floors of a building on an average of 3.5 m per floor in 6 sec. Power of the elevator, neglecting other losses, will be
- 3.43 × 104 watt
- 4.33 × 104 watt
- 2.21 × 104 watt
- 5.65 × 104 watt
Answer. 4. 5.65 × 104 watt
Question 65. When the momentum of a body increases by 100 %, then its K.E. increases by
- 20 %
- 40 %
- 100 %
- 300 %
Answer. 1. 20 %
Question 66. No work is said to have been done when an object moves at an angle of _____ with the direction of the force.
- 0°
- 90°
- 180°
- between 90° and 180°
Answer. 4. between 90° and 180°
Question 67. When a body is whirled in a circle, then work done on it is
- positive
- negative
- zero
- infinite
Answer. 2. negative
Question 68. A crane is used to lift 1000 kg of coal from a mine 100 m deep. If the time taken by the crane is 1 hr, then find the power of the crane, assuming the efficiency of the crane to be 80 %. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
- 2567 watts
- 2403 watts
- 3403 watts
- 3761 watts
Answer. 3. 3403 watts
Question 69. The flowing water of a river possesses
- gravitational energy
- potential energy
- electrical energy
- kinetic energy
Answer. 3. electrical energy
Question 70. The mass of an object P is double the mass of object Q. If both move with the same velocity, then the ratio of K.E. of P to Q is
- 1 : 2
- 2 : 1
- 1 : 4
- 4 : 1
Answer. 4. 4 : 1
Question 71. A truck can move up on a road having the gradient of 1 m rise for every 50 m with a speed of 15 km/hr. The resisting force is equal to 1/25 th the weight of the truck. How fast will the same truck move down the hill with the same horse power?
- 30 km/hr
- 45 km/hr
- 60 km/hr
- 75 km/hr
Answer. 2. 45 km/hr
Question 72. A body of mass 1 kg strikes elastically with another body at rest and continues to move in the same direction with one fourth the initial velocity. The mass of the other body is
- 3 kg
- 0.6 kg
- 2.4 kg
- 4 kg
Answer. 2. 0.6 kg
Question 73. A body rolling down a hill has
- K.E. only
- P.E. only
- Neither K.E. nor P.E.
- Both (a) and (b) above
Answer. 2. P.E. only
Question 74. A total of 4900 joules was expended in lifting a 50 kg mass. The mass was raised to the height of
- 98 m
- 960 m
- 245 m
- 10 m
Answer. 4. 10 m
Question 75. A ball of mass 200 g falls from a height of 5 m. What is its K.E. when it just reaches the ground?
- 9.8 J
- 98
- 980 J
- None of these
Answer. 4. None of these
Question 76. A stretched spring possesses
- kinetic energy
- elastic potential energy
- electric energy
- magnetic energy
Answer. 1. kinetic energy
Question 77. When a person climbs a hill, he possesses
- only K.E
- only P.E.
- both K.E. and P.E.
- none of these
Answer. 2. only P.E.
Question 78. An iron sphere of mass 30 kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere whose mass is 10.5 kg. The spheres are dropped simultaneously from a cliff. When they are 10m from the ground, they have the same
- acceleration
- momentum
- potential energy
- K.E.
Answer. 3. potential energy
Question 79. A stone of mass m kg is whirled in a vertical circle of radius 20 cm. The difference in the kinetic energies at the lowest and the topmost positions is
- 4 mg joules
- 0.4 mg joules
- 40 mg joules
- None of these
Answer. 1. 4 mg joules