WBBSE Chapter 8 Aspects Of Culture In Ancient India Topic B Science And Arts In The Ancient India Subcontinent Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe the story of Lakshman and the ‘Shaktishel’.
Answer:
The story of Lakshman and the ‘Shaktishel’:
In the Ramayana, we find a story that Lakshman became unconscious when he was hit by a powerful missile called shaktishel.
Physician Sushena advised that Bishalyakarani, a medicinal plant if applied to the wound would help Lakshman to recover. Hanuman went to Gandhamadan mountain to collect the herb but failed to identify it.
So he carried the entire hillock on his shoulder and brought it to Lakshman. Lakshman recovered when Bishalyakarani was applied. The term Bishalyakarani means the medicine which is applied after surgery.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 History
Question 2. What is the importance of Charaka- Samhita and Shushuruta-samhita in the study of science in the ancient period?
Answer:
The importance of Charaka- Samhita and Shushuruta-samhita in the study of science in the ancient period:
Charaka-Samhita and Shushruta-samhita are very important in the study of science in ancient India.
1. Charaka-Samhita:
Charaka in his Charaka- samhita discussed about seven hundred medicinal plants. He also discussed about different aspects of diseases. In his writings, there are also references how an ideal hospital should be equipped.
2. Shushuruta-samhita:
From Shushruta- samhita much is known about the dissection of corpses or cadavers. Shushruta had discussed about surgical treatment in his book.
He was an expert in joining bones or broken noses putting together a severed ear, etc. He was an expert in this field.
Important Definitions Related to Ancient Indian Sciences

Question 3. Who was Jivaka? Write in detail about him.
Answer:
Jivaka:
Jivaka was an eminent physician and a contemporary of Buddha.
Life and Works of Jivaka
Jivaka was born in Rajagriha (a royal family). He was the physician of King Bimbisara. He received his education from Guru Atreya in Taxila.
After completion of his studies, Guru Atreya sent his disciples to the forest with the task of finding plants with no medicinal properties. Each disciple came back with many plants which they felt had no medicinal value.
Only Jivaka came empty-handed and said that he could not find any plant which had no medicinal value. The Guru was happy and he realized that Jivaka had acquired full knowledge of medicinal herbs and plants. Later on Jivaka successfully treated King Bimbisara and Gautama Buddha.
Question 4. What were the causes of conflict that arose between the Dharmashastra and medical science? Or, What were the problems that appeared in the cultivation of medical science in ancient India?
Answer:
The causes of conflict that arose between the Dharmashastra and medical science:
In ancient times differences arose between the Dharmashastra and medical science.
1. Intense caste distinction:
Due to caste distinctions problems arose in the cultivation of medical science. There was a belief that by performing good deeds (punya) in an earlier birth, it was possible to be free from diseases in the present birth. This was contradicted by medical science.
2. Prohibition of food items:
According to medical science, different kinds of food were necessary for a speedy recovery from diseases. But Dharmashastras prohibit the consumption of several food items. This led to differences between Dharmashastras and medical science.
3. Dissection of corpses:
Dharmashastra prohibited the touching of corpses. But the dissection of corpses was an important part of medical science.
Due to the prohibition of Dharmashastra the practice of surgical science and the study of anatomy declined. In this way, conflict arose between Dharmashastras and medical science.
Question 5. What were the contributions of Aryabhatta, Varahamihira, and Brahma- Gupta to science in the Gupta period?
Answer:
The contributions of Aryabhatta, Varahamihira, and Brahma- Gupta to science in the Gupta period:
1. Aryabhatta:
Aryabhatta was a great mathematician and astronomer of the Gupta period. He raised the status of mathematics to the level of an independent discipline.
In his work ‘Aryabhatiya’ he introduced the concept of zero which led to the emergence of the decimal system. He also propounded the theories of the rotation of the earth, its spherical shape. and the cause of the lunar eclipse. He has also discussed about the stars and planets.
WBBSE Class 6 Science and Arts in Ancient India Notes
2. Varahamihira:
Varahamihira was also a famous astronomer who introduced many new concepts. In his works Suryasidhhanta and Panchasidhantika he had discussed the connection between clouds, winds and the amount of rainfall.
Early warning signals of an earthquake was also discussed in Varahamihira’s work.
3. Brahmagupta:
Brahmagupta was a famous mathematician and astronomer who made an exceptional contribution to Mathematics. His famous work was Brahmasphuta Siddhanta.
Question 6. Give an account of the development of Astronomy and Mathematics during the Gupta period.
Answer:
The development of Astronomy and Mathematics during the Gupta period:
During the Gupta period there was considerable development of astronomy and science.
1. Astronomy:
Aryabhatta was a great astronomer of the Gupta period. In his work ‘Aryabhatiya’ he propounded the theories of the rotation of Earth, its spherical shape and the cause of the lunar eclipse.
He also discussed about the stars and planets. Varahamihira was also a famous astronomer who introduced many new concepts. In his works Suryasidhhanta and Panchasidhantika he had discussed the connection between clouds, winds, and the amount of rainfall.
Early warning signals of an earthquake are also mentioned in his works.
2. Mathematics:
Aryabhatta raised the status of Mathematics to the level of an independent discipline. In his work ‘Aryabhatiya’ he introduced the concept of zero which led to the emergence of the decimal system.
Brahmagupta was a famous mathematician who made exceptional contributions to Mathematics. His famous work was Brahmasphutasiddhanta where he discussed about different aspects of Mathematics.
Question 7. What do you mean by environmental concerns in ancient India?
Answer:
Environmental concerns in ancient India:
There was much concern for the various aspects of the environment in ancient India.
1. Areas of concern:
The main areas of concern were forests, plants, birds, and animals. The rulers were very keen about forests because different types of natural resources were available from the forests. In Kautilya’s Arthashastra there are discussions on forests.
Short Questions on Ancient Indian Science
2. System of punishment:
People who damaged the forests were punished. The Mauryan emperor Ashoka prohibited the killing of birds and animals.
3. Forests:
Around the 6th century BC forests were cleared both for agricultural purposes and urban settlements. In the Vedic literature, villages were referred to as familiar whereas forests were unfamiliar.
Residents of the forests were looked down upon and were considered as strange. From the epics, we come to know that sometimes members of the royal family were banished to the forests in order to put them in trouble.
4. Tree worship:
Projects were started to save trees. To stop cutting of trees, worshipping of trees like Banyan and Pipal started.
5. Water:
Water was very important in the everyday life of the people, for religious purposes and for agriculture. So wealthy people made efforts to store water and build tanks and irrigation canals.
Question 8. What do you know about the cultivation of science in ancient India?
Answer:
The cultivation of science in ancient India:
In ancient India, the standard of scientific studies was quite high.
Cultivation of science in the Indian subcontinent
1. Meaning:
The word ‘science’ implies attaining specialized knowledge in a particular subject.
2. Scientific element in literature:
In the later Vedic and Buddhist literature, we find references to different types of medicines and surgical operations.
Charaka in his Charaka-Samhita mentioned about seven hundred medicinal plants and also discussed about different aspects of diseases. It also dwells on how an ideal hospital should be equipped.
Common Questions About Indian Astronomy
3. Astronomy and Mathematics:
The famous were astronomers of ancient India Aryabhatta and Varahamihira and famous mathematicians were Nagarajuna and Brahmagupta.
Aryabhatta in his work Aryabhatiya propounded the theories of the rotation of the earth, its spherical shape, and the causes of a lunar eclipse.
4. Medical Science:
Shushruta had discussed about physiology and surgical treatment in his ‘Shushuruta-samhita’. Here he advises physicians to discuss their specific requirements for surgical tools.
Question 9. Give an account of the cultivation of art during the Mauryan age.
Answer:
The cultivation of art during the Mauryan age:
After the Harappan civilization, evidence of art are found mainly in the Mauryan age.
1. Guhavasa:
Ashoka and the later Mauryan emperors built artificial caves by cutting mountains for the Ajivikas. People resided in these caves. This is known as ‘guavas’.
2. Stupa:
The Mauryan emperors also built stupas for the Buddhists. At first, the stupas were made of mud. But from Ashoka’s reign, stupas were made of bricks. The famous stupas at Sanchi and Sarnath were rebuilt during Ashoka’s reign.
3. Stone Pillars:
The pillars of Ashoka may be regarded as the best specimens of Mauryan art. The pillars were made of a single block of stone. The pillars looked like a piece of chalk. Ashokan Pillar in Sarnath is a remarkable piece of Mauryan art.
Practice Questions on Arts and Crafts in Ancient India
Question 10. Give an account of the cultivation of art during the Gupta and Pallava period.
Answer:
The cultivation of art during the Gupta and Pallava period:
The Gupta and Pallava period were famous for vast progress in the field of art and architecture.
1. Stupas and Chaityas:
A number of stupas and chaityas were constructed during the Gupta period. A remarkable stupa, the Dhamekh stupa of Sarnath, was built with bricks and stone.
2. Temples:
Temple architecture also began in the Gupta and Pallava period. Temples were built of brick or stone. Sometimes rock cut temples were also constructed. The temple at Mahabalipuram built by the Pallavas deserves a mention.
3. Sculpture:
On the walls of the temples of the Gupta and Pallava period, images of different Gods and Goddesses were engraved. Mention may be made here of the sculpture of the Dashavatara temple and the Ramayana panel of the Kailasha temple.

4. Painting:
Ajanta cave paintings of the Gupta period are the most remarkable paintings of Gupta art. In these paintings, human figures and different kinds of plants are depicted.
The colors used in the Ajanta cave paintings were made of stone, earth, and plant components. Paintings have also been found in the Ellora and Bagh caves.
Class 6 History Chapter 8 WBBSE
Question 11. Give an account of the cultivation of art in ancient India.
Answer:
The cultivation of art in ancient India:
In ancient India, there was widespread cultivation of art.
1. Art in the Mauryan period:
During the Mauryan period, the material which was widely used for art was stone. The Mauryan emperors built artificial caves for the Ajivikas known as ‘Guhavasa’.
They also built stupas for the Buddhists. The best specimens of Mauryan art are the pillars built by Ashoka.
2. Art in the Shunga-Kushana-Satavahana period:
During this period sculpture was made with both terracotta and stone. Art was influenced by the life of common people and religious concepts and beliefs. The best examples of this period are the stupas, chaityas, and viharas.
The Gandhara and Mathura styles of art developed during this period centering Buddha’s life and beliefs.
3. Art in the Gupta and Pallava period:
In the Gupta age, a new style of architecture, that is, construction of different types of temples began, for example, the Dashavatara temple of Deogarh.
On the walls of the temples of the Gupta and Pallava period, images of different Gods and Goddesses were engraved.
Question 12. What do you know about the ruins of the archaeological site of Chandraketugarh?
Answer:
The ruins of the archaeological site of Chandraketugarh:
In the district of North 24 Parganas of West Bengal in Berachampa the archaeological ruins of Chandraketugarh have been found.
- Chandraketugarh of ancient Bengal was connected to the river Ganga by the river Vidyadhari. It was a thriving urban commercial center.
- Many archaeological remains of pre- Mauryan age (c600-300 BC) till Palas-Senas ages (c750-1250 AD) have been found here.
- The artifacts recovered are a variety of pottery, seals, statues, and terracotta figures. The terracotta figures are mostly female figurines.
Examples of Famous Sculptures and Architecture in Ancient India
Question 13. What are stupas, chaityas and viharas?
Answer:
Stupas, chaityas and viharas:
Stupas were semi-circular earthen mounds which contained the cremated remains of dead persons. They had railings and four gateways which were sculpted and called ‘Torana’.
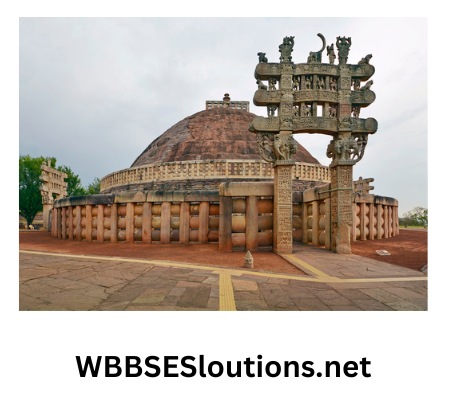

Chaityas were cave shrines built along with stupas and made by directly cutting into the sides of rocks. Viharas or sangharamas were specimens of architectural monuments which acted as residences and educational centers of Buddhist monks.
WBBSE Chapter 8 Topic B Science And Arts In The Ancient India Subcontinent Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Mention two features of Mathura art.
Answer:
Two features of Mathura art were:
- The main theme of Mathura’s art was the life of Buddha and Buddhism.
- Mostly red sandstone was used in the Mathura school of sculpture.
Question 2. Write a note on art during the Mauryan age.
Answer:
Art during the Mauryan age:
During the Mauryan period the material which was widely used for art was stone. The Mauryan emperors built artificial caves known as ‘Guhavasa’ for the Ajivikas by cutting mountains. They also built stupas for the Buddhists. The best specimens of Mauryan art are the pillars built by Ashoka. Human figures are rarely found in Mauryan art.
Question 3. What are the main features of the Ashokan Pillar?
Answer:
The main features of the Ashokan Pillar:
The pillars of Ashoka may be regarded as the best specimens of Mauryan art.
Conceptual Questions on Cultural Contributions of Ancient India
The main features of the Ashokan pillar are
- The pillars were made of a single block of stone.
- The pillars look like a piece of chalk.
- The base of the pillar was under the earth.
- The pillars stood upright without any support.
- On the top of the pillars were placed animal figures like lions, elephants, ox, etc.
Question 4. Differentiate between a monastery and a stupa.
Answer:
Difference a monastery and a stupa:
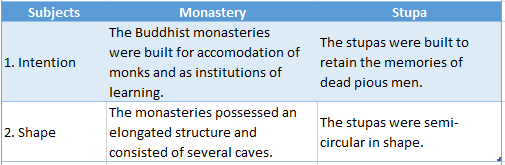
Question 5. Give an account of Shunga-Kushana- Satavahana art.
Answer:
Shunga-Kushana- Satavahana art:
The Shunga-Kushana-Satavahana art was mainly based on the lives of common people. -Religion formed the main theme of art. The structures were related mainly to the Buddhist religion. Stupa, Vihara, and Chaitya are the best specimens of art.
Question 6. Write a note on Ajanta Cave paintings.
Answer:
Ajanta Cave paintings:
Ajanta Cave paintings are the most remarkable paintings of the Gupta period. In these paintings, human figures and different kinds of plants are depicted.
The colors used in the Ajanta cave paintings were made of stone, earth, and plant components.
Question 7. What is the importance of Chandra- ketubah as an archaeological site?
Answer:
The importance of Chandra- ketubah as an archaeological site:
Archaeological ruins have been discovered at Chandraketugarh in West Bengal. Many archaeological remains from the pre-Mauryan age till the Palas-Senas ages have been found here.
The artifacts recovered here are earthen pottery, seals, statues, and terracotta figurines. The terracotta figurines are mostly female figurines.
History Class 6 Chapter 8 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 8. What was discussed in Charaka-Samhita?
Answer:
In Charaka-Samhita there were discussions on seven hundred medicinal plants and different diseases. There are also references on how an ideal hospital should be equipped.
Question 9. What was Sankhyayan?
Answer:
Sankhyayan:
Arithmetic, Algebra, and Geometry-these three combined together was Mathematics to the Buddhists. This was known as Sankhyayan to the Jains.
Question 10. Who was Nagarjuna?
Answer:
Nagarjuna:
Nagarjuna was a famous Buddhist scholar of the 1st century AD. He was a mathematician.
Question 11. Who was Varahamihira? What were the two works of Varahamihira?
Answer:
Varahamihira was a famous astronomer of the Gupta age. His two works are-Suryasidhhanta and Panchasidhantika.
Question 12. Who was Brahmagupta? Why is he famous?
Answer:
Brahmagupta was a famous mathematician and astronomer of the Gupta period. He is famous for his work Brahmasphuta Siddhanta.
Question 13. Why was Shushruta famous?
Answer:
Shushruta famous:
Shushruta was an expert in joining broken bones or noses. He could also join together a severed ear etc. Thus he was famous in this particular field.
Question 14. What do the words ‘Charaka’ and ‘Shushruta’ mean?
Answer:
The word ‘Charaka’ means. those who wander about. We come to know about Charan Vaidya or physicians who wandered about offering treatment from one of the Vedas. The word ‘Shushruta’ means one of those who had listened properly.
Question 15. Give an idea of the Mehrauli Pillar.
Answer:
Mehrauli Pillar:
The Mehrauli Pillar is an example of the development of metallurgy in ancient times. Till today the iron pillar is rust-free.
Question 16. What is ‘guhavasa’?
Answer:
Guhavasa:
Ashoka and the later Mauryan emperors built artificial caves by cutting mountains for the Ajivikas. People resided in these cave dwellings. This is known as ‘guhavasa’.
Question 17. What was the period about which we come to know from the archaeological remains of Chandraketugarh?
Answer:
From the archaeological remains of Chandraketugarh we come to know about pre- Mauryan period (c 600-300 BC) to the times of the Palas and Senas (c 750-1250 AD).
Question 18. Name some artifacts recovered from the archaeological ruins of Chandraketugarh.
Answer:
The artefacts recovered from the archaeological ruins of Chandraketugarh are different types of earthen pottery, seals, statues, and terracotta figurines.
WBBSE Chapter 8 Topic B Science And Arts In The Ancient India Subcontinent Very Short answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is Bishalyakarani?
Answer: Bishalyakarani was a medicinal plant used for preparing medicine to be applied after surgery.
Question 2. Who proposed to apply Bishalyakarani to the wound of Lakshman?
Answer: Sushena, a physician proposed to apply Bishalyakarani to the wound of Lakshman.
Question 3. Who was Jivaka?
Answer: Jivaka was the royal physician of king Bimbisara.
Question 4. From whom did Jivaka receive an education?
Answer: Jivaka received education from Guru Atreya.
Question 5. How was ‘punya’ and disease-related?
Answer: There was a belief that by performing good deeds (punya) in an earlier birth it was possible to be free from diseases in the present birth.
Question 6. What was prohibited in the Dharmashastras?
Answer: In the Dharmashastras touching a corpse was prohibited.
Question 7. Why the study of Anatomy and surgical science began to decline?
Answer: Touching a corpse was prohibited by the Dharmashastras. As a result, the study of Anatomy and surgical science began to decline.
Question 8. What is the meaning of the word Charaka?
Answer: The word Charaka means those who wander.
Question 9. What is the meaning of the word ‘Charan Vaidya’?
Answer: Charan Vaidya means physicians who used to wander about from place to place offering treatment to the people.
Question 10. Name a famous Buddhist mathematician.
Answer: The famous Buddhist mathematician was Nagarjuna.
Question 11. What was the name of the book written by Aryabhatta?
Answer: The name of the book written by Aryabhatta was Aryabhatiya.
Question 12. Who was Aryabhatta?
Answer: Aryabhatta was a famous astronomer and mathematician of the Gupta period.
Question 13. In which book did Aryabhatta use the concept of zero?
Answer: Aryabhatta, in his book Aryabhatiya, used the concept of zero.
Question 14. Who put forward the idea that the Earth is round and it rotates around its own axis?
Answer: Aryabhatta put forward the idea that the Earth is round and it rotates around its own axis.
Question 15. What was Aryabhatta’s concept of lunar eclipse?
Answer: Aryabhatta’s conception was that a lunar eclipse occurs when the shadow of the earth fell on that of the moon.
Question 16. Who was the author of Brahmasphuta- Siddhanta?
Answer: The author of Brahmasphutasiddhanta was Brahmagupta.
Question 17. Which book discussed about the science of agriculture?
Answer: The book Krishiparashara discussed about the science of agriculture.
Question 18. What were the main concerns of the environment in ancient India?
Answer: The main concerns of the environment in ancient India were birds, animals, plants, and forests.
Question 19. For whom did the Mauryan emperors build artificial cave dwellings?
Answer: The Mauryan emperors built artificial cave dwellings for the Ajivikas.
Question 20. Name two stupas built during the reign of Ashoka.
Answer: Two stupas built during the reign of Ashoka were stupas at Sarnath and Sanchi.
Question 21. What figures have been used in the Ashokan pillar?
Answer: Figures of lions, elephants, ox, etc. were used in the Ashokan pillar.
Question 22. What was the principal theme of Gandhara and Mathura art?
Answer: The principal theme of Gandhara and Mathura art was the life of Buddha and Buddhism.
Question 23. What is the main influence on Gandhara sculpture?
Answer: Greek and Roman influences are dominant on Gandhara art.
Question 24. What was mostly used in the Mathura school of sculpture?
Answer: Redstone was mostly used in the Mathura school of sculpture.
Question 25. What is ‘torona’?
Answer: The stupas in the Mauryan age had railings and four gateways on four sides. These are known as ‘torona’.
Question 26. What are stupas?
Answer: Stupas are semi-circular earthen mounds which contained the cremated remains of dead persons.
Question 27. What are viharas?
Answer: Viharas were a collection of several caves which acted as residences and educational centers.
Question 28. Which are the most remarkable specimens of Gupta art?
Answer:
The most remarkable specimens of Gupta art are the paintings and sculptures of the Ajanta caves.
Question 29. Why are Ellora and Bagh caves famous?
Answer:
Ellora and Bagh caves are famous for their paintings.
Question 30. Give two examples of Gupta art.
Answer:
Two examples of Gupta art are the Ajanta cave painting and the Ellora cave painting.
Question 31. Name the archaeological site of North 24 Parganas in West Bengal.
Answer:
The archaeological site of North 24 Parganas in West Bengal is Chandraketugarh in Berachampa.
WBBSE Chapter 8 Topic B Science And Arts In The Ancient India Subcontinent Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. ________ (History / Science / Philosophy) means specialized knowledge.
Answer: Science
Question 2. Jivaka was the royal physician of king ________ (Bimbisara/Bindusara / Kanishka).
Answer: Bimbisara
Question 3. Bishalyakarani was a ________ (water/thorny/medicinal) plant.
Answer: Medicinal
Question 4. Nagarjuna was a ________ scholar (Hindu/ Jain / Buddhist).
Answer: Buddhist
Question 5. Aryabhatiya was written by ________ (Varahamihira / Aryabhatta / Brahma- Gupta).
Answer: Aryabhatta
WBBSE Class 6 History Chapter 8 Questions And Answers
Question 6. ________ (Varahamihira / Aryabhatta / Nagarjuna) was the author of Suryasidhhanta.
Answer: Varahamihira
Question 7. The ________ pillar of Mehrauli is remarkable (iron /stone/copper).
Answer: Iron
Question 8. The science of agriculture is discussed in the book ________ (Aryabhatiya / Shushuruta- samhita / Krishiparashara).
Answer: Krishiparashara
Question 9. A chariot-like temple was built during the Pallava period at ________ (Ajanta / Ellora / Mahabalipuram).
Answer: Mahabalipuram
Question 10. There are discussions on forests in the ________ (Krishiparashara / Arthashastra / Charaka-samhita).
Answer: Arthashastra
Question 11. Gandhara and Mathura styles of art became popular in ________ (Saka-Kushana / Maurya- Kushana/Satavahana / Gupta) age.
Answer: Saka-Kushana
Question 12. Initially, the stupas were made of ________ (red sandstone/bricks/mud).
Answer: Mud
Question 13. Mauryan art evolved mainly due to the patronage of the Mauryan ________ (people/rulers/preachers).
Answer: Rulers
Question 14. Stupa and Chaitya were linked mainly to the practices of the ________ (Buddhists/Hindus / Ajivikas).
Answer: Buddhists
Question 15. ________ (Buddha / Mahavira / Ashoka) was the theme of most of the sculptures of the Shunga-Kushana period.
Answer: Buddha
Question 16. Buddhist ________ (chaityas/viharas / pillars) were built for the residence and education of Buddhist monks.
Answer: viharas
WBBSE Chapter 8 Topic B Science And Arts In The Ancient India Subcontinent True Or False
Question 1. The term Bishalyakarani means the medicine which is applied after surgery.
Answer: True
Question 2. Jivaka, a famous physician, successfully treated Mahavira and restored his health.
Answer: False
Question 3. It was said that one can be free from diseases in the present birth by performing good deeds in an earlier birth.
Answer: True
Question 4. The word Charaka means ‘to apply’.
Answer: False
Question 5. To the Buddhists, Mathematics consisted of Arithmetic, Algebra, and Astronomy.
Answer: False
Question 6. It was in the book ‘Aryabhatiya’ that Aryabhatta discussed the stars and planets.
Answer: True
Question 7. In the Shushuruta-samhita the hand has been held up as the greatest tool.
Answer: True
Question 8. Bimbisara prohibited the killing of birds and animals.
Answer: False
Question 9. Ashoka built cave dwellings for the Jains.
Answer: False
WBBSE Class 6 History Chapter 8 Questions And Answers
Question 10. Ashoka erected many stupas for the Buddhists.
Answer: True
Question 11. The Sarnath stupa was built by Ashoka.
Answer: True
Question 12. Scenes of royal court were seen in the sculptures of the Kushana period.
Answer: False
Question 13. Gandhara sculpture is mainly influenced by Greek and Roman art.
Answer: True
Question 14. White sandstone was used in the Mathura school of sculpture.
Answer: False
Question 15. The railings and four gateways on four sides of the stupa were known as ‘torona’.
Answer: True
Question 16. The Dashavatara temple of Chandraketugarh is an example of a stone temple.
Answer: False
