Geometry Chapter 3 Symmetry Exercise 3 Solved Example Problems
Introduction
In the natural world around us we come across various shapes and objects in our daily life. Some of them are symmetrical and some of them are not so.
Imagine a straight line on a two-dimensional shape or object and if the portions of the shape or object on both sides of that straight line become identical then the shape or object is called symmetrical.
For example, if you imagine a vertical straight line just through the middle of the blackboard of your classroom, you will find that the parts of the blackboard on the left-hand and the right-hand side of that straight line are identical.
Hence, the blackboard is a symmetrical object.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 7 Maths
Again, take a piece of coal of irregular shape in your hand. No straight line or plane can be imagined through it so that the portions on both sides of this straight line or plane are identical.
Hence, a piece of coal of irregular shape is not a symmetrical object.

Different types of symmetry
Symmetry are mainly of two types.
- Linear symmetry and
- Rotational symmetry.
Linear symmetry
If an image is cut into two identical parts by a straight line then it is said that the image is symmetrical with respect to that straight line and the straight line is called the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry.
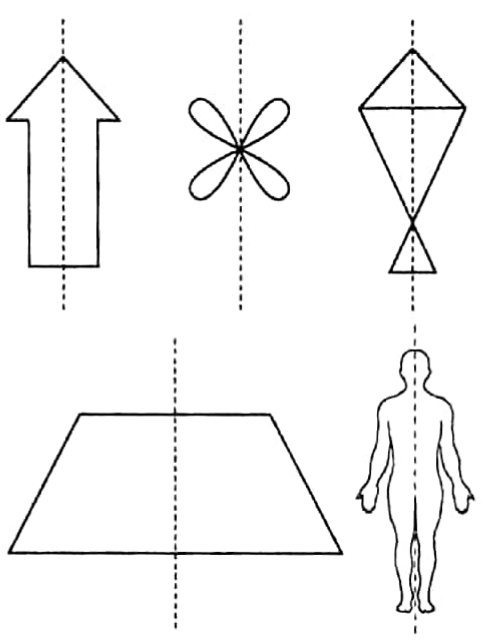
If these are folded along the dotted lines (line of symmetry) then the portions on the left-hand side of the dotted lines would coincide or match exactly on the portions on the right-hand side of it.
Hence, they are parted or divided into two identical portions with respect to the dotted lines.
To examine whether a figure has linear symmetry or not we have to fold it along the line of symmetry and we have to observe whether the two parts of the figure coincide or not.
A geometric may or may not have a line of symmetry. Also, a geometrical image may have more than one line of symmetry.
WBBSE Class 7 Symmetry Solutions
Linear symmetry geometrical images
1. A scalene triangle has no line of symmetry (or axis of symmetry).
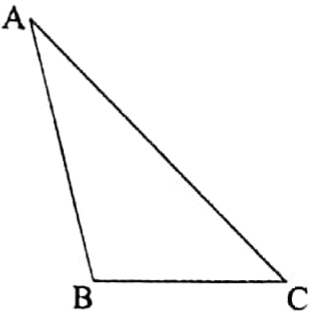
ΔABC is a scalene triangle. This triangle has no line of symmetry.
2. An isosceles triangle has one line of symmetry. This line of symmetry is the perpendicular bisector of the base.
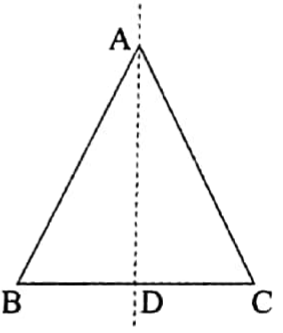
ΔABC is an isosceles triangle of which AD is the perpendicular bisector of the base BC.
AD has divided the triangle ABC into two congruent triangles ΔABD and ΔACD. Hence, the line of symmetry of the triangle ABC is the straight line AD.
3. An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry. The perpendicular bisectors of each side are its three lines of symmetry.
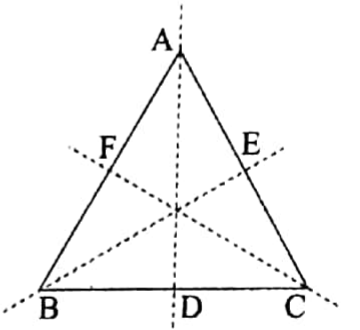
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle. Each of the three perpendicular bisectors of BC, CA and AB namely AD, BE and CF is a line of symmetry.
4. A non-isosceles trapezium has no line of symmetry.
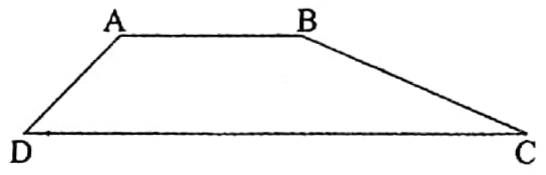
ABCD is a non-isosceles trapezium. That means its sides AD and BC are unequal. This trapezium has no line of symmetry
WBBSE Class 7 Symmetry Examples
5. An isosceles trapezium has one line of symmetry. This line of symmetry is the line, joining the mid-points of the two parallel sides.
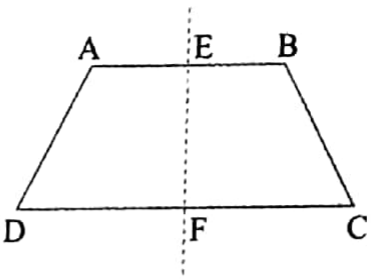
ABCD is an isosceles trapezium of which the lengths of the sides AD and BC are equal.
Now, E and F are the mid-points of the parallel sides AB and DC. The straight line EF is the line of symmetry of the trapezium ABCD.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Class 7 Symmetry Problems
6. A parallelogram has no line of symmetry.
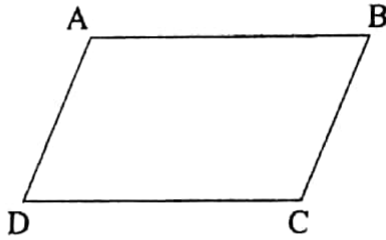
ABCD is a parallelogram. The parallelogram has no line of symmetry.
7. A rectangle has two lines of symmetry
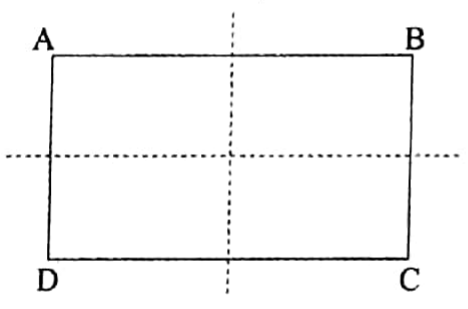
ABCD is a rectangle. It has two lines of symmetry. One is the line joining the mid-points of AB and DC.
Solved Problems for Class 7 Symmetry
8. A square has four line of symmetry
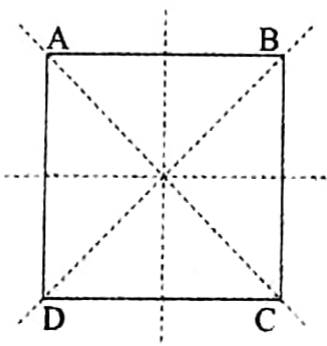
ABCD is a square. It has four lines of symmetry.
- The line joining the midpoints of AB and DC
- The line joins the midpoints of AD and BC.
- The straight line along the diagonal AC.
- The straight line along the diagonal BD.
9. A rhombus has two lines of symmetry
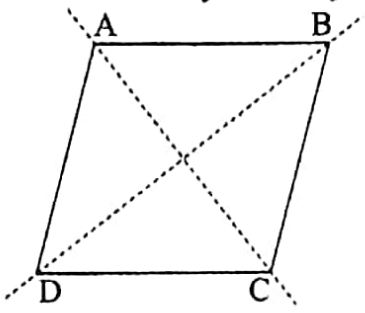
ABCD is a rhombus. Its two lines of symmetry are the two straight lines along the diagonals AC and BD.
10. A kite has one line of symmetry
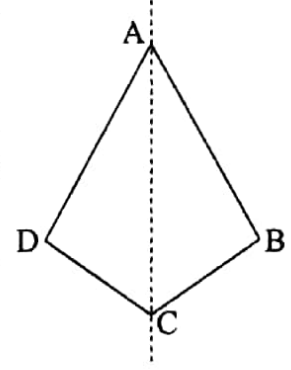
ABCD is a kite. Its one line of symmetry is the straight line along the diagonal AC.
11. An arrowhead has one line of symmetry
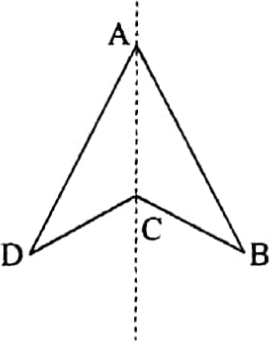
ABCD is an arrowhead. Its one line of symmetry is the straight line along AC.
12. A line segment has two lines of symmetry.
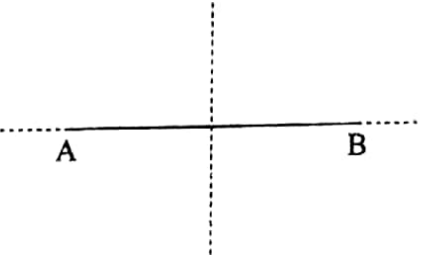
AB is a line segment. It has two lines of symmetry. One is the perpendicular bisector of AB and the other is the straight line along AB.
13. An angle with equal arms has one line of symmetry.
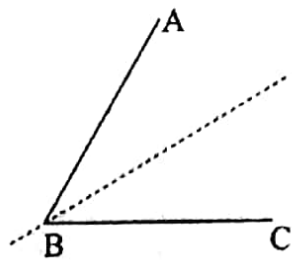
∠ABC is an angle with equal arms such that AB = AC. Its one line of symmetry is the internal bisector of ∠ABC.
Linear symmetry of some regular polygons
Class 7 Maths Exercise 3 Solutions on Symmetry
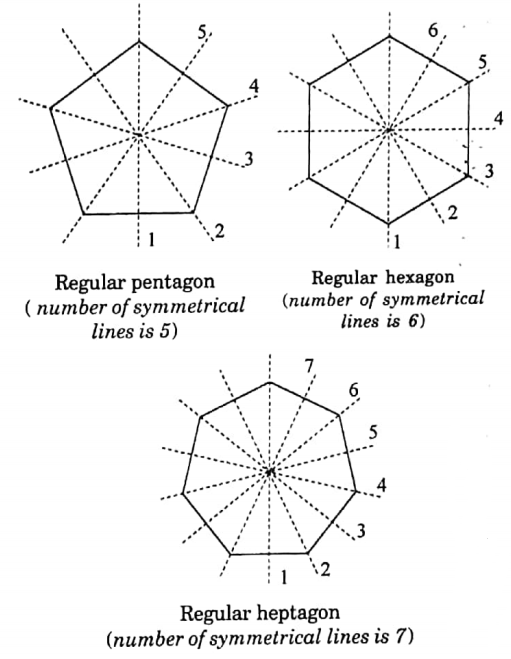
We have seen earlier that, an equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry and a square has four lines of symmetry.
Now, we shall show that a regular pentagon has 5 lines of symmetry, a regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry and a regular heptagon has 7 lines of symmetry.
Linear symmetry of a circle
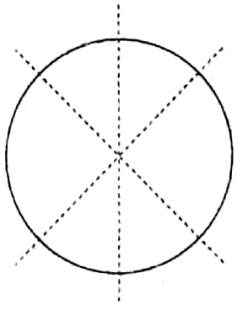
A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Any straight line along any diameter of a circle is its line of symmetry.
Since a circle has an infinite number of diameters therefore it has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Linear symmetry of the letters of the English alphabet

Some letters from A to Z of the English alphabet have no axis of symmetry, some have one axis of symmetry and some have two axes of symmetry.
The axes of symmetry are marked with dotted lines.
Reflection in the plane mirror and symmetry
West Bengal Board Class 7 Geometry Assistance
When reflection takes place in a plane mirror then the image formed in the plane mirror has some characteristics. For example :
- Size of object = size of the image.
- Distance of object from the mirror = Distance of image from the mirror.
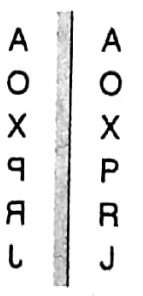
We can understand these two things easily. Because, when we stand in front of a mirror we Find our image identical with ourselves. If we proceed towards the mirror then the image also proceeds towards the mirror.
Hence, it is found that the concept of symmetry is associated with the reflection by the plane mirror.
But if you watch carefully you will find in the mirror shows your right hand as the left hand and the left hand as the right hand. This phenomenon is called lateral inversion.
That means the phenomenon of inversion of the image of an object by the plane mirror is called lateral inversion.
In this case, it should be noticed that symmetric objects do not undergo any lateral inversion. Then the formed by a mirror of some letters is shown below.
Also, from the phenomenon of reflection by a plane mirror, it can be said that, the axis of symmetry of the symmetrical image is such a line of reflection that, when the image is reflected with respect to that line it remains unaltered in the same position. The original image and its image coincide.
The image of the right-hand side of the letter ‘A’ coincides with the left-hand side of the letter ‘A’.
Hence, the reflecting line l is the axis of symmetry of the letter A.
WBBSE Class 7 Chapter 3 Symmetry Guide
The symmetry of rotation (or rotational symmetry)
Suppose, a body changes its position while moving in a circular path, about a fixed point and along a plane.
Now, if the angle between the two straight lines, obtained by joining the initial and terminal positions of any point on the body, with the centre remains unchanged throughout, then the motion of the body is called rotation.
It can be said in easy language that —
If each point of a moving body rotates through equal angle then its motion is called rotation.
The fixed point about which an object rotates is called the centre of rotation. As a result of rotation, an object does not change its shape.
When due to the rotation of a geometrical figure about a fixed point within it, the image, coincides with itself time and again then we say that, the image, has the symmetry of rotation.
The point about which there is rotational symmetry is called the centre of symmetry of rotation.
The measure of a minimum number of degrees through which angle, when a geometrical image, is rotated to make it coincide with itself, is called the angle of symmetry of rotation of that figure.
The number, through which a geometrical image, coincides with its initial position when it makes a complete rotation, which means it rotates through an angle 360°, is called the order of rotation.
Understanding Symmetry for Class 7 Students
Therefore, if an image which is symmetrical with respect to the rotation has a symmetry of rotation of order n then the measure of the angle symmetry of rotation of that image is 360°/n
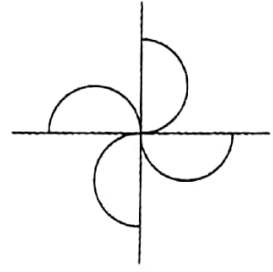
If the side is rotated through 90° about the centre of symmetry of rotation the image comes back to its initial position.
The order of the symmetry of rotation of this image is 4.
Also, the measure of its angle of symmetry of rotation is 360°/4 = 90°. 4
The symmetry of rotation of some geometrical images
1. A scalene triangle and an isosceles triangle have no symmetry of rotation.
2. An equilateral triangle has the symmetry of rotation. An equilateral triangle has three axes of symmetry. Their point of intersection is the centre of symmetry of rotation.
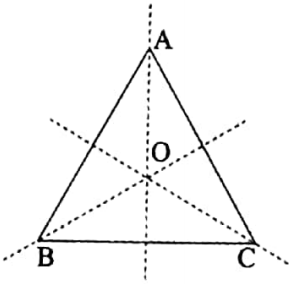
The centre O of the symmetry of rotation of the equilateral triangle ABC is the point of intersection of the three axes of
Its order of symmetry of rotation is 3 and the angle of symmetry of rotation is 120°.
3. A trapezium has no symmetry of rotation.
4. A parallelogram has the symmetry of rotation.
ABCD is a parallelogram. If the parallelogram is rotated through 180° about the point of intersection O of the diagonals the parallelogram it will coincide with itself.
Therefore, in the case of a parallelogram, the centre of symmetry of rotation is the point of intersection of its diagonals. The angle of symmetry of rotation is 180°. The order of symmetry of rotation is 2.
5. A rectangle has the symmetry of rotation.
In the image, below ABCD is a rectangle. If the rectangle is rotated through 180° with respect to the point of intersection O of the diagonals then the rectangle will coincide with itself.
Therefore, in the case of a rectangle, the centre of symmetry of rotation is the point of intersection of its diagonals.
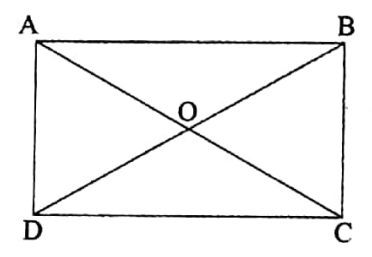
The angle of symmetry of rotation is 180°. The order of symmetry of rotation is 2.
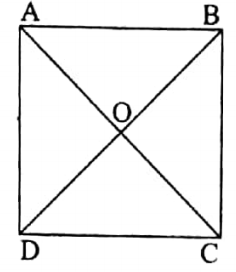
6. A square has the symmetry of rotation.
The next page ABCD is a square. If the square is rotated through 90° about the point of intersection of the diagonals then the square will coincide with itself.
Therefore, in case of a square, the centre of symmetry of rotation is the point O of the intersection of the diagonals.
The angle of symmetry of rotation is 90°. The order of symmetry of rotation is 4.
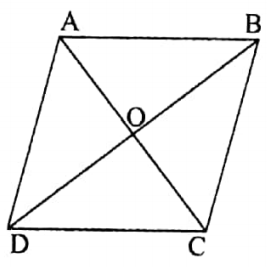
7. A rhombus has the symmetry of rotation.
Below ABCD is a rhombus. If the rhombus is rotated through 180° about the point of intersection of the diagonals then the rhombus will coincide with itself.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 3 Solved Examples
Hence, in case of a rhombus the centre of symmetry of rotation is the point of intersection of the two diagonals. The angle of symmetry of rotation is 180°.
The order of symmetry of rotation is 2.
8. A kite has no symmetry of rotation.
9. An arrow head has no symmetry of rotation.
10. A given line segment has the symmetry of rotation with respect to its mid-point. The angle of symmetry of rotation is 180°.
The order of symmetry of rotation is 2.
The symmetry of rotation of some regular polygons
- The centre of symmetry of rotation of a regular pentagon is the point of intersection of the five axes of symmetry. Its angle of symmetry of rotation is 72° and the order of symmetry of rotation is 5.
- The centre of symmetry of rotation of a regular hexagon is the point of intersection of the six axes of symmetry. Its angle of symmetry of rotation is 60° and the order of symmetry of rotation is 6.
- Similarly, the centres of symmetry of rotation of different regular polygons are the point of intersection of their axes of symmetry. The angle of symmetry of rotation = (360° + number of sides). The order of symmetry of rotation = a number of sides.
Point symmetry
It is said to have symmetry with respect to a point if the image, remains unaltered when it is rotated in that plane through 180° about the point.
That point is called the point of symmetry or centre of symmetry.
Since in this case there is a rotation of 180° therefore such type of symmetry is also called half-turn symmetry.
The following letters have point symmetry about the point marked by a dot.

