WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Why is Europe called the most developed continent in the world?
Answer:
Reasons to call Europe the most developed continent:
The continent of Europe has been at the forefront of science, philosophy, literature, art and manufacturing. There are several reasons to call Europe the most developed continent.
These are as follows-
1. Geographical expeditions:opic A
Due to the geographical expeditions of the enthusiastic sailors of this continent in the sixteen century, many unfamiliar, unknown countries, islands, and continents of the world became familiar and famous.
2. Industrial Revolution:
The first industrial revolution took place in Europe. Modern mechanical processes make it possible to produce and preserve all products. As a result, it is possible to get all the necessities quickly.
3. Colonization:
Several countries of Europe, such as England, Spain, France, Portugal, Holland, etc. had established colonies in different countries of the world through trade expeditions. As a result, trade, education, science, etc. also improved in these colonized countries.
4. Modern agricultural technique:
In Europe, various modern techniques are practised in agriculture. Mixed farming is one of those. As a result, agricultural productivity is very high.
5. Mineral and energy resources:
This contine nt is rich in petroleum, coal, iron ore and other mineral resources. Besides, huge amounts of hydropower and nuclear energy are generated here. These are very conducive for industrial development.
6. Most developed industrial regions:
Ruhr in Germany, Donetsk in Ukraine, Moscow in Russia, Paris basin in France, and London basin in the United Kingdom are the most developed industrial regions of this continent.
Read And Learn Also WBBSE Solutions For Class 7 Geography
Question 2. Discuss the geographical significance of the continent of Europe. Or, Elucidate the factors for the development of Europe.
Answer:
The geographical significance of the continent of Europe:
Europe is the sixth-largest continent in terms of size, but in terms of science and technology, literature, art and culture, research, and agriculture, it has always led the rest of the world. Its geographical significance is great.
1. Central location:
Europe is surrounded by the continents of Asia, Africa and North America. This continent occupies the central position of the landmass of the northern hemisphere.
As a result of this, maintaining communication with other continents as well as trade relations has historically been easy.
2. Favourable climate:
Europe is surrounded by water on three sides. This continent extends from 36° N latitude to 71° N latitude. So most of the continent falls under the temperate climatic zone while the southwestern part experiences the Mediterranean climate.
This type of climate makes the local population hard and hardworking.
3. Influence of ocean currents:
Warm ocean currents flow along the northwest coastline of Europe. As a result, the ports remain ice-free even during the winter. This ensures that waterways remain navigable throughout the year and this facilitates trade and commerce throughout the year.
4. Abundance of forest resources:
The temperate climate of Europe helps to grow huge forestlands of coniferous trees. The wood from these trees is an important raw material for paper, household goods, shipbuilding and so on.
5. Mineral and energy resources:
The countries of the continent of Europe have rich reserves of minerals and energy such as coal, iron ore, mineral oil, bauxite and so on. The rivers are fast-flowing, so they are used to generate enormous amounts of hydel power.
6. Agriculture and animal rearing:
Though there is not much arable land in Europe, advanced processes and techniques of cultivation, irrigation, mixed-farming and crop rotation make it agriculturally very developed. Ukraine is the world’s highest producer of high-quality of wheat.
At the same time, premium breeds of animals such as cows, pigs, sheep and bulls are also reared here for commercial purposes.
7. Industrially most developed:
Europe is the most industrially developed continent of the world. Here, iron and steel, engineering, ship-building, paper and chemical industries have achieved the peak of advancement.
Many industries have also flourished in the London Basin, Ruhr industrial region, and Moscow industrial region -all in Europe.

Question 3. Describe the topography of the continent of Europe.
Answer:
Topography of the continent of Europe:
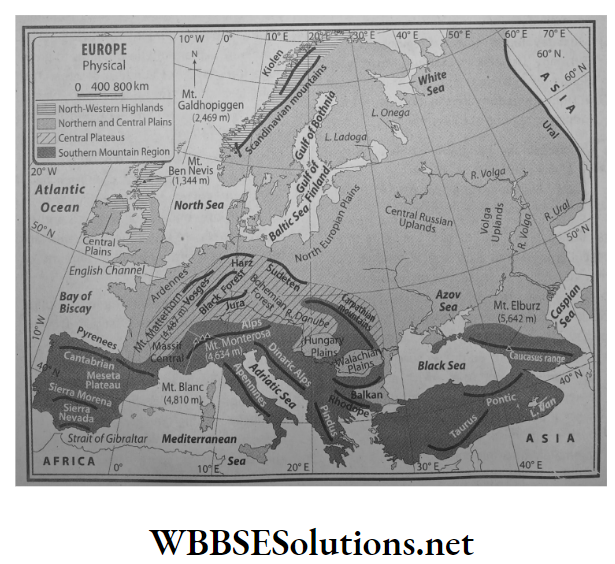
According to the differences in physiography, the continent of Europe can be delineated into the following:
- North-western highlands,
- Northern and central plains,
- Central plateaus,
- Southern mountain region.
1. North-western highlands:
Location:
North-western highlands of Europe consist of many parts. These are the mountainous region of the Scandinavian peninsula (Norway, and Sweden are part of this peninsula), the mountainous region of Finland, the northern and central parts of the British Isles and the hilly regions of the Northern Ireland.
Characteristics:
- This is a dissected plateau, separated by deep valleys and fjords.
- This is made up of old volcanic and metamorphic rocks.
- Another feature is that several fjords and lakes can be observed in the coastlines of Norway and Sweden.
2. Northern and central plains:
Location:
- North-central plains lie to the south of the north-west Highlands. This region extends from the Ural mountains in the east to the Atlantic Ocean and the Bay of Biscay in the west.
- The southern part of the British Isles, the northern part of France, Netherlands, Belgium, Poland, the northern part of Germany, the western part of Russia – almost more than half of Europe falls under this physical region.
Characteristics:
- This extensive plainland has an average elevation of 180 metres.
- The main rivers of Europe, like the Rhine, Volga, Don, and Dnieper all flow through this plain land.
- The erosional activities of glaciers or the subsidence of land has caused the formation of several large lakes. For instance, Ladoga (area of 17,700 sq. km) and Onega (9,700 sq. km) in Russia. Among these, Ladoga is the largest lake in Europe.
- A large part of the Netherlands which takes up the north-west part of this plain has been reclaimed from the sea.
3. Central plateaus:
Location:
South of the north-central plains lies the dissected plateau of the Central Uplands. Spain, Germany and France fall under this physical region.
Characteristics:
- Geologically, this plateau is quite ancient. Erosional activities on fold mountains which were formed about many years ago have resulted in the formation of this plateau.
- The erosional activities of rivers have made this entire region a collection of small, separated plateaus. For example-Meseta of Spain, The Central Massif of France and the Don Massif of Russia.
4. Southern mountain region:
Location:
Almost all of southern Europe is part of the southern mountain region. From Spain in the west to France, Switzerland, Germany, Italy, Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania are all part of this physical zone.
Characteristics:
The Alps Mountain Range is a part of this region. The highest peak in the Alps is the Mont Blanc (4,810 m). It is situated in the border of France and Switzerland and is the second-highest peak in Europe.
Some mountain ranges have radiated from the Alps such as the Pyrenees, Cantabrian and the Caucasus ranges. The highest peak in Europe in Elburz (5642 m).
Question 4. Name the mountain ranges that are extended from the Alpine arc.
Answer:
Names of mountain ranges extending from the Alpine arc:
The Alps Mountain Range is located at the heart of the southern mountainous region. Different ranges are extended from the Alpine arc. These are as follows-
1. Towards west:
Mountain ranges that are extended towards the west are-
- Pyrenees (border of France and Spain),
- Cantabrian (in the north of France),
- Sierra Nevada (in the south of Spain).
2. Towards south:
Mountain ranges that are extended towards the south from the Alpine arc are-
- Apennine (Italy),
- Dinaric Alps (Serbia, Albania),
- Pindus (Greece),
- Rodhope
3. Towards north:
Mountain ranges that (Bulgaria, Turkey), etc. extended towards the north are-
- Bohemian and Jura Mountain (France),
- Massif and Sudetes Mountains (Czechoslovakia).
4. Towards east:
Mountain ranges that are extended towards the east are-
- Caucasus (in between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea),
- Carpathian Mountain (Czech Republic, Slovakia),
- Balkan Mountain (Bulgaria).
Question 5. Describe the different climatic regions of the continent of Europe.
Answer:
Different climatic regions of the continent of Europe:
The continent of Europe can be divided into different climatic regions on the basis of regional variations of temperature and rainfall. These are as follows-
1. Tundra climate:
Location:
The northern part of Europe including Norway, Sweden, Finland and northern Russia experience the Tundra climate.
Temperature:
Summer temperature ranges between 0°C-10°C and in winter temperature ranges between -35°C to -45°C.
Rainfall:
Annual average precipitation is about 25 cm.
Characteristics:
This region is severely cold throughout the year.
- The duration of summer is very short.
- The temperature remains below freezing point and thus snowfall occurs.
- Land remains covered in ice for 9 to 10 months in a year.
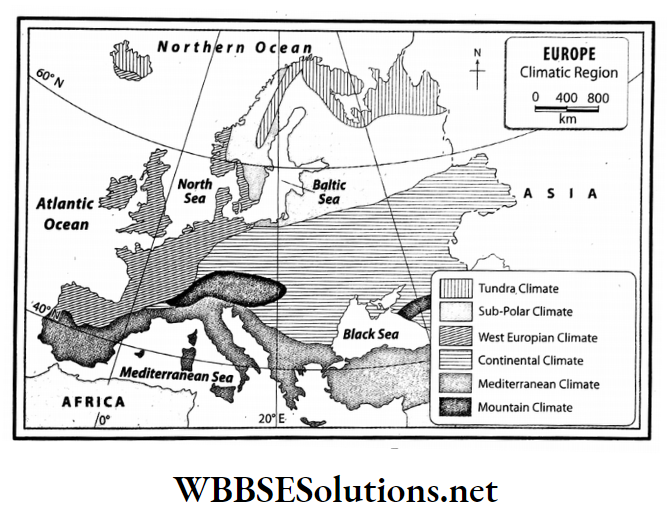
2. Sub-polar climate:
Location: Some parts of Sweden, Finland, Norway and Russia.
Temperature: Average summer temperature is 10°C and average winter temperature ranges between -25°C to -35°C.
Rainfall: This climatic zone experiences low rainfall in summer and snowfall in winter.
Characteristics:
- The duration of the summer season is 4-5 months.
- The temperature of winter months remains below freezing point and heavy snowfall occurs.
- The ground remains snow-covered for 6-8 months.
- Low rainfall in summer and huge snowfall in winter are the main features of this climate.
3. West European climate:
Location:
Some parts of the north-west Europe-United Kingdom, western France, western Germany, Holland, Denmark, Belgium and in some parts of Norway.
Temperature:
The summer temperature lies between 15°C-20°C and the winter temperature is 5°C.
Rainfall:
The annual average rainfall is 100- 150cm.
Characteristics:
- The temperature in summer and winter are moderate.
- Rainfall mostly occurs in winter due to westerlies.
- Snowfall occurs in the northwestern part of the continent during winter.
4. Mediterranean climate:
Location: Mediterranean coast including Italy, Spain, France, Greece, etc.
Temperature: Summer temperature ranges between 21°C-27°C and winter temperature ranges between 5°C-10°C.
Rainfall: Annual average rainfall is 40- 75 cm.
Characteristics:
- The main climatic feature of this region is dry summer and wet winter.
- Rainfall occurs in winter due to westerlies.
5. Continental climate:
Location: Central and Eastern Europe mainly Russia and Ukraine.
Temperature: Summer temperature ranges between 20°C-22°C and in winter temperature drops below freezing point.
Rainfall: Annual average rainfall is 25- 50 cm.
Characteristics:
- Hot summer and cold winter is the main feature of this climate.
- Rainfall mainly occurs in summer.
6. Mountain Climate:
Location: Alps, Caucasus, Carpathian mountainous region.
Temperature: Temperature remains below freezing point throughout the year.
Rainfall: Snowfall occurs throughout the year.
Characteristics:
- The weather remains cold throughout the year.
- In winter snowfall occurs.
Conceptual Questions on Europe’s Cultural Diversity
Question 6. Discuss the different categories of natural vegetation of Europe.
Answer:
The different categories of the natural vegetation of Europe:
The different categories of the natural vegetation of Europe are as follows-
1. Tundra forest:
Location: Northern part of Europe including Norway, Sweden, Finland and northern Russia experience the Tundra climate.
Species of trees: Moss, lichen, birch, willow, juniper, etc.
Climatic features:
- This region faces severe cold weather throughout the year.
- The duration of the summer season is very short.
- The temperature remains below freezing point and thus snowfall occurs.
- Land remains covered in ice for 9 to 10 months in a year.
Features of natural vegetation:
- Moss and lichen grow on the snow-covered ground.
- Once the snow melts trees like willow, birch and juniper grow. These are called Tundra shrubs.
2. Coniferous forest:
Location: Some parts of Sweden, Finland, Norway and Russia.
Species of trees: Pine, larch, fir, spruce, birch, alder, etc.
Climatic features:
- Duration of summer. the season is 4-5 months.
- The temperature of winter months remains below freezing point and heavy snowfall occurs during the season.
- The ground remains snow-covered for 6-8 months.
- Low rainfall in summer and huge snowfall in winter are the main features of this climate.
Features of natural vegetation:
- Trees are cone-shaped.
- Leaves are narrow and needle-shaped.
- The trees are softwood trees.
3. Temperate deciduous forest:
Location: Some parts of north-west Europe including the United Kingdom, western France, western Germany, Holland, Denmark, Belgium and in some parts of Norway.
Species of trees: Oak, elm, maple, alder, etc.
Climatic features:
- The temperature in summer and winter is moderate.
- Rainfall mostly occurs in winter under the influence of westerlies.
- Snowfall occurs in the northwestern part of the continent during winter.
Features of natural vegetation:
- Trees start shedding their leaves in autumn.
- These trees have lots of branches, leaves are large in size and the trees are hardwood trees.
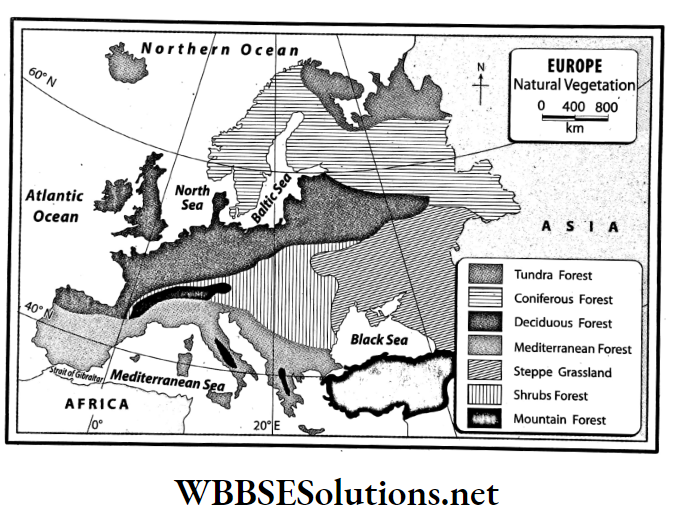
4. Mediterranean forest:
Location: Mediterranean coast including Italy, Spain, France, Greece, etc.
Species of trees: Olive, oak, cork, walnut, cedar, pine, fir, grapes, laurel, orange, etc.
Climatic feature:
- The main climatic feature of this region is dry summer and wet winter.
- Rainfall occurs in winter due to westerlies.
Features of natural vegetation:
- These trees are evergreen.
- They have long roots and thick leaves and bark.
- The leaves have a waxy coating in order to prevent water loss during evapotranspiration.
5. Steppe grasslands:
Location: Central and Eastern Europe, mainly Russia and Ukraine.
Species of trees: Willow, elm, maple, thorny bushes, shrubs, grasses.
Climatic features:
- Hot summer and cold winter is the main feature of this region
- Rainfall mainly occurs in summer.
Features of natural vegetation:
In these regions, some large trees such as willow grow along with shrubs and thorny bushes. These grasses are not very long.
6. Shrubs forest:
Location: Germany, Poland, France, Switzerland.
Species of trees: Oak, maple, poplar, alder, willow, etc.
Climatic features:
- A cold climate prevails all through the year.
- The maximum rainfall occurs in winter and snowfall also occurs.
Feature of natural vegetation:
Deciduous, evergreen and coniferous trees grow together in these forests.
7. Mountain forest:
Location: Alps, Apennine, Pindus, Caucasus, Carpathian mountainous region.
Species of trees: Pine, poplar, alder, etc. Climatic feature: Temperatures remain below freezing point.
Features of natural vegetation:
- Trees are cone-shaped.
- The trees are softwood trees.
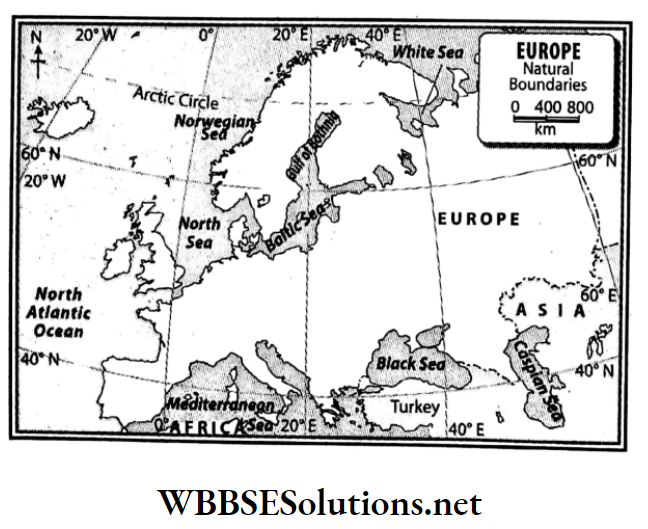
Question 7. Mention the boundaries of the continent of Europe.
Answer:
Boundaries of the continent of Europe:
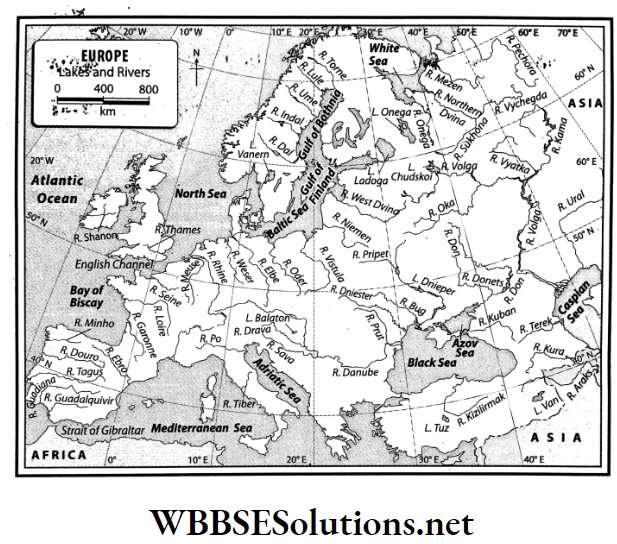
Europe is bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean, the White Sea, the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Baltic Sea; on the south by the Straits of Gibraltar, the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Black Sea, the Ionian Sea, the Aegean Sea and the Tyrrhenian Sea; on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, the Bay of Biscay and the North Sea.
To the east, Europe is bounded by the continent of Asia. Apart from this, a narrow part of the east is bounded by the Caspian Sea.
Question 8. In your opinion, in which direction is the general slope of Europe and why?
Answer:
The middle and southern parts of the continent of Europe are taken up by high mountains and dissected highlands and high plains. So, the land of the continent of Europe slopes in three directions-
- From the middle to the north
- From the middle to the south
- From the middle to the west
Reasons:
We know that rivers usually flow from the higher lands to the lower lands. In Europe, the rivers flow in three directions which are as follows-
1. North-flowing rivers:
These rivers flow to the north from central Europe. The main among these are Seine, Rhine, Elb, Vistula and Oder.
2. West-flowing rivers:
These rivers flow to the west from central Europe. The main among these are Minho, Douro, Tagus and Guadiana.
3. South-flowing rivers:
These rivers flow to the south from central Europe, for example-Po, Danube, Dnieper, etc.
Question 9. Give a description of the north-western highlands or the western uplands.
Answer:
North-western highlands or the western uplands:
In the north-west part of Europe lies the mountainous region of the Scandinavian peninsula (Norway and Sweden are part of this peninsula), the mountainous region of Finland, the northern and central parts of the British Isles and the hilly regions of northern Ireland are all parts of this physical region.
Characteristics:
- This is a dissected plateau, separated by deep valleys and fjords.
- This is made up of old volcanic and metamorphic rocks.
- Several fjords and lakes can be observed in the coastlines of Finland, Norway and Sweden. That is why Finland is known as the country of lakes.
Question 10. Give a description of the northern and central plains.
Answer:
Northern and central plains:
To the south of the north-western highlands, lie the north-central plains that extend from the Ural Mountains in the east to the Atlantic Ocean and the Bay of Biscay in the west.
The southern part of the British Isles, the northern part of France, Netherlands, Belgium, Poland, the northern part of Germany, the western part of Russia – almost more than half of Europe falls under this physical region.
Characteristics:
- This extensive plainland has an average elevation of 180 metres.
- The main rivers of Europe such as the Rhine, Volga, Don, and Dnieper all flow through this region.
- The erosional activities of glaciers or the subsidence of land has formed several large lakes, such as Ladoga (17,700 sq. km) and Onega (9,700 sq. km) in Russia. Ladoga is the largest lake in Europe.
- A large part of the Netherlands i.e. the north-west part of this region has been reclaimed from the sea. This land. is known as polderland.
Question 11. What do you know about the central uplands of Europe?
Answer:
Central uplands of Europe:
In the south of the north-central plains lies the dissected plateau of the central uplands. Spain, Germany and France fall under this physical region.
Characteristics:
- Geologically, this plateau is quite ancient. Erosional activities on fold mountains which were formed about many years ago have resulted in the formation of this plateau.
- The erosional activities of rivers have made this entire region a collection of small, separated plateaus.
For example-
- Meseta of Spain,
- The central Massif of France and
- Don Massif of Russia, etc.
Real-Life Scenarios Involving European Rivers and Mountains
Question 12. Write about the southern mountainous region of Europe.
Answer:
Southern mountainous region of Europe:
Almost all of southern Europe is part of the southern mountain region. From Spain in the west to France, Switzerland, Germany, Italy, Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania are all part of this physical zone.
The Alps Mountain Range is a part of this region. The highest peak in the Alps is the Mont Blanc (4,807 m). It is situated in the border of France and Switzerland and is the second-highest peak in Europe.
The highest peak in the Caucasus range is Mt. Elburz (5642m). It is the highest peak in Europe. Some mountain ranges have radiated from the Alps which are-
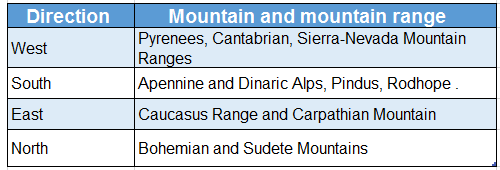
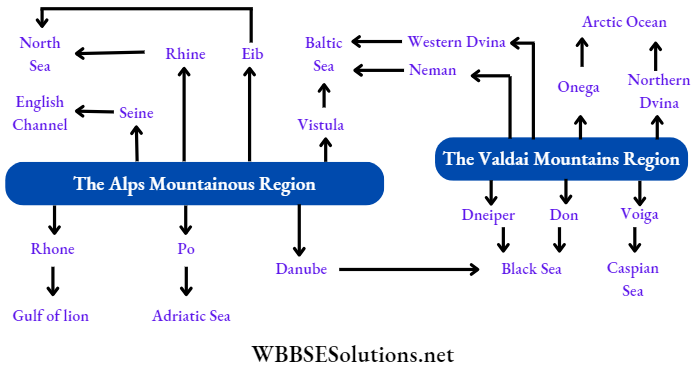
Question 13. Classify the rivers of Europe.
Answer:
Rivers of Europe:
Most of the rivers of Europe originate in the Central Uplands and then flow in various directions. On the basis of the direction in which they flow, the rivers of Europe can be classified into four types. These are-
- North-flowing: Elb, Vistula, Pechora, North Dvina, Onega, etc
- West-flowing: Seine, Rhine, Loire, West Dvina, Neman
- South-flowing: Danube, Dnieper, Don, Po, Rhone
- Inland: Volga, Ural
Question 14. What are the special features of European rivers?
Answer:
The special features of the rivers of Europe are as follows-
- Most European rivers are snow-fed and so, they are perennial.
- Most rivers have originated from the Central Uplands and the southern mountainous region.
- Most of these rivers are fast-flowing.
- These rivers help to generate hydel power.
- Most of the rivers are navigable.
- Most of the rivers are not very long.
- The north-flowing rivers in Europe remain covered in ice for about 3-4 months of the year and when the snow or ice melts in spring and autumn, the rivers often flood their banks.
Question 15. Describe the temperature range in Europe.
Answer:
The temperature range in Europe:
In summer, the south-eastern parts of the continent experience average temperatures of about 27°C and the north experiences temperatures of about 14°C.
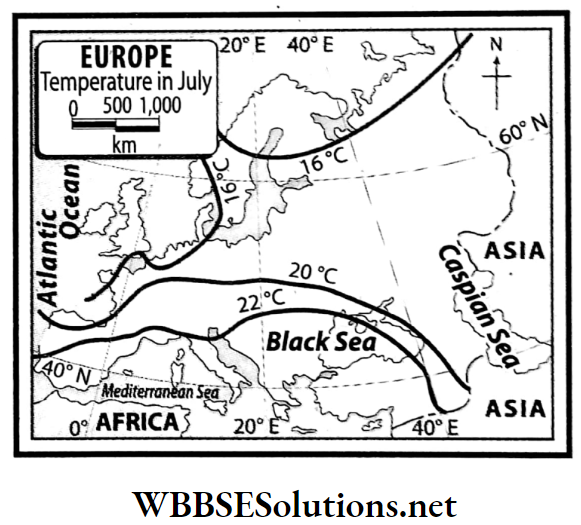
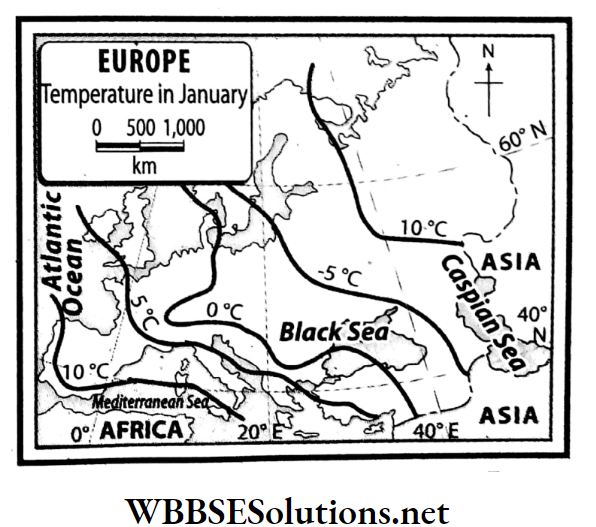
- Again, in winter, warm currents cause the temperatures to drop moderately in the western parts to some extent but the temperatures drop significantly in the eastern and central parts of the continent.
- In the northeast stretches of the continent, around this time, the temperature stays below the freezing point (-14°C).
Examples of Real-Life Applications of European Geography
Question 16 Write what you know about the variations of rainfall patterns in Europe.
Answer:
In summer, apart from some areas in southern Europe, moisture-laden westerly winds cause rainfall. Again, in winter, westerly winds bring rainfall to the entire continent.
- However, the average annual rainfall is higher in the west and southern coastal areas than in the inland areas of the continent. The average annual rainfall in the coast of Finland is above 200 cm.
- Southern and central Europe experience about 50-100 cm average rainfall and in the western areas, average rainfall is in the range of 25-50 cm.
However, the Alps, the Pennines and other mountainous regions receive about 100-200 cm of rainfall annually.
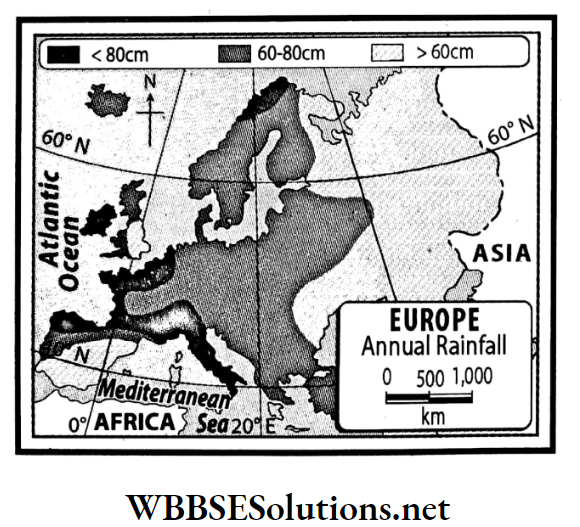
Question 17. Name the natural vegetation zones in Europe.
Answer:
The natural vegetation zones in Europe:
- The natural vegetation of any region is determined by the climate of that region.
- The temperature of the air, amount of rainfall, and moisture content of the air are all factors of climate that influence the nature and form of the natural vegetation of that region.
- Based on the climate, the continent of Europe can be divided into seven natural vegetation zones.
These are-
Tundra forest,
- Coniferous forest,
- Deciduous forest,
- Mediterranean forest,
- Woodlands,
- Mountain forest,
- Steppe grassland.
Question 19. Write about the special characteristics of the vegetation of the Coniferous forests.
Answer:
The special characteristics of the vegetation of Coniferous forests are as follows-
- The trees are usually conical in shape and have downward-drooping limbs to help them shed snow.
- Trees are tall and without many branches, and leaves are needle-shaped.
- Trunks are of softwood.
Question 18. Can you find any similarities between these two maps?
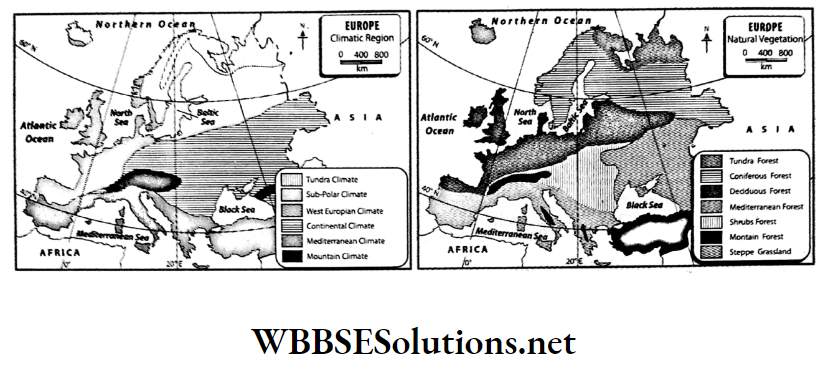
Answer:
The characteristics of the natural vegetation of any region depend on the temperature and rainfall of that region. So there are many similarities between the maps of climate and the natural vegetation of a region. These are-
WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Explain why dissected plateaus have developed in central Europe.
Answer:
- Millions of years ago, fold mountains were formed in central Europe. With the passage of time, as processes of erosion acted on them, the fold mountains became reduced to a plateau. In France and Germany, this is known as the Hersenean plateau.
- Earlier, this existed at a stretch from the plateau region of Spain and France to the Caucasian and Anatolian highlands. This plateau was then reduced when various factors acted on it.
- Several faults were also formed-this finally resulting in a dissected plateau.
Question 2. Mention the names of three major rivers in Europe and their source and mouth.
Answer:
The three major rivers along with their sources and mouths are tabulated below.
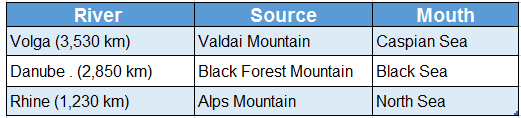
Question 3. Describe the course of the river Danube.
Answer:
The course of the river Danube:
- The Danube is the second longest river of Europe with a length of about 2,850 kilometres. The source of the Danube is in the Black Forest region of the German Alps.
- The river then flows through Germany, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Serbia, Romania and Bulgaria before discharging into the Black Sea. This river is an important international waterway and the primary international river of Europe.
- Sava, and Drava are its main tributaries. Many important cities and towns have developed and flourished on its banks like Vienna in Austria, Budapest in Hungary and Belgrade in Serbia.
Question 4. Write about the course of the river Volga.
Answer:
The course of the river Volga:
- The Volga is the longest river of Europe with a length of about 3,530 kilometres. The source of the Volga is in the Valdai Mountains to the northeast of Moscow in Russia.
- After this, the river flows through the eastern part of Russia and then discharges into the Caspian Sea. Two important tributaries of the Volga are the Oca and Kama.
Question 5. Why are the north-flowing rivers of Europe are flood-prone?
Answer:
- The rivers of Pechora, Megen, Onega, West Dvina, North Dvina and other north-flowing rivers flow from the low latitudes to the high latitudes.
- This means that as the rivers flow from a hotter to a less hot region and during the spring the ice of the source region starts melting, but the mouth region is still frozen. This is why the north-flowing rivers of Europe are flood-prone.
Question 6. What are the special characteristics of the climate of Europe?
Answer:
The special characteristics of the climate of Europe:
Broadly speaking, the climate of the whole of Europe is mainly of temperate type. This type of climate is usually pleasant and moderate. During any time of the year, some parts or other parts of the continent experience rainfall.
The reason for this is:
- About 90% of Europe falls in the temperate zone and 10% falls in the frigid zone.
- No part of this continent is too far from the seas or oceans.
- The hot North Atlantic current flows along the western coastline of the continent throughout the year.
- Though the northeast trade winds blow over some parts of southern Europe in the summer, the westerlies blow over most areas of Europe throughout the year.
- The Alps Mountainous Region also influences the climate of the continent.
Question 7. What are the wind patterns that are observed over Europe?
Answer:
- Mostly, planetary winds blow over the continent of Europe. In the northern hemisphere, in summer the pressure belts move a little to the north and so, the dry north-east trade winds blow over southern Europe and the rest of the continent experiences moisture-laden westerlies.
- In winter, the pressure belts shift south. Because of this, westerly winds blow over the whole of Europe. However, at that time, eastern-central Europe experienced severe cold and so a high-pressure zone developed over this region.
- As a result, the interiors of the continent do not experience much wind or breeze.
Question 8. Write a note on why Europe is supposed to be the industrially most developed in the world.
Answer:
- Favourable environmental and economic factors are the major cause of the industrial development of Europe.
- Several industries such as the iron and steel industry, engineering industries (motor vehicle manufacturing, aircraft construction and such others), chemical, paper, woollen textile, aluminium, electronics and others have grown in this region.
- The most developed industrial region of Europe is Ruhr in Germany, the Donetz Basin of Ukraine, Moscow in Russia, the Paris Basin of France and the London Basin of the British Isles. This is why Europe is thought to be the industrially most developed in the world.
Question 9. Which climatic regions of Europe, do you think, are expected to be the most and least populous?
Answer:
- In Europe, the countries with the highest population density are the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, the British Isles, Italy and so on. These countries fall in the temperate and Mediterranean climatic zones.
- Again, areas with low population density such as Sweden, Norway, and northern parts of Russia are part of the Tundra climatic zone and have the tundra and alpine forest zones.
Question 10. State the area of Europe.
Answer:
Area of Europe:
- In terms of area, Europe is the sixth-largest continent in the world. Its area is only 10.9 million square kilometres. Though it is about three times the area of India, it is just 1/4 of the total land area of the continent of Asia.
- Europe takes up about 6.8 per cent of the total land area of the Earth.
Important Definitions Related to European Geography
Question 11. What is meant by Eurasia?
Answer:
Eurasia:
- Since there is no geographical boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia, (apart from the Ural highlands, Ural river and the Caspian Sea), these two continents together form a gigantic, continuous landmass.
- This landmass is known as Eurasia. In Eurasia, climate, soil, flora fauna etc. are all similar.
Question 12. What is the location of the continent of Europe with respect to both latitudes and longitudes?
Answer:
The continent of Europe extends from the 35° N latitude (Cape Tarifa in Spain) to 71° N latitude (North Cape in Norway) and from 65° East longitude (Ural highlands) to 24° West longitude (westernmost point in Iceland).
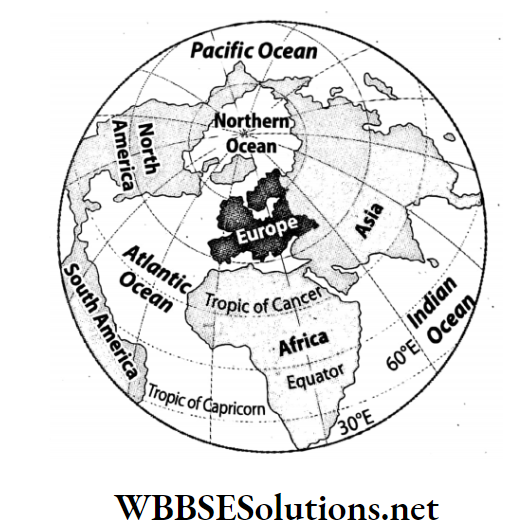
Question 13 Name the main bays and the main peninsulas which are situated at the boundaries of Europe.
Answer:
The main bays which lie on the boundaries of the continent of Europe are the Gulf of Lyon, the Gulf of Finland, the Bay of Riga, Genoa Bay, the Bay of Biscay, and the Gulf of Bothnia.
The main peninsulas are-
- Balkan Peninsula,
- Crimean Peninsula,
- Italian Peninsula,
- Scandinavian Peninsula.
Question 14. Mention the major cities of Europe.
Answer:
The major cities of the continent of Europe are-
- London,
- Paris,
- Amsterdam,
- Rome,
- Berlin,
- Moscow,
- Madrid,
- Vienna etc.
Question 15. What are the physical divisions of Europe?
Answer:
Physical divisions of Europe:
The topography of the continent of Europe is very diversified. Based on the variety of landforms, Europe can be divided into the following 4 physical divisions:
- North-western highlands or Western the south are mostly in Italy such as Etna on the Uplands
- Northern and Central plains
- Central plateaus
- Southern mountain region
Question 16. What is meant by the ‘Lighthouse of the Mediterranean?
Answer:
Lighthouse of the Mediterranean:
- The Stromboli volcano is situated on the island of Lipari in the Mediterranean Sea. This is an active volcano with continuous minor eruptions. Due to these small but regular eruptions, Stromboli is visible from a large area around it.
- Luminous phosphorus gas is also released along with this eruption. So it seems as if the mouth of the volcano is always glowing. Thus, Stromboli has come to be known as the ‘Lighthouse of the Mediterranean’.
Question 17. Write a short note on the volcanoes of Europe.
Answer:
Volcanoes of Europe:
- There are some volcanoes in the western and southern parts of Europe. In the west, there are Krafla and Hekla in Iceland. The volcanoes in island of Sicily, Stromboli on the island of Lipari, Vesuvius in eastern Italy and so on.
- Stromboli is an active volcano with minor eruptions that happen almost hourly. These small but regular eruptions throw out glowing lava and make Stromboli visible from a large area around. Stromboli is known as the ‘Lighthouse of the Mediterranean’.
Question 18. Write the names of the main rivers flowing through Europe.
Answer:
Among the rivers flowing through Europe, the following are significant-
- Volga,
- Danube,
- Don,
- Rhine,
- Rhone,
- Po,
- Seine,
- Thames,
- Dnieper,
- Dniester,
- The Vistula,
- Dvina,
- Pechora,
- Elb etc. Volga (3692 km) is the longest river in Europe.
Question 19. Write the names of the riverine plains of Europe.
Answer:
In the southern part of Europe, riverine plains lie between the ridges and peaks of the fold mountain region.
Erosional and depositional activities of the rivers flowing through this region over millions of years have resulted in the formation of these plains. Some examples are-
- Rhone Plain in France.
- Po River Basin in Italy.
- Hungarian Plain.
- Danube plains in Romania and Bulgaria and so on.
Question 20. Write a short note on the river Rhine.
Answer:
River Rhine:
- The main river of the Ruhr industrial region in Germany is the river Rhine. Its entire length is 1,233 km. After originating in the Alps Mountains, it flows through Switzerland.
- Then it flows through the rift valley between the Black Forest Mountains in Germany and the Vosges Mountains in France. After that, it enters the Netherlands and then finally discharges into the North Sea.
- The main tributaries of the river Rhine are the Lippe, Aare, Neckar, and Main.
Question 21. What do you mean by an ‘International river’?
Answer:
‘International river’:
- A river that flows through more than one country along its course from source to mouth is known as an International river.
- For instance, the Danube in Europe, the Nile in Africa, and the Indus and the Brahmaputra in India are all examples of International rivers. The Danube in Europe flows through ten sovereign countries.
- These rivers have great significance as international waterways.
Question 22. How many climatic regions can we divide Europe into? What are they?
On the basis of differences in temperature and rainfall patterns, Europe can be divided into a few climatic zones.
These are-
- Tundra climate,
- Sub-polar climate,
- West European climate,
- Continental climate,
- Mediterranean climate,
- Mountain climate.
Question 23. What is Steppe grasslands?
Answer:
Steppe grasslands:
The temperate grasslands found in the continental climate in the central and eastern parts of Europe are called Steppe grasslands.
Location:
The western part of Russia and the coastal region of the Black Sea in Ukraine.
Characteristics:
The annual average rainfall is low. So, the grasslands have been created here. Along the banks of the rivers willow, elm, maple etc trees are found
WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Which is the sixth-largest continent in the world?
Answer: Europe.
Question 2. How many nations are there in Europe?
Answer: 56.
Question 3. In terms of population, where does Europe rank?
Answer: Third.
Question 4. What is the northernmost boundary of the continent of Europe?
Answer: North Cape in Norway.
Question 5. What is the southernmost boundary of the continent of Europe?
Answer: Cape Tarifa in Spain.
Question 6. What is the westernmost boundary of the mainland of Europe?
Answer: Cape Roca in Portugal.
Question 7. Which strait separates Europe from Africa?
Answer: Gibraltar.
Question 8. Which country is called the ‘land of the midnight sun’?
Answer: Norway.
Question 9. Which country in Europe is known as the ‘Country of Thousand Lakes’?
Answer: Finland.
Question 10. What do you call a place where many mountain ranges converge?
Answer: Mountain Arc.
Question 11. Which is the highest peak in the Alps?
Answer: Mont Blanc.
Question 12. What do we mean by the “Lighthouse of the Mediterranean”?
Answer: Stromboli Volcano.
Question 13. Which is the highest peak in Europe?
Answer: Elburz in the Caucasus Mountains.
Question 14. Mention two block mountains of Europe.
Answer: Vosges Mountain and Black Forest Mountain.
Question 15. Which is the longest river in Europe?
Answer: Volga.
Question 16. Which is the most important international river in the world?
Answer: Danube.
Question 17. What is the name of the largest lake in Europe?
Answer: Ladoga.
Question 18. What kind of climate does Europe have?
Answer: Temperate.
Question 19. In which parts of Europe is the coniferous forest found?
Answer:
In the middle of the 50°-70° north latitude of the continent of Europe, coniferous forests are found in parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland and some parts of Russia. The coniferous forest in Europe is known as Taiga.
Question 20. In Europe, which climatic zones are densely populated and which climatic zones are sparsely populated?
Answer:
In Europe, regions which experience the temperate marine climate and those which fall under the Mediterranean climatic zone are densely populated. Regions which are categorised as experiencing the Tundra climatic type are sparsely populated.
Question 21. Where is the Strait of Gibraltar located?
Answer:
The narrow strip of water (about 13 km wide and 300 metres deep) that connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean is known as the Strait of Gibraltar. This strait also acts as a geographic divide between Spain in Europe and Morocco in Africa.
WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The continent of Europe is in the _________ hemisphere.
Answer: Northern
Question 2. The _________ of Europe were formed because of the erosional activities of glaciers in the Ice Age.
Answer: Fjord
Question 3. Europe’s highest peak, _________is part of the _________ range.
Answer: Elburz, Caucasus
Question 4. Two mountain passes in the Alps Mountain range are _________ and _________.
Answer: Brenner, Simplon
Question 5. _________ in France and in Germany are two examples of block mountains.
Answer: Vosges, Black Forest
Question 6. Two mention-worthy peaks in Switzerland are _________ and _________.
Answer: Monte Rosa, Matterhorn
Question 7. The _________ volcano in the Lipari islands is known as the ‘Lighthouse of the Mediterranean.’
Answer: Stromboli
Question 8. The two water divides in Europe are and _________.
Answer: Alps, Valdai
Question 9. _________ is the biggest lake in Europe.
Answer: Ladoga
Question 10. The source of the river Rhone is in the _________ region.
Answer: Alps Mountain
Question 11. Europe’s longest river, the _________, has its origin in the Mountain.
Answer: Volga, Valdai
Question 12. Aine is a tributary of river _________.
Answer: Rhone
Question 13. The longest river of France is _________.
Answer: Seine
Question 14. Paris is situated on the banks of the river _________.
Answer: Seine
Question 15. The climate of Europe is primarily of the _________ type.
Answer: Temperate
Question 16. Mostly _________ forests grow in Europe.
Answer: Coniferous
Question 17. The name of the world’s largest coniferous forest is _________.
Answer: Taiga
WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe True Or False
Question 1. The longest river of Europe is river Volga.
Answer: True
Question 2. Moscow is called the ‘Port of Five Seas’.
Answer: True
Question 3. Poland is called the ‘City of Thousand Lakes’.
Answer: False
Question 4. The famous volcano in the island of Sicily is Stromboli.
Answer: False
Question 5. The highest peak in the Alps is Mt. Elburz.
Answer: False
Question 6. The Pyrenees is at the boundary of Spain and France.
Answer: True
Question 7. The largest lake in Europe is Onega.
Answer: False
Question 8. The highest peak in Europe is Mont Blanc.
Answer: False
Question 9. The river Rhine flows through the rift valley between the Vosges Mountains in France and Black Forest Mountains in Germany.
Answer: True
Question 10. The longest river in Europe is the Danube.
Answer: False
Question 11. The most important international river in Europe is the Volga.
Answer: False
Question 12. The boundary between Europe and Asia is delineated by the Ural Mountains.
Answer: True
Question 13. Meseta is a famous plateau of Spain.
Answer: True
Question 14. The Seine River discharges into the English Channel.
Answer: True
Question 15. Moscow is a large city in the northernmost part of the world.
Answer: True
Question 16. In places with a Mediterranean climate, convectional rainfall occurs every evening.
Answer: False
WBBSE Chapter 11 Continent Of Europe Topic A General Introduction Of The Continent Of Europe Match The Columns
Question 1.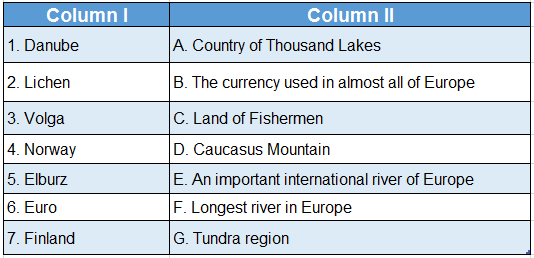
Answer: 1. E, 2. G, 3. F, 4. C, 5. D, 6. B, 7. A
