Arithmetic Chapter Square Measure Exercise 6 Solved Example Problems
Plane
If we keep the face of a solid on a flat white paper with which it coincides and indicate its boundary with a pencil, we obtain a plane.
Keeping a rectangular parallelopiped on a white paper, and moving a pencil through its edge we obtain a rectangle. If a cube is taken and the same process is applied we obtain a square.
In other words, the portion of a plane enclosed by three or more straight lines or by one or more curves is called a plane.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 7 Maths
Area
The measure of the portion of a plane enclosed by a plane figure is called its area. The plane area enclosed by the straight lines is called a polygon.
The measure of the portion enclosed by the sides of a polygon is called its area.
Perimeter
The sum of the lengths of the sides of a polygon is called its perimeter.

Rectangle
A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are equal and the angles are right angles is called a rectangle.

Square
The quadrilateral whose four sides are equal and the angles are right angles is called a square.
Some useful measurements
- Area of rectangle Length x Breadth.
- Perimeter of rectangle = 2 x (Length + Breadth).
- Area of square = (Side)2.
- Perimeter of square = 4 x Side.
Areas in connection with a room: A rectangular or square-shaped room has the following parts
- One floor and one roof
- Two walls along the length of the room (equal in size & shape and placed opposite to each other)
- Two walls along the breadth of the room (equal in size & shape and placed opposite to each other)
- There may be one or more doors and windows in the four walls.
The following images gives a clear idea about the above parts
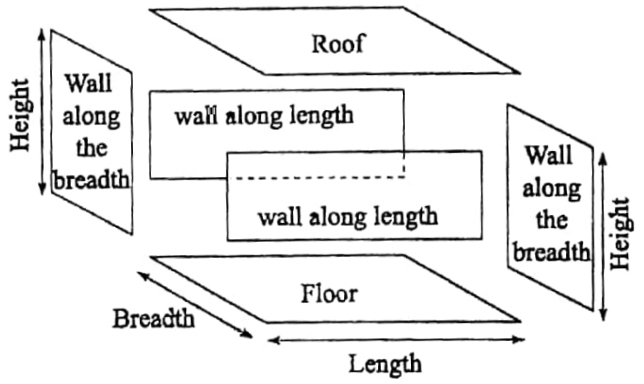
Useful measurements in connection with a room:
- Area of the roof or floor of the room = Length x breadth
- Area of two walls along the length of the room = 2 x length x height
- Area of two walls along the breadth of the room = 2 x breadth x height
- Area of the four walls of the room =2 (length + breadth)x height = Perimeter of room (or floor) x height
- Number of floor tiles = \(\frac{Area of floor}{Area of one tile}\)
- One has to consider the total area of the four walls and that of the roof to either paint or whitewash or plaster the room.
- If the room contains windows and/or door(s), then their total area has to be subtracted from the total area of roof and four walls to get the effective total area.
Height and Area of a triangle
The perpendicular drawn from any vertex on its opposite side is called the height of the triangle. In the image a perpendicular AD is drawn from the vertex A on its opposite side BC in the triangle ABC.
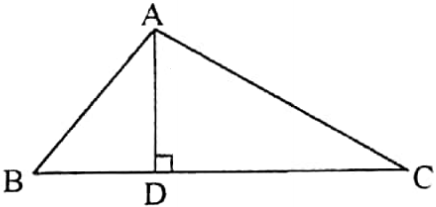
Hence AD is the height of the triangle. Here BC is the base of the triangle. If AC is taken as the base of the triangle, then the perpendicular drawn on AC from the opposite vertex B shall be taken as the height of the triangle.
Similarly, if AB is taken as the base of the triangle, then the perpendicular drawn on AB from the opposite vertex C shall have to be taken as the height of the triangle ABC.
The following images show the heights of an equilateral triangle, an isosceles triangle and a right-angled triangle.
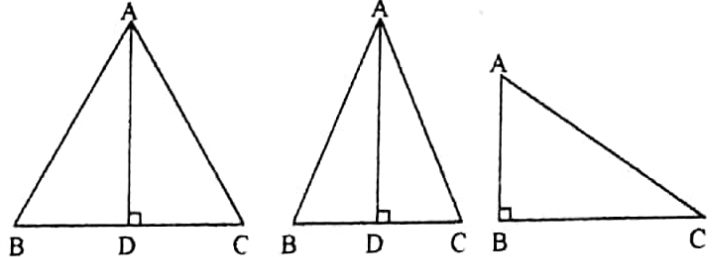
It is not mandatory that the height of a triangle should lie within its area enclosed by the three sides.
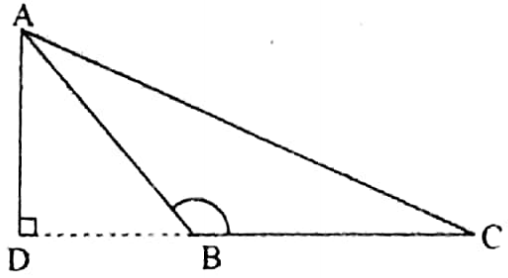
The adjacent figure shows that if one of the adjacent sides of the obtuse angle of an obtuse-angled triangle is taken as the base of the triangle, then the height of the triangle shall lie outside the area of the triangle bounded by its three sides.
The images shows that AD lies outside the bounded area of the triangle ABC when BC is taken as the base.
Some useful measurements in connection with a triangle:
- Perimeter of a triangle = Sum of lengths of three sides = AB + BC + CA
- Half or semiperimeter of a triangle = \(\frac{AB + BC + CA}{2}\)
- Area of triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) X base x height = \(\frac{1}{2}\) X BC X AD
- Area of a right-angled triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) X BC X AB
Unit of area
While writing the unit of area we have to write the word, ‘square’.
For example square metre, square centimetre etc.
Some points to note
1. To indicate the area of rectangle having length 10 cm and breadth 6 cm we write 10 cm x 6 cm, and read it as 10 cm by 6 cm.
2. Metre x Metre = Square metre.
10 square metres + 5 metres = 2 metres.
10 sq metres + 8 sq metres = 18 sq metres.
10 sq metres-8 sq metres = 2 sq metres.
25 sq metres + 5 sq metres = 5.
3. 12 inches = 1 foot, 144 sq inches = 1 sq foot.
3 feet = 1 yard, 9 sq feet = 1 sq yard.
4840 sq yards = 1 acre.
640 acres = 1 sq mile.
4. 10 mm = 1 cm, 100 sq mm = 1 sq cm
10 cm = 1 dm, 100 sq cm = 1 sq dm.
10 dm = 1 m, 100 sq dm 1 sq m.
10 m = 1 Dm, 100 sq m = 1 sq Dm.
10 Dm 1 Hm, 100 sq Dm = 1 sq Hm.
10 Hm = 1 Km, 100 sq Hm = 1 sq km.
1 are = 1 sq Dm = 100 sq m.
100 centiares = 1 are.
100 are 1 hectare.
100 hectares = 1 sq Kilometres.
5. To calculate area, both length and breadth must be reduced to same unit. The area is expressed in terms of sq unit.
Example 1. The length of a rectangle is 15 m 25 cm and its breadth is 10 m 2 cm. Find its area.
Solution:
Given:
The length of a rectangle is 15 m 25 cm and its breadth is 10 m 2 cm.
Here, length = 15 m 25 cm = 1525 cm breadth = 10 m 2 cm = 1002 cm
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth = 1525 x 1002 sq cm
= 1528050 sq cm
= 152 sq m 80 sq dm 50 sq cm
∴ 152 sq m 80 sq dm 50 sq cm.
Area = 152 sq m 80 sq dm 50 sq cm.
Example 2. The page of an exercise book is 15 cm long and 12 cm broad. A margin of width 2 cm is drawn on all sides and something was written on the remaining portion. What is the area of the written portion? What is the area of the portion where nothing was written?
Solution:
Given:
The page of an exercise book is 15 cm long and 12 cm broad. A margin of width 2 cm is drawn on all sides and something was written on the remaining portion.
Area of the page = 15 cm x 12 cm = 180 sq cm.
The portion on which something was written, was of length (15-2x 2) cm 11 cm and breadth (12-2 × 2) cm = 8 cm
∴ Area = 11 cm x 8 cm = 88 sq cm.
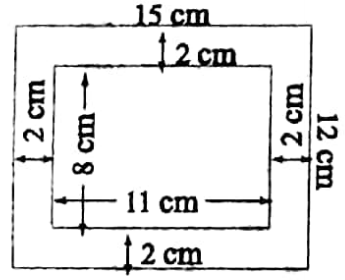
The portion on which nothing was written was of area (180 -88) sq cm = 92 sq cm.
∴ 88 sq cm, 92 sq cm.
= (4 × 100 + 50) sq cm = 450 sq cm. its breadth = 10 cm
The area of the portion where nothing was written = (4 × 100 + 50) sq cm = 450 sq cm. its breadth = 10 cm
WBBSE Class 7 Arithmetic Square Measure Examples
Example 3. The area of a rectangle is 4 sq dm 50 sq cm Find the area of the path. and its breadth 10 cm. Find its length.
Solution:
Given:
The area of a rectangle is 4 sq dm 50 sq cm
Area of the rectangle = 4 sq dm 50 sq cm
= (40 x 100 + 50) sq cm
= 450 sq cm.
its breadth = 10 cm
∴ Its length = \(\frac{Area}{breadth}\) = \(\frac{450 sq cm}{10 cm}\)
∴ 45 cm.
Length = 45 cm.
Example 4. The length and breadth of a rectangular plot are 36 m and 24 m. There is a path 2 m wide all around outside of the plot.
1. Find the length and breadth of the plot of land including the path.
2. Find the area of the plot of land excluding the path.
3. What is the area of the path?
Solution:
1. Length of the rectangular plot including the path (36+2×2) m = 40 m
Breadth of the rectangular plot including path = (24+2×2)m = 28 m
∴ 40 m, 28 cm.
2. Excluding the path, area of the rectangular plot = 36 x 24 sq m = 864 sq m
∴ 864 sq m.
3. Area of the path = (40 x 28-36 x 24) sq m = (1120-864) sq m = 256 sq m.
Example 5. How many tiles, each 5 dm by 2 dm will be required to cover the floor of a room 15 m by 12 m?
Solution:
The area of the floor = 15 x 12 sq m = 180 sq m = 18000 sq dm.
The area of each tile = 5 dm x 2 dm
∴ The number of tiles required = \(\frac{18000}{10}\) = 1800
∴ 1800
The number of tiles required = 1800.
Example 6. There is a square plot of land of side 20 m. A path 1 m wide runs all around outside of it.
Solution:
Given:
There is a square plot of land of side 20 m.
Including the path, length of the square plot of land (20+2 x 1) m = 22 m.
Including the path, area of the square plot of land = 22 x 22 sq m = 484 sq m.
Excluding the path, area of the square plot of land = 20 x 20 sq m = 400 sq m.
∴ Area of the path = (484-400) sq m = 84 sqm.
∴ 84 sq m.
Area of the path 84 sq m.
Solved Problems for Class 7 Square Measure
Example 7. Find the perimeter of a rectangle whose length is 15 m 5 dm and breadth is 8 m 7 dm.
Solution:
The perimeter of the rectangle = 2 x (length + breadth)
= 2x (155+ 87) dm
= 2x (242) m = 484 dm = 48 m 4 dm
∴ 48 m 4 dm.
The perimeter of a rectangle 48 m 4 dm.
Example 8. The area of a square plot of land is 6400 sq m. Find the cost of fencing all around the land at 3.50 per metre.
Solution:
Given:
The area of a square plot of land is 6400 sq m.
Area of the square plot of land = 6400 sq m
length of side of the square plot of land = √6400 m = 80 m
The perimeter of the square plot of land = 4 x 80m = 320 m
Cost of fencing 1 m = ₹ 3.50
Cost of fencing 320 m = ₹ 3.50 x 320 = ₹ 1120
Example 9. One plot is 4 sq metres and another plot is 4 metres square. Which one is of the greater area?
Solution:
Given:
One plot is 4 sq metres and another plot is 4 metres square.
By 4 sq metres is meant a plot whose area rectangle. is 4 sq metres.
[It may be a square, the length of whose side is 2 m and hence its area = 2 m x 2 m = 4 sq m
or, it may be a rectangle whose length is 4 m and breadth is 1 m and hence its area = 4
or, it may be triangular or circular or it may have the shape of any plane whose area is equal to 4 sq m.
On the other hand, by the sentence ‘a plot is 4 metres square’ we mean only a square the length of whose side is 4 metres i.e., its area (4)2 sq m = 16 sq m.
∴ The plot ‘4 metres square’ is of the greater area.
Example 10. The length of a rectangular plot of land is twice its breadth and its area is 578 sq m. Find the length, breadth and perimeter of the land.
Solution:
Given:
The length of a rectangular plot of land is twice its breadth and its area is 578 sq m.
Let, the breadth of the rectangular plot of land = x m then its length = 2x m.
∴ 2x x x = 578
or, 2x2 = 578 or, x2 = 289
or, x= √28917
∴ Breadth 17 m, Length = 2 x 17 m = 34 m Perimeter = 2 × (34 +17) m = 102 m
∴ Length is 34 m, breadth is 17 m and perimeter is 102 m.
Example 11. How much fencing will be required to fence a square field of area 625 sq metres?
Solution:
The area of the square field = 625 sq metres
∴ The length of its side = √625 m = 25 m .
∴ Its perimeter = 4 x 25 m = 100 metres.
Since the total length of fencing is equal to the 4 x 80 m = 320 m perimeter, therefore the required length of fencing 100 metres.
Cost of fencing 1 m = 3.50 Cost of fencing 320 m = 3.50 x 320=1120
Class 7 Maths Exercise 6 Solutions on Square Measure
Example 12. The length of a rectangle is 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) times its breadth. If the area of a square be 100 sq m and its perimeter be equal to the perimeter of the rectangle then find the length of the rectangle.
Solution:
Area of the square = 100 sq m
Length of side of the square = √100 m = 10m
∴ Perimeter of the square= 4 x 10 m = 40 m
Let, the breadth of the rectangle = xm, 3х then length of the rectangle = \(\frac{3x}{2}\) m
∴ 2 X (x + \(\frac{3x}{2}\)) = 40
or, \(\frac{5x}{2}\)=20
or, x =\(\frac{2 X 20}{5}\) = 8
∴ Length of the rectangle = \(\frac{3 X 8}{2}\)
∴ 12 m.
Length of the rectangle =12 m.
Example 13. The length of a room is 8 m, its breadth is 6 m and its height is 5 m. What will be the cost of polishing the floor of the room at 70 per sq m?
Solution:
Given:
The length of a room is 8 m, its breadth is 6 m and its height is 5 m.
Area of the floor of the room = 8 x 6 sq m = 48 sq m
Cost in 1 sq m = ₹ 70
Cost in 48 sq m = ₹ 70 x 48 = ₹ 3360
∴ ₹ 3360
Cost in 48 sq m = ₹ 3360
Example 14. A rectangular plot of length 200 m and breadth 120 m has been divided in 4 equal parts by two paths 10 m wide parallel to length and breadth. What is the area of that path?
Solution:
Given:
A rectangular plot of length 200 m and breadth 120 m has been divided in 4 equal parts by two paths 10 m wide parallel to length and breadth.
Area of the path parallel to length = 200 x 10 sq m = 2000 sq m
Area of the path parallel to breadth = 120 x 10 sq m = 1200 sq m
Area of the portion where the two paths intersect 10 x 10 sq m = 100 sq m
∴ The required area of the path =(2000+ 1200-100) sq m = 3100 sq m
∴ 3100 sq m
The required area of the path = 3100 sq m
Example 15. If both length and breadth of a rectangle are doubled then how many times will be its area?
Solution:
Let, length of the rectangle = x m and its breadth = y m
∴ Area of the rectangle = x y sq m
Changed length = 2x m and breadth = 2ym
∴ Changed area = 2x × 2y sq m = 4 xy sq m
∴ Area of the rectangle will be 4 times
∴ 4 times.
Example 16. The length of a rectangular stage of a theatre is twice its breadth. It costs ₹ 6048 to cover the whole stage with tarpaulin. If one sq m of tarpaulin costs ₹21, find the length and breadth of the stage.
Solution:
Given:
The length of a rectangular stage of a theatre is twice its breadth. It costs ₹ 6048 to cover the whole stage with tarpaulin. If one sq m of tarpaulin costs ₹21
Since the total expenditure is ₹ 6048 to cover the stage at the rate ₹21 per square metre, therefore, the area of the stage = (6048 ÷ 21) sq m = 288 sqm
Let, the breadth of the stage = x m then its length = 2x m.
∴ 2x X x = 288 or, 2x2 = 288
or, x2 = \(\frac{288}{2}\) = 144
or, x=√144 = 12
∴ Breadth = 120m and length = 2 x 12 m = 24 m
∴ Length is 24 m and breadth is 12 m
Example 17. A garden is 30 m long and 20 m broad. All round outside of it, there is a path 3 m broad. What is the area of the path?
Solution:
Given:
A garden is 30 m long and 20 m broad. All round outside of it, there is a path 3 m broad
Length of the garden including the path = (30+3×2) m = (30 + 6) m = 36 m
Breadth of the garden including the path = (20 + 3 x 2) m = (20 + 6) m = 26 m
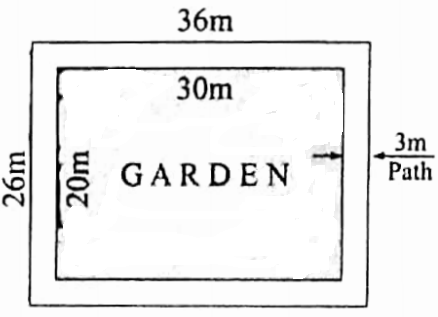
Area of the garden including the path = 36 m x 26 m = 936 sq m
Area of the garden excluding the path = 30 m x 20 m = 600 sq m.
Area of the path = (936- 600) sq m = 336 sq m
∴ 336 sq m
Area of the path = 336 sq m
Example 18. The length and breadth of a rectangular garden are 60 m and 40 m respectively. Two 5 m wide path is divided Find the cost of paving the path at ₹80 per rectangular garden into four equal parts. sq. metre. Find also the area of each part of the land.
Solution:
Given:
The length and breadth of a rectangular garden are 60 m and 40 m respectively. Two 5 m wide path is divided Find the cost of paving the path at ₹80 per rectangular garden into four equal parts. sq. metre.
Area of the path parallel to the length = 60 x 5 sq m = 300 sq m.
Area of the path parallel to the breadth = 40 x 5 sq m = 200 sq m.
Area of the portion where two paths intersect each other = 5 x 5 sq m = 25 sq m.
Area of the path = (300 + 200- 25) sq m = 475 sq m
cost of paving 1 sq m path = ₹ 80
cost of paving 475 sq m path = ₹ 80 x 475 = ₹ 38000
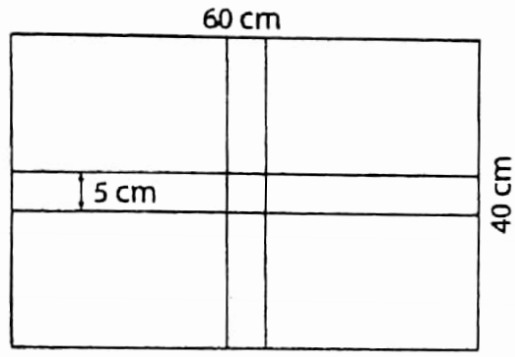
length of one part of the garden =\(\frac{60 -5}{2}\) m = \(\frac{55}{2}\)
breadth of one part of the garden = \(\frac{40 -5}{2}\) m = \(\frac{35}{2}\)
area of one part of the garden = \(\frac{55}{2}\) x \(\frac{35}{2}\) sq m
= \(\frac{1925}{4}\) sq m = 481.25 sq m
∴ ₹ 38000, 481 .25 sq m.
West Bengal Board Class 7 Square Measure Assistance
Example 19. A garden is 25 metres square. All around inside of it, there is a path 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) m broad. What is the area of the path?
Solution:
Given:
A garden is 25 metres square. All around inside of it, there is a path 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) m broad.
Area of the garden = 25 x 25 sq m = 625 sq m
Length of the side of the garden excluding the path
= (25 – \(\frac{5}{2}\) x 2) m = 25 -5 m = 20 m
∴ Area of the garden excluding the path = 20 m x 20 m = 400 sq m.
∴ Area of the path = (625-400) sq m = 225 sq m.
∴ 225 sq m.
Area of the path = 225 sq m.
Example 20. The path that leads to a man’s house is 2 m wide. The path divides the garden in front of the house in two equal squares. The path is constructed for 8000 at the rate of 500 per sq m. Calculate the area of each square portion of the garden. The house is built in rectangular land. If the length of the rectangular land is 4 m, calculate the area occupied by the house.
Solution:
Given:
The path that leads to a man’s house is 2 m wide. The path divides the garden in front of the house in two equal squares. The path is constructed for 8000 at the rate of 500 per sq m. Calculate the area of each square portion of the garden.
Since the total expenditure of constructing the path is ₹ 8000 at the rate of ₹ 500 per sq m therefore, area of the path
\(\frac{8000}{500}\) sq m = 16 sq m
Since the breadth of the path = 2 m
therefore its length = \(\frac{16}{2}\) m = 8 m
∴ Area of each square portion of the garden = 8 x 8 sq m = 64 sq m
Length of the portion occupied by the house = (8 + 2 + 8)m = 18m and its breadth = 4 m.
Therefore, its area = 18 x 4 sq m = 72 sq m
∴ 64 sq m, 72 sq m
Area= 64 sq m, 72 sq m
Example 21. The length, breadth and height of a room are 4 m, 3 m and 5 m respectively. What will be the cost of cementing the floor of that room at? ₹15 per square metre? What will be the cost of white washing the four walls at ? ₹5 per square metre?
Solution:
Given:
The length, breadth and height of a room are 4 m, 3 m and 5 m respectively.
Area of the floor of the room = 4 x 3 sq m = 12 sq m.
cost of cementing 1 sq m = ₹ 15
cost of cementing 12 sq m = ₹ 15 x 12 = ₹ 180
Again, the area of the four walls of the room = 2 x (4+3) x 5 sq m
= 2x7x5 sq m = 70 sq m
cost of whitewashing 1 sq m = ₹ 5
cost of whitewashing 70 sq m = ₹ 5 x 70 = ₹ 350
∴ Cost of cementing the floor =₹ 180.
Cost of whitewashing the four walls = ₹ 350.
WBBSE Class 7 Chapter 6 Square Measure Guide
Example 22. The cost of cultivating a 30 m long piece of land is ₹ 150. Had the breadth of the land been 5 m less, the cost would have been ₹ 120. Calculate the breadth of the land.
Solution:
Given:
The cost of cultivating a 30 m long piece of land is ₹ 150. Had the breadth of the land been 5 m less, the cost would have been ₹ 120.
Let the breadth of the land = xm
The area of the land = 30x sq m
Had the breadth of the land been 5 m less the breadth would have been (x-5) m.
The area would have been 30 (x-5) sq m
According to the question,
\(\frac{30x}{30(x -5)}\) = \(\frac{x}{x – 5}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
or, 5x-25= 4x or, 5x-4x= 25 or, x = 25
∴ The breadth of the land is 25 m.
Example 23. The area of four walls of a room is 154 sq m If its length and breadth be 6 m and 5 m respectively then what will be its height?
Solution:
Given:
The area of four walls of a room is 154 sq m If its length and breadth be 6 m and 5 m respectively
2 × (length + breadth) x height = area of four walls.
or, 2 x (6+ 5) m x height = 154 sq m or, 22 m x height = 154 sq m
or, height = \(\frac{154}{22}\) m = 7 m
∴ 7 m.
Height = 7 m.
Example 24. The length and breadth of a rectangular hall are 30 m and 18 m respectively. Find how many square tiles of side 3 dcm will be required for flooring the hall.
Solution:
Given:
The length and breadth of a rectangular hall are 30 m and 18 m respectively.
Area of the floor of the hall = 30 x 18 sq m = 540 sq m.
Area of one tile = 3 dcm x 3 dcm = .3 mx .3 m = .09 sq m
∴ Number of tiles = \(\frac{540}{.09}\) = 6000
∴ 6000 tiles will be required.
Example 25. Find the greatest measure of each stone of the same square shape to cover a rectangular courtyard 36 m long and 28 m broad. Find the number of such stones.
Solution:
The H.C.F. of 36 m and 28 m is 4 m.
∴ Each stone of the greatest area will be 4 metres square.
∴ Area of each stone = (4)2 sq m = (4×4) sq m
∴ The required number of stones = \(\frac{36 X 28}{4 X 4}\) =63
∴ Each stone is 4 metres square and a number of stones is 63.
Example 26. Mahim’s family has an 18 m x 14 m rectangular plot of land. There is a square portion of the garden of side 3.4 m within the rectangular plot of land. Calculate the area of the plot of land without the garden. Find how many square tiles of side 2 dcm will be required to cover the empty portion of land.
Solution:
Given:
Mahim’s family has an 18 m x 14 m rectangular plot of land. There is a square portion of the garden of side 3.4 m within the rectangular plot of land.
Area of a rectangular plot of land = (18 x 14) sq m = 252 sq m.
Area of the square portion of the garden of side 3.4 m = (3.4 x 3.4) sq m = 11.56 sq m.
Area of the empty portion of land excluding the garden (252-11.56) sq m = 240.44 sq m.
Area of one tile = 2 dcm x 2 dcm = .2 m x .2 m = .04 sq m
∴ Number of tiles = \(\frac{240.44}{.0.4}\) = 6011
∴ Area of empty plot of land = 240.44 sq m, 6011 tiles will be required.
Understanding Square Measure for Class 7 Students
Example 27. Find the perimeter of a square field having twice the area of a rectangular field of length 25 m and breadth 8 m.
Solution: Area of the rectangular field = 25 x 8 sq m = 200 sq m
∴ Area of the square field = 2 x 200 sq m = 400 sq m
∴ Each side of the square field = √400 m = 20 m
∴ Perimeter of the square field = 4 × 20 m = 80 m
∴ 80 metres.
Perimeter of the square field = 80 metres.
Example 28. The length, breadth and height of a room of a school are 8 m, 6 m and 5 m respectively.
1. Find the cost of cementing the floor at ₹ 75 per square metre.
2. Find the cost of whitewashing the ceiling at ₹ 52 per square metre.
3. The room has 2 doors each 1.5 m wide and 1.8 m high and has 2 windows each 1.2 m wide and 1.4 m high. Calculate the cost of painting doors and windows at ₹ 260 per square metre.
4. Calculate the total cost of plastering the four walls without doors and windows at ₹ 95 per square metre and painting the walls at ₹ 40 per square metre.
Solution:
1. Area of the floor = (8 x 6) sq m = 48 sq m.
The cost of cementing 48 sq m at the rate ₹ 75 per square metre ₹ 75 x 48= ₹3600
∴ ₹ 3600.
2. Area of the ceiling area of the floor = 48 sq m.
Cost of whitewashing 48 sq m at the rate ₹ 52 per square metre = ₹ 52 x 48= ₹ 2496
∴ ₹ 2496.
3. Total area of two doors each 1.5 m wide and 1.8 m high = 2x (1.5 x 1.8) sq m = 5.4 sq m.
Total area of two windows each 1.2 m wide and 1.4 m high = 2 × (1.2 x 1.4) sq m = 3.36 sq m.
Total area of the doors and windows = (5.4+ 3.36) sq m = 8.76 sq m.
Cost of painting doors and windows at the rate ₹ 260 per square metre ₹ (260 x 8.76)= ₹ 2277.60
∴ ₹ 2277.60.
4. Total area of the four walls = 2 × (length +breadth) x height = 2 x (6+8) x sq m = 140 sq m
area of the four walls without doors and windows (140-8.76) sq m = 131.24 sq m.
cost of plastering and painting per square metre (95+40) = ₹ 135
Total cost in 131.24 sq m at the rate of ₹135 per square metre ₹ (135 x 131.24)= ₹ 17717.40
∴ ₹ 17717.40.
Example 29. What will be the cost of paper 3 m wide, at 25 paise per metre for covering the four walls of a room 15 m long, 12 m broad and 10 m high?
Solution:
The area of the paper =the area of the four walls
= 2 x (length + breadth) x height
= 2 x (15 m + 12 m) x 10 m
= 2 x 27 x 10 sq m
The length of the paper used = \(\frac{2 X 27 X 10}{3}\) m = 180 m
The required cost = 180 x 25 paise = 4500 paise = ₹ 45
∴ ₹45.
The required cost ₹45.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 6 Solved Examples
Example 30. A club room is square in the shape of side 15 m long and 5 m high. There are 4 doors in the club room each 1.5 m wide and 2 m high. Calculate the cost of oil painting its four walls without doors at 350 per square metre.
Solution:
Given:
A club room is square in the shape of side 15 m long and 5 m high. There are 4 doors in the club room each 1.5 m wide and 2 m high
Area of the 4 walls of the club room =2x (15+15) x 5 sq m = 300 sq m.
Area of 4 doors each 1.5 m wide and 2 m high = 4 x (1.5 × 2) sq m = 12 sq m.
Area of 4 walls without doors (300-12) sqm=288 sqm
Cost of oil painting 4 walls without doors at the rate ₹350 per sq m = ₹350 x 288 = ₹100800.
∴ ₹ 100800.
Cost of oil painting 4 walls without doors at the rate ₹350 per sq m = ₹ 100800.
Example 31. The length, breadth and height of a room are equal. If the area of four walls be 100 sq m then find its length, breadth and height.
Solution:
Given:
The length, breadth and height of a room are equal. If the area of four walls be 100 sq m
Let, the length of the room = its breadth = its height = a metres.
∴ 2x (a + a) x a = 100
or, 2 x 2a x a = 100
or, 4a2 = 100
or, a2 = 100 = 25
or, a = √25 = 5
∴ Each of length, breadth and height is equal to 5 m.
Example 32. What will be the cost of preparing a road of length 12 km and breadth 4 m at ₹ 3.50 per square metre?
Solution:
Area of the road= 12000×4 sq m. = 48000 sq m.
∴ Cost of preparing the road
= ₹ 48000 x 3.50 = ₹ 168000
∴ ₹ 168000
Cost of preparing the road is ₹ 168000
Example 33. ₹57800 is required to fence a square park with iron railing at 50 per metre. Find the length of one side of the park.
Solution:
Since, to fence the square park with iron railing at ₹ 50 per metre, ₹ 57800 is needed therefore, the perimeter of the square park
= \(\frac{57800}{50}\) metres = 1156 metres
Hence, the length of its one side = \(\frac{1156}{4}\) metres = 289 metres.
∴ 289 metres.
The length of its one side 289 metres.
Example 34. The length of a rectangular field is three times its breadth and its area is 192 sq metres. How much greater will be the area of the square field than that of the rectangular field if the perimeter of the square field is equal to that of the rectangular field?
Solution:
Given:
The length of a rectangular field is three times its breadth and its area is 192 sq metres.
Area of the rectangle = 192 sq m
∴ length x breadth = 192 sq m.
or, 3 x breadth x breadth = 192 sq m
or, (breadth)2 = \(\frac{192}{3}\) sq m = 64 sq m
or, breadth = 8 m
∴ Length = 3 x 8 m = 24 m
Hence, the perimeter of the rectangular field = 2 (24 + 8) m = 64 m
Therefore, the perimeter of the square field is also 64m
∴ Length of each side of the square field = \(\frac{64}{3}\) = 16 m
∴ Area of the square field = (16)2 sq m = 256 sq m
∴ Area of the square field is greater than that of the rectangular field by (256- 192) sq m = 64 sq m
∴ Greater by 64 sq m
Step-by-Step Solutions for Class 7 Square Measure Problems
Example 35. The length, breadth and height of a room are 6 m, 5 m and 3.5 m respectively. There are two doors each measuring 1.75 m by 1.2 m and two windows each measuring 1.4 m by 1 .2 m. What will be the cost of cementing the floor at? ₹65 per sq m? What will be the cost of whitewashing the four walls? ₹15 per sqm leaving the doors and the windows?
Solution:
Given:
The length, breadth and height of a room are 6 m, 5 m and 3.5 m respectively. There are two doors each measuring 1.75 m by 1.2 m and two windows each measuring 1.4 m by 1 .2 m.
Area of the floor of the room = 6 x 5 sq m = 30 sq m.
Total cost of cementing the floor at the rate of ₹ 65 per sq m = ₹ 65 x 30 = ₹ 1950.
The area of the four walls of the room = 2 x (6 + 5) x 3.5 sq m = 77 sq m
Total area of two doors and two windows = (2 x 1.2 x 1.75 + 2 x 1.4 x 1.2) sqm
= (4.2 + 3.36) sq m = 7.56 sq m
∴ Area of the four walls excepting the doors and the windows = (77-7.56) sq m = 69.44 sq m.
Total cost of whitewashing at the rate of ₹ 15 per square metre = ₹ 69.44 × 15 = ₹ 1041.60.
∴ ₹ 1950, 1041.60.
Example 36. There is a path 1 metre broad all round outside of a square garden of side 20 m. Find the cost of paving the path at ₹ 35.50 per sq m.
Solution:
Given:
There is a path 1 metre broad all round outside of a square garden of side 20 m.
Length of the square garden including the path = (20 + 2) m = 22 m.
∴ Area of the square garden including the path = (22)2 sq m = 484 sq m.
area of the square garden excluding the path = (20)2 sq m = 400 sq m.
∴ Area of the path =(484-400) sq m = 84 sq m.
The total cost of paving the path at ₹ 35.50 per square metre = ₹ (35.50 x 84) = ₹ 2982.
∴ The required cost is ₹ 2982.
Example 37. Boundary walls are made along the bank of a pond to surround it. The length of the pond is 6 m more than its breadth. Now widening the edge of this pond by 8 m, a railing of length 192 m was made towards the waterside. What is the outside length and breadth of the boundary walls along the bank? What is the perimeter of the pond along the outside boundary?
Solution:
Given:
Boundary walls are made along the bank of a pond to surround it. The length of the pond is 6 m more than its breadth. Now widening the edge of this pond by 8 m, a railing of length 192 m was made towards the waterside.
Considering the water side 2 x (length + breadth) = 192 m
or, length + breadth = 96 m
or, breadth + 6 m + breadth = 96 m
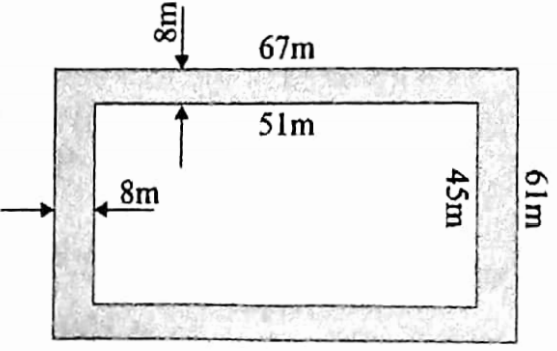
or, 2 x breadth = 90 m or, breadth =\(\frac{90}{2}\) 45 m
Hence, length (45+6) m = 51 m.
Now, the outside length of the boundary wall along the bank = (51 +16) m = 67 m and the outside breadth = (45+16) m = 61 m.
Perimeter of the pond along the outside boundary=2x (67 +61) m = 256 m.
Example 38. Find the height of a triangle if its area and length of the base be x sq. units and y units respectively.
Solution:
Area of triangle =\(\frac{1}{2}\) x base x height
or, x = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x y x height
or, height = \(\frac{2x}{y}\)
∴ \(\frac{2x}{y}\) unit.
Example 39. The perimeter of a triangle is (3a + b)cm. If the length of its two sides are (2a-b)cm and b cm, then find the length of the third side.
Solution:
Given:
The perimeter of a triangle is (3a + b)cm. If the length of its two sides are (2a-b)cm and b cm
Sum of lengths of two sides = (2a – b) + b = 2a cm.
∴ Length of third side = (3a + b) – 2a = (a + b) cm.
∴ (a + b) cm.
Length of third side = (a + b) cm.
Example 40. If the adjacent sides of the right angle in a right-angled triangle measure 4 cm and 10 cm in length, then find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
If one side adjacent to the right angle be considered as the base, then the other side becomes the height or altitude of the right angles triangle.
∴ Area of the triangle
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 4 x 10 sq.cm = 20 cm
Area of the triangle = 20 cm.
Example 41. The length of the base of a triangular-shaped land is thrice its height. A sum of ₹4,50,000 has been expended to cultivate the land at a rate of ₹30 per sq.m. Calculate the length of height of the land.
Solution:
Given:
The length of the base of a triangular-shaped land is thrice its height. A sum of ₹4,50,000 has been expended to cultivate the land at a rate of ₹30 per sq.m.
Area of land = sq.m 15000 sq.m.
Let the height of the triangular-shaped land be x m.
∴ Length of its base = 3x m.
∴ Area of triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 3x X x = 3x2/2 sq.m
Therefore, 3x2/2= 15000
or, x2 = 3 x 15000 = 10,000
or, x=√10,000 = 100
∴ Height of land, x = 100m and length of the base, 3x=300m.
∴ 300m and 100m.
Height of land = 300m and 100m.
Example 42. The ratio of the lengths of the two sides = (2a – b) + b = 2a cm. adjacent to the right angle in a right-angled triangle is 3 4. If the area of the triangle is 1014 sq. cm, then find out the length of these sides.
Solution:
Given:
The ratio of the lengths of the two sides = (2a – b) + b = 2a cm. adjacent to the right angle in a right-angled triangle is 3 4. If the area of the triangle is 1014 sq. cm
Let the lengths of the two sides be 3x and 4x.
∴ Area of triangle =\(\frac{1}{2}\) x 3x x 4x=\(\frac{12}{2}\) x2 = 6x2
Therefore, 6x2 =1014
or, x2 = \(\frac{1014}{6}\) = 169
or, x =√169 = 13
∴ Length of two sides, 3×13 = 39 cm and 4×13 = 52 cm.
∴ 39 cm and 52 cm.
Length of two sides = 39 cm and 52 cm.
