Chapter 12 Waste Products Review Questions Environment Review Questions MCQs
Question 1. The following waste is not from households.
- Plastic
- Glass
- Methane
- Paper
Answer: 3. Methane
Question 2. The following waste is not biodegradable in nature.
- Paper
- Plastic
- Vegetable Waste
- Animal hide
Answer: 2. Plastic
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 School Science
Question 3. The E-waste from a television set contains
- Lead
- Mercury
- Cadmium
- All of them
Answer: 4. All of them
Question 4. Leather industry waste includes
- Cadmium
- Nickel
- Chromium
- Cobalt
Answer: 3. Chromium
Question 5. Building waste may contain
- Sand
- Cement
- Both
- Plastic
Answer: 3. Both
Question 6. Solid waste includes
- Metal
- Glass
- Paper
- All Of Them
Answer: 4. All Of Them
WBBSE Class 6 Waste Products MCQs
Question 7. The bio-plastic is so-called because
- It Is Produced By Biological Organism
- It Is Biodegradable
- Both
- None
Answer: 3. Both

Question 8. Organic solvent includes
- Water
- Benzene
- Both
- None
Answer: 2. Benzene
Question 9. Pulper is the other name of
- Glass grinder
- Stone grinder
- Paper grinder
- Stone crusher
Answer: 3. Paper grinder
Question 10. Cullet is the other name for small pieces of
- Glass
- Metal
- Pebbles
- Cardboard
Answer: 1. Glass
Question 11. An ingot is the other name for molten
- Iron
- Cadmium
- Aluminium
- Calcium
Answer: 3. Aluminium
Common MCQs on Waste Disposal Methods
Question 12. The common ingredients of cement is
- Chromium
- Calcium
- Iron
- Aluminium
Answer: 2. Calcium
Question 13. Recycling of metals involves
- Collection
- Melting
- Rolling
- All Of Them
Answer: 4. All Of Them
Question 14. The approximate time required for recycling aluminium is
- 15 days
- 30 days
- 45 days
- 60 days
Answer: 4. 60 days
Question 15. Recycling plastic makes it
- Black
- Blue
- Both
- White
Answer: 3. Both
Question 16. If one refuses a plastic carry bag from the shop, indicate which of the 4R system does it belong to?
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Recycle
- Refuse
Answer: 4. Refuse
Question 17. DDT is released into nature from
- Households
- Factories
- Agricultural fields
- Ponds
Answer: 3. Agricultural fields
Question 18. Which one is not possible to be recycled?
- Iron
- Aluminium
- Computer
- Rotten vegetables
Answer: 4. Rotten vegetables
Chapter 12 Waste Products Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Biodegradable waste is degraded by __________ and __________.
Answer: Bacteria, Fungi
Question 2. The commercial cans are made of __________.
Answer: Aluminium
Question 3. Cement mostly includes salts of __________.
Answer: Calcium
Question 4. Loss of resources can be prevented by __________.
Answer: Recycling
Question 5. Pulping is carried out for recycling of __________.
Answer: Paper
Question 6. Solid waste may be used in __________.
Answer: Landfill
Question 7. Recycling of metal involves a cycle of __________.
Answer: 60 days
Question 8. Rolling of metal will make them into __________.
Answer: Sheet
Question 9. Benzene is an __________ waste.
Answer: Organic
Question 10. Metals are drawn into a sheet by __________.
Answer: Rolling
Question 11. The paper grinding machine is also called __________.
Answer: Vat or pulper
Question 12. Television sets may release high amounts of __________ metals.
Answer: Heavy
Question 13. Long organic plant materials are also called __________.
Answer: Fibres
Question 14. Biodegradable plastics are degraded by __________ enzymes.
Answer: Bacterial
Question 15. Liquid aluminium is also called __________.
Answer: Ingots
Chapter 12 Waste Products Identify As True Or False
Question 1. WEEE is organic waste.
Answer: False
Question 2. Methane is a greenhouse gas.
Answer: True
Question 3. Metals are recycled after rolling.
Answer: True
Question 4. Bio-plastics are generated by fungi.
Answer: False
Question 5. Paper is biodegradable waste.
Answer: True
Question 6. Pulper is used for plastic recycling.
Answer: False
Question 7. Virgin plastic is white in colour.
Answer: True
Question 8. Municipal waste is mostly mixed in nature.
Answer: True
Question 9. Plastic pollution can kill soil-borne microbes.
Answer: True
Question 10. Liquid iron is called an ingot.
Answer: False
Question 11. Calcium is used in the making of cement.
Answer: True
Question 12. Recycling results in the loss of resources.
Answer: False
Question 13. DVD players may have heavy metals.
Answer: False
Question 14. Benzene is an organic solvent.
Answer: True
Question 15. Building material waste is organic in nature.
Answer: False
Chapter 12 Waste Products Match The Columns
Question 1.
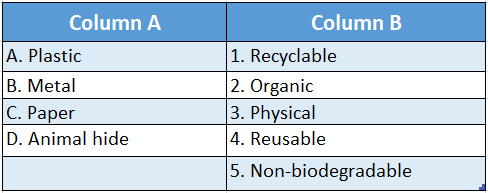
Answer: A-5, B-4, C-1,D-2
Question 2.
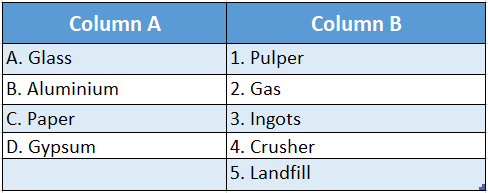
Answer: A-4, B-3, C-1, D-5
Chapter 12 Waste Products Answer In Words Or A Sentence
Question 1. What is the term given to the accumulation of excess waste?
Answer: Pollution.
Question 2. Name two greenhouse gases.
Answer: Carbon dioxide and methane.
Question 3. Name the organism producing bio-plastic.
Answer: Bacteria.
Question 4. Which waste is used in the landfill?
Answer: Solid waste
Question 5. Name two heavy metals.
Answer: Mercury and cadmium.
Question 6. Name the heavy metal released from the tannery.
Answer: Chromium.
Question 7. Name two building wastes.
Answer: Sand and cement chunks.
Question 8. State the duration of the metal recycling cycle.
Answer: 60 days.
Question 9. Name the metal that is mostly recycled globally.
Answer: Aluminium.
Question 10. State the colour of the virgin plastic.
Answer: White.
Question 11. What type of waste is a gunny bag?
Answer: It is a biodegradable waste.
Question 12. Give an example of waste that is generated by the hospitals.
Answer: Used syringes/blood-stained gloves.
Chapter 12 Waste Products Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is pollution?
Answer: Accumulation of waste products in excess in nature is called pollution.
Question 2. What is municipal waste?
Answer: Municipal waste is a mixture of biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste which is generated from households, schools, colleges, offices, marketplaces, restaurants etc.
Question 3. What is meant by automobile end-of-life waste?
Answer: It is the waste product generated from used cars.
After the car has been used to its fullest extent, it is sent to a scrapyard, the recyclable materials are recycled, but the products which are not suitable for recycling are crushed and may be sent to a landfill.
Though in India, the materials are always recycled.
Question 4. What do you mean by the 4R process of waste management?
Answer: The 4R process (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Refuse) is a systematic waste management process that consists of the collection, transportation and proper disposal of garbage, sewage and other waste products including offering various solutions for recycling the items and putting the waste to productive use for sustainability.
Question 5. What is meant by repulping?
Answer: The waste papers are shredded into small pieces, taken in a vat and heated at high temperature to melt the organic compound and they are removed from the pulp.
Question 6. What is meant by drinking?
Answer: The ink glue or any other sticky substance adhering to the paper pulp is removed by thorough washing, as a result of which the pulp is ideal for the manufacturing of recycled paper.
Question 7. What is meant by virgin pulp?
Answer: The virgin pulp in the fresh pulp is made from soft plant material, it is used in the making of fresh paper and also sometimes mixed with the used paper pulp after bleaching to brighten up its colour.
Question 8. What is meant by bio-plastic?
Answer: The biodegradable plastic produced within bacterial cells is called bio-plastic. It is degraded completely in the long run with the help of bacterial enzymes.
Question 9. What is meant by cullet?
Answer: The glass is purified from impurities like plastic, cork etc., and it is then crushed into small pieces with the help of a crusher, to be reused again for the manufacturing of glass.
Small pieces of clear glass are called cullet.
Important Definitions Related to Waste Products
Question 10. How aluminium cans are prepared for recycling?
Answer: The cans are cleared of impurities, the associated iron or steel pieces are removed with the help of a big magnet and thus it is ready for getting melted and rolled.
Question 11. What are the main benefits of resource recycling?
Answer: The resources are saved by recycling, hence it is good for the economy of the country.
The pollution from the waste material is prevented, hence it is good for the environment. Finally, it saves the energy involved in the processing of the waste.
Chapter 12 Waste Products Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How are waste products classified on the basis of the waste generated?
Answer:
On the Basis of the Source
On the basis of source, waste materials can be classified into 7 different types as detailed below:
1. Municipal waste:
This includes trash or garbage from households, schools, offices, marketplaces, restaurants and other public places.
They include everyday items like food debris, used plastic bags, soda & soft drink cans and plastic water bottles, broken furniture, grass clippings, product packaging, broken home appliances and clothing.

2. Medical/Clinical waste:
Medical/clinical waste normally refers to waste produced by healthcare facilities, such as hospitals, clinics, surgical theatres, veterinary hospitals and laboratories.
They tend to be classified as hazardous waste rather than general waste. Items in this group include surgical items, pharmaceuticals, blood, body parts, wound dressing materials, needles and syringes.

3. Agricultural waste:
Typically, this is waste generated by agricultural activities. These vegetable peels, old blades, rotten food items, old electronic items etc.
These include horticulture, fruit growing, seed growing, livestock breeding, markets, gardens and seedling nurseries.
Waste items in this group include empty pesticide containers, old silage wrap, out-of-date medicines and wormers, used tyres, surplus milk, cocoa pods and corn husks.


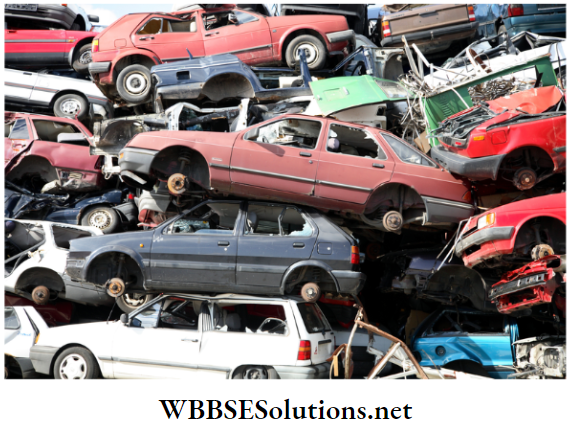
4. End-of-life Automobiles:
When cars stop working, where do they end up? Many people just leave them to rust in the fields, but there is a better way to deal with them.
In many cities, these vehicles are sent to the plant, where all the removable parts are taken out for recycling.
The rest is flattened up and shredded into pieces for recycling. The last bits that cannot be used again are sent to a landfill.

Understanding Waste Management
5. Industrial waste:
Since the Industrial Revolution, the rise in the number of industries manufacturing glass, leather, textile, food, electronics, plastic and metal products has significantly contributed to waste production.
Take a look at the things in your home, every item was manufactured and one day it will be of no use, and waste will be produced as a result.

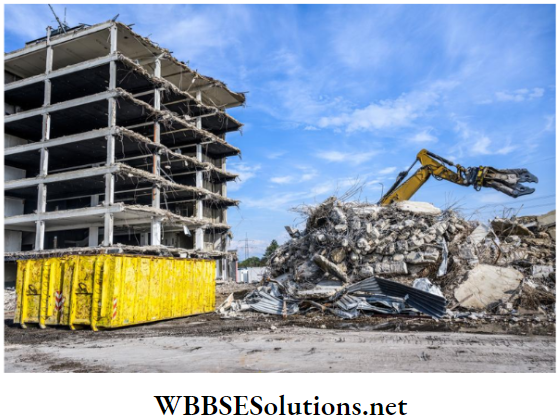
6. Construction/demolition waste:
Construction waste is that resulting from the construction of roads and buildings. Sometimes old buildings and structures are pulled down (demolished) to make space for new ones.
This is particularly common in old cities, that are undergoing modernization. This is called demolition waste.
Waste items include concrete debris, wood, earth, huge package boxes and plastics from the building materials etc.

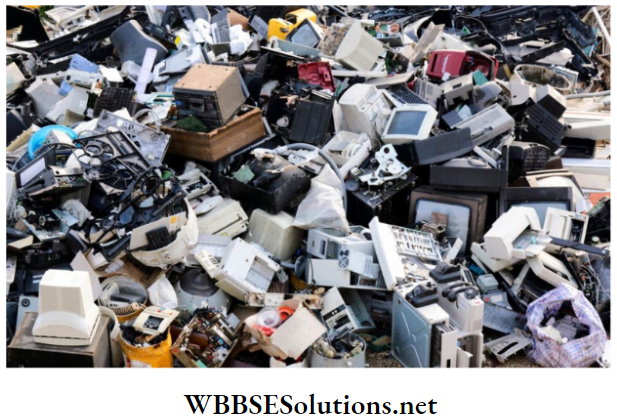
7. Electronic or e-waste:
This is waste from electronic and electrical devices. Think of DVD and music players, TV, telephones, computers, vacuum cleaners and all the other electrical stuff in your home.
These are also called e-waste, e-scrap, or waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Some e-waste (like TV) contains lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants.
These are TIS harmful to humans and the environment. It is therefore important that the right authorities ensure the proper disposal of such waste.

Short Answers on Types of Waste
Question 2. How is waste classified on the basis of physical properties?
Answer:
On the Basis of Physical Nature
On this basis, the waste material can be classified as solid waste, liquid waste and gaseous waste.
1. Solid waste:
Solid wastes include metallic and non-metallic waste including plastic, glass, and paper, which are disposed of in a landfill or maybe incinerated at high temperatures.

2. Liquid waste:
They include water-soluble compounds, or simply organic solvents. If these are added to a water body, it causes water pollution and reduces the oxygen level of the water body.
3. Gaseous wastes:
These are oxides of carbon, sulphur, nitrogen, several toxic hydrocarbons, aerosols, methane and green. house gases like CFC (chlorofluorocarbon). These are largely emitted from factories, chemical plants, vehicles etc.

Question 3. How is waste classified on the basis of degradable properties?
Answer:
On the Basis of Degradational Ability
On this basis, the waste products can be classified as non-biodegradable and biodegradable.
1. Non-biodegradable waste:
This waste product cannot be recycled by the normal microbial degradational process, it includes plastic, heavy metals etc.

2. Biodegradable waste:
These materials. include household products which may be vegetables or cooked food materials that are easily degraded by microbes. It also includes agricultural waste.

Examples of Real-Life Applications in Waste Management
Question 4. What is waste management? State the principles of waste reduction.
Answer:
Waste Management
It is the collection, transport and disposal of garbage, sewage and other waste products.
Waste management encompasses the management of all processes and resources for proper handling of waste materials, maintenance of waste, and transportation by trucks and dumping facilities in compliance with health codes and environmental regulations.
The four principles (4R process) of waste reduction are Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Refuse.

1. Reduce:
Those waste products which increase garbage in our environment should be reduced on day to day basis, for example, plastic bags, thermal, plastic bottles etc.
2. Reuse:
Reusing the waste materials instead of discarding them, for example, vegetable peels, rechargeable batteries, etc.
3. Recycle:
This involves making new useful products from waste products, for example, plastic toys, old iron, glass materials, papers, aluminium, etc.
4. Refuse:
People should learn to refuse to accept such materials which would eventually produce non-biodegradable
Question 5. How is waste paper recycled?
Answer:
Paper waste:
Paper waste items include books, newspapers, magazines, cardboard boxes and envelopes.
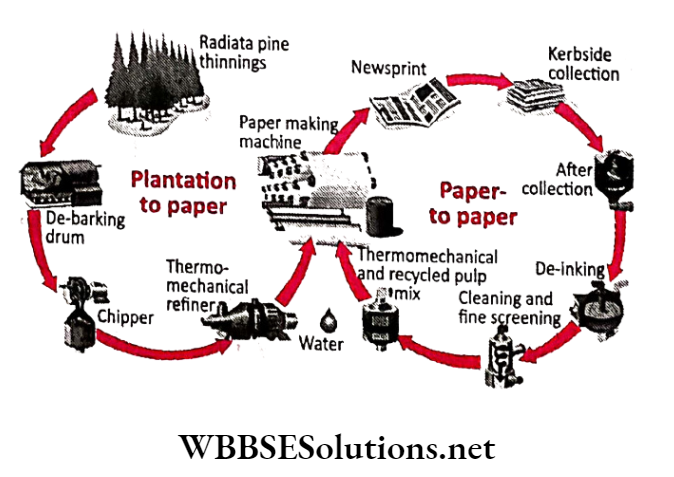
Recycling of Paper Waste:
1. Collection, transportation and storage:
The biggest task for paper recycling companies probably includes the collection, transporting and sorting of waste paper.
This is because we always add paper to other waste items and get them contaminated with food, plastic and metals.
Sometimes collected paper is sent back to the landfills because they are too contaminated to use.
Waste paper should be kept in separate grades at home or in the office, for example, newspapers and corrugated boxes should not be mixed.
All paper recovered is sent to the recycling centre, where it is packed, graded, put into bales and sent to the paper mill. At the mill, all the paper is stored in a warehouse until it is needed.
2. Repulping and Screening:
From the storage shelves, they are moved into a big paper grinding machine called a vat (pulper).
Here the paper is chopped into tiny pieces, mixed with water and chemicals and heated up to break it down into organic plant material called fibre.
After that, it is screened to remove contaminants such as bits of plastic and globes of glue.
3. Deinking:
This involves ‘washing’ the pulp with chemicals to remove printing ink and glue residue. Sometimes, a process called floatation is applied to further remove got stubborn stains and sticky substances.
Floatation involves the use of chemicals not and air to create bubbles, which absorb the art stickies in the pulp.
4. Refining, Bleaching and Colour Stripping:
Refining involves beating the recycled pulp to make them ideal for paper-making.
After refining, additional chemicals are added to the bay to remove any dyes from the paper. It is then bleached to whiten and brighten it up.
5. Papermaking:
At this stage, the pulp is ready to be used for manufacturing paper. Sometimes new pulp (virgin pulp) is added to give it extra strength and smoothness.
Water is added to the pulp and sprayed onto a large metal screen in continuous mode. The water is drained on the screen and the fibres begin to bond with each other.
As it moves through the paper-making machines, press rollers squeeze out more water, heat them dry and coat them up. They are then finished into rolls.
Conceptual Questions on the 3Rs of Waste Management
Question 6. How is the recycling of glass carried out?
Answer:
Glass waste:
All glass products like broken bottles, beer and wine bottles can be recycled.
1. Recycling of Glass:
Recycling glass starts in your home. There is a reason why many 916 local councils provide different containers for green, brown, plain glass and even glass hot from broken windows.
The reason is that they are all made very differently and mixing them can create huge problems at the recycling centre.
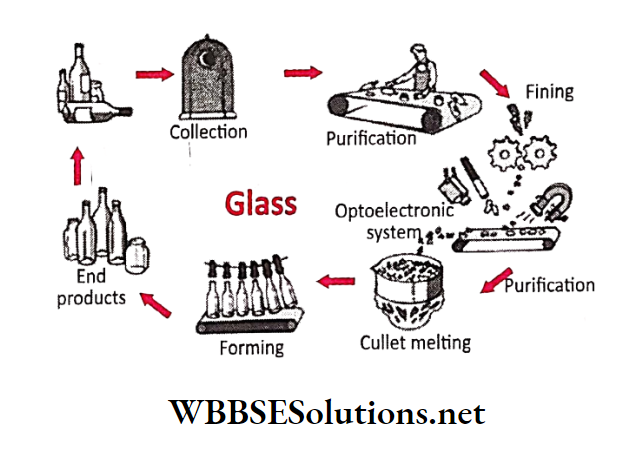
2. Collection:
Many cities have collection spots. Trucks may also pick them up from your home, or you may be required to drop them off at a point in your town.
In all cases, try to do what the authorities have suggested. So, be sure you know the various glass types that are collected from your home.
They are washed and separated into the required grades for collection.
3. Cleaning and Crushing:
The glass is transported to the processing plant, where contaminants such as metal caps and plastic sleeves are removed.
Different grades are treated separately. Clean glass is then crushed into small pieces called cullet. Cullet is in high demand from glass manufacturers.
It melts at a lower temperature and it is cheaper than raw glass materials.
4. Ready for use:
The cullet is then transported to glass-making factories. Here, it is mixed with sand, soda ash and limestone.
It is heated at a very high temperature and melted into liquid glass. This liquid is then poured into moulds that give glass its shape.
Glass is used for many things, depending on what grade they were recycled from. A few items made of recycled glass include fibre-glass, countertops, bottles and jars.
Question 7. How is the recycling of aluminium carried out?
Answer:
4. Aluminium waste:
Cans from soda drinks, tomatoes, fruit cans and all other cans can be recycled.
When these are collected, they are sent to the recycling unit, where all the waste from each type is combined, crushed, melted and processed into new materials.
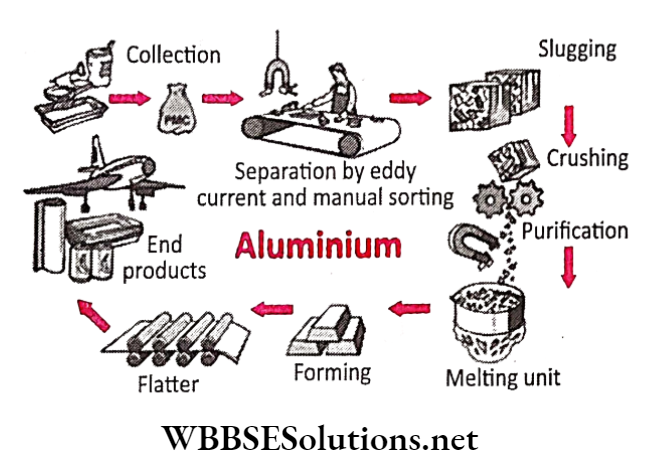
Real-Life Scenarios Involving Landfills and Recycling
1. Aluminium recycling:
In recent times, there has been a massive improvement in recycling aluminium cans. Those cans, hoil-placed end-to-end, could make 171 circles around the earth.
Every minute, an average of 105,800 aluminium cans are recycled. It is clear that can recycling is very important in the present life.
2. Collection:
People may use special cans. recycling containers (bins) that are clearly marked. This helps people to know what to place in them.
Can include soda, fruit and vegetable cans. Trucks come for these at pick-up spots at the recycling centres. Cans may also be metallic or steel, but usually, common people do not know the difference.
3. Preparation:
At the collection centre, a huge magnet is rolled over them as they move on the conveyor belt to pull out all the metal and steel cans.
Only the aluminium cans are washed, crushed, and condensed into 30 pounds. briquettes for other companies for further processing. The rest is also sorted and sent to their appropriate recycling centres.
4. Melting:
The crushed cans are loaded into a burning furnace, where all printing and designs on the cans are removed, melted and blended with new (virgin) aluminium.
The molten (liquid) aluminium is poured into moulds and made into bars called ingots.
5. Sheets:
The ingots are then fed into powerful rollers, which flatten them into. thin sheets of aluminium. These thin sheets are rolled into coils and sold or sent to can-making factories.
They use aluminium coils to prepare cans and containers for other food and drink manufacturers.
It is estimated that cans collected at collection points take up to 60 days to reappear in the shops again as new cans containing your favourite soda, juice or food.
Question 8. Give examples to show how the 4R process can be followed in households to minimize pollution of surrounding localities.
Answer: Every citizen should implement the 4R process of waste management in his/her household for a sustainable environment.
Reduce:
Vegetable peels may be fed to cows. Leftover kitchen waste or semi-rotten cooked fish/meat may be fed to crows.
Reuse:
Carry bags (plastic or jute or cloth) may be used time and again when somebody goes to the market or local shop for buying products. Gift wrappers may be reused instead of discarding them after one time use.
Recycle:
Kitchen waste, vegetable peels, leaves etc may be dumped in a pit in the garden to prepare good quality compost fertiliser.
Refuse:
Everyone should be conscious enough to refuse plastic carry bags from local shops or supermarkets to minimize their accumulation and associated pollution.
