Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Summary
WBBSE Class 10 Environmental Pollution Overview
- The unwanted change of the biosphere of the environment through the introduction of harmful, poisonous substances in the environment is called pollution and the substances causing pollution are called pollutants.
- Different types of greenhouse gases, like CO2, CH4, etc. are the main causes of air pollution. Except these, some suspended particulate matter (SPM) also can cause air pollution. Acid rain and various diseases of the respiratory tract (COPD) are the main harmful effects of air pollution.
- The major causes of water pollution are agricultural waste, microbes, etc. One of the notable harmful effects of water pollution is eutrophication which is caused by excessive plant and algal growth due to the addition of excessive levels of inorganic and organic nutrients in the water bodies.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Life Science And Environment
- Due to this phenomenon, the quality of the water gets deteriorated. Cholera and typhoid are some of the diseases caused by the water pollution.
- Microbes and chemical fertilisers, chemical pesticides induce soil pollution. From the polluted soil, these pollutants can directly enter in to a human body. Non-biodegradable pollutants get accumulated in the environment and may cause in bioaccumulation and biomagnification.
- Bioaccumulation is the accumulation of pollutants in an organism and biomagnification is the increase in concentration of pollutants along the successive higher trophic levels in a food chain.
- Various types of sounds from industries and vehicles are the major causes which contribute to noise or sound pollution. Noise pollution causes hearing impairment, cardiac diseases, stress, sleep disturbance, etc. Sound intensity is measured by the unit decible (dB).

Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. ‘A lot of indiscriminate activities of humans pollute environment-Support the statement by giving three examples in favour of it.
Mention the different types of pollution.
Answer:
Three examples in favour of the statement:
A lot of indiscriminate activities of human beings pollute the environment in large scale. These are-
- Combustion of fossil fuels causes an excessive increase in the level of greenhouse gases which in turn result in global warming.
- Excessive use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides causes soil pollution.
- Industrial sewage, oil spill, etc. create water pollution. These examples justify the statement correctly.

Different types of pollution:
Based on the nature of the environmental resources, pollution can be classified into four types. These are-
- Air pollution,
- Water pollution,
- Soil pollution and
- Noise pollution.
Question 2. What is air pollution? Mention the causes of air pollution.
Answer:
Air pollution:
Air pollution is the natural or man-made undesirable change in the atmosphere, with the addition of harmful, hazardous substances in such higher concentrations that these exert toxic effects on vegetation and animal life with a degradation of biotic and abiotic resources.
Air pollution results in the accumulation of harmful smoke, gases, vapour, suspended particulate matter, etc. in the atmosphere beyond admissible level.
Causes of air pollution
Main causes of air pollution are-Greenhouse Gases (GHG) and Suspended Particulate Matters (SPM).
1. Greenhouse gases:
Various gases present in the atmosphere, like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), nitrous oxide (N2O), etc. prevent the dissipation of heat from earth surface and make the atmosphere warmer.
These gases are called greenhouse gases. By different human activities or natural processes, these gases get accumulated in the atmosphere. The sources of a few greenhouse gases are as follows-
Carbon dioxide:
Combustion of fossil fuel, forest fires, burning of organic matter, furnaces of factories, etc. add CO2, in the atmosphere.
Chlorofluorocarbon:
This gas is liberated from air conditioners and refrigerator factories, jet engine exhausts. It is also present in aerosol sprays and deodorants.
Nitrogen oxides:
It is released from nitrogenous fertilisers and chemical factories. Lightning naturally produces nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere.
2. SPM:
Different light and fine particulate matters remain suspended in the air. These are called suspended particulate matter, which causes air pollution. These matters include particles below 10 μ in diameter, denoted as PM-10.
Smaller particles below 2.5 μ are marked as PM-2.5. Besides these, there are very fine particles of aerosols, which are below 1u in diameter. Important SPMs are dust particles, pollen grains, ash, smoke, etc.
Types of Environmental Pollution Explained
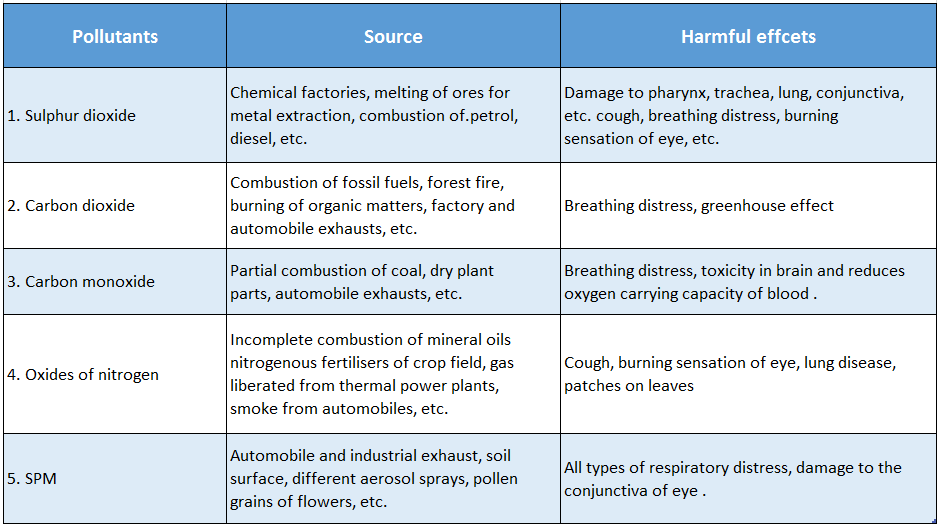
Question 3. Name five air pollutants and mention their sources and harmful effects.
Answer:
Names, sources and harmful effects of five air pollutants
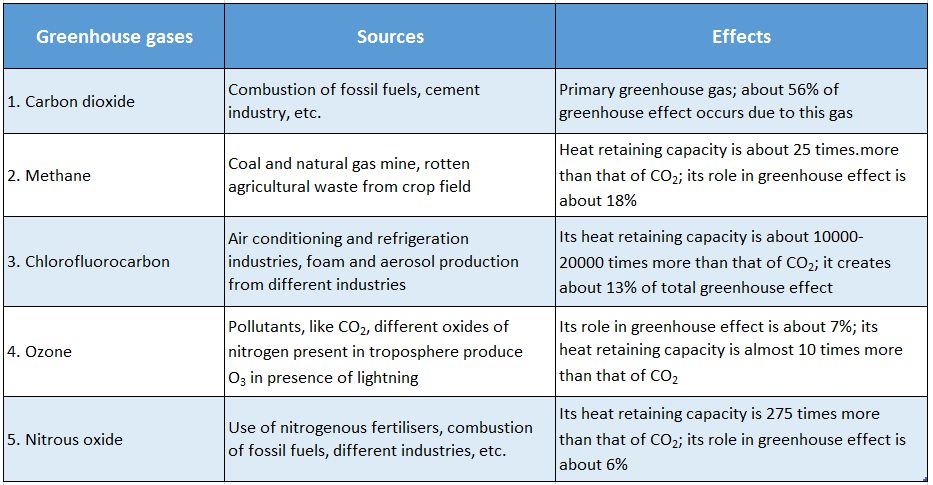
Question 4. Name different greenhouse gases and mention their sources and effects.
Answer:
Sources and effects of different greenhouse gases
Question 5. Briefly describe any five measures to reduce the effect of greenhouse gases.
Answer:
Measures to reduce the effect of greenhouse gases
Five different measures to reduce the greenhouse effect are discussed below.
1. Reducing the use of fossil fuels:
By reducing the use of fossil fuels like coal, petrol, diesel, etc., the production of CO2 can be minimised.
2. Reducing the use of CFC-producing devices:
CFC is liberated from refrigeration industries and different aerosol sprays like perfumes, deodorants, etc. Reducing the use of CFC in these products may reduce the CFC-created greenhouse effect.
3. Afforestation:
Plants consume CO2 from the atmosphere. By planting of more trees, the area of forests can be widened and this practice can reduce the CO2 content of the atmosphere.
4. Use of non-conventional sources of energy:
The use of non-conventional sources of energy like solar energy, geothermal energy, wind energy, etc. can bring down the use of fossil fuels and thereby, reduce the chances of production of greenhouse gases.
5. Processing of sewage:
Proper processing of sewage before disposal can reduce the possibility of the production of methane. Thus the occurrence of the greenhouse effect can be lessened.
Causes of Environmental Pollution
Question 6. What is acid rain? Mention the cause of acid rain.
Answer:
Acid rain:
Atmospheric pollutants like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide react with water vapour present in the atmosphere to produce secondary air pollutants like sulphuric acid and nitrous or nitric acids.
These acids come down to earth with rainwater, dew or snowfall and cause serious environmental and health hazards. This is called acid rain. The pH of acid rain goes down below 5.
Cause of acid rain:
The principal cause of acid rain is air pollution. These pollutants are generated from different human activities. Chemical factories release huge quantities of sulphur dioxide (SO2). Automobile exhaust releases nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Sulphur dioxide reacts with oxygen present in nature to produce sulphur trioxide (SO3). SO, and NO, react with atmospheric moisture and produce sulphuric acid (H2SO4), nitrous (HNO2) and nitric acid (HNO3).
The following reactions take place in the atmosphere when these acids are generated.
2NO2 + H2O → HNO3 + HNO2
2SO2 + O2 →2SO3, SO3 + H2O H2SO4
Finally, these acids come down on earth with rainwater as acid rain.
Question 7. Briefly explain the effects of acid rain on the environment. Mention two damages as a result of acid rain.
Answer:
Effects of acid rain on the environment:
Various harmful effects of acid rain on different components of the environment can be seen.
1. Effect on animals and plants:
Acid rain acidifies water bodies and as a result, fishes die. If the pH of a water body goes below 4 due to acid rain, all types of aquatic animals and plants die.
Acid rain damages the leaves of plants. In terrestrial habitats, several agricultural crops are severely damaged due to acid rain.
2. Effect on soil:
Acid rain makes the soil acidic. As a result of this, fertile soil gradually loses fertility. The productivity of crops also drops radically. Many beneficial micro and macroorganisms die due to the acidification of soil.
3. Effect on forests:
Acid rain may damage wide area of forestland. The leaves get bleached and burnt. Finally, a large number of trees dry up. A similar effect can be observed on corp plants. As a result of this, crop productivity also decreases drastically.
4. Effect on human health:
Acid rain has very moderate harmful effects on human beings. The mostly first splash of acid rain causes damage to human hair and skin. Prolonged intake of acidified water may cause serious gastrointestinal problems.
5. Effect on marble architecture:
Marble and limestone are composed of calcium carbonate, Acids present in acid rain react with this to produce calcium nitrate and calcium sulphate. Because of this chemical change, marble gets corroded and becomes rough and porous.
This is popularly known as ‘stone leprosy’ or ‘stone cancer. Several marble monuments such as the Taj Mahal, and Victoria Memorial have faced the adverse effect of acid rain.
Effects of Air Pollution on Health
Question 8. Briefly mention different types of lung diseases caused due to air pollution.
Answer:
Different types of lung diseases caused due to air pollution:
Polluted air, when enters in to the lungs through a respiratory path, causes various diseases. These are
- Air pollutants like CO2 and different oxides of nitrogen may cause several lung diseases like asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis and even lung cancer.
- Workers of metallurgical industries, chemical factories, etc. may develop different lung diseases caused by different air pollutants.
- Over the time, cool miners get exposed to coal dust. Due to this, their lungs become black. Hence, this disease is called black lung disease.
- Workers of asbestos and silicon factories are exposed to airborne fine asbestos fibres and silicon dust. These often develop asbestosis and silicosis respectively.
- Due to smoking and inhaling various air pollutants, the trachea becomes narrow. As a result, numerous individuals suffer from COPD or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Question 9. ‘Luxurious and comfortable lifestyle is one of the major reasons of air pollution’-Support the statement with arguments. How does the amount of methane increase in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Explanation to support the statement:
‘Luxurious and comfortable lifestyle is one of the major reasons of air pollution-this statement can be well supported and explained by the facts, like-
- CFC used in refrigerators and air conditioners caused global warming, destroys the ozone layer and renders the harmful effects of UV rays on the environment to increase.
- Methane gas produced during natural gas extraction causes global warming.
- Different oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and smoke from agricultural and industrial field enhances the chances of acid rain and causes different respiratory disorder.
Reason of the increase of methane in the atmosphere:
Methane is produced due to the partial combustion of certain organic matters, putrefaction of dead plants and animals in wetlands and emission from coal mines. These processes increase the percentage of methane in the atmosphere.
Question 10. State the causes of water pollution. Make your opinion based on your experiences how the sources of fresh water become polluted.
Answer:
Causes of water pollution:
Different causes of water pollution are-
1. Agricultural wastes:
During heavy showers, the toxic materials like insecticides, herbicides, etc. are washed away from the agricultural fields and mixed in the water bodies in order to make the water polluted.
This runoff also contains nitrate-rich, phosphate-rich chemical fertilisers, etc. which increase the nutrient level of water bodies and result into algal bloom. This phenomenon is called eutrophication. This increases the BOD of the water body and makes it unsuitable for living for aquatic animals.

2. Domestic and industrial sewage:
Domestic wastes contain several organic matters, detergents, excreta, etc. On the other hand, industrial sewage contains boiling water (produced by thermal power plants) and numerous toxic chemicals.
Sewage also carries numerous pathogenic germs. These materials when disposed of in streams, rivers and seas, cause massive water pollution.
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
3. Oil spill:
Mineral oils often spill from large oil vessels.These oils make a thin film over the surface of sea and cause seawater pollution.

4. Heavy metals:
Chemical factories dispose of waste matter in streams, which contain many harmful metals like lead, cadmium, nickel, mercury, etc. Due to excessive use of underground water, the water level goes down.
As a result, the amount of certain toxic elements like arsenic, and fluorine increases. All these elements cause water pollution and turn potable water unfit for human use.
5. Indiscriminate use:
The pond water in village areas is used indiscriminately for washing, and bathing purposes for both man and domestic animals. This practice makes the water polluted.
Moreover, animal wastes, viz.-faecal matters of both livestock and human beings, and urine disposed of in open areas can create huge environmental hazards.
Water Pollution Sources and Solutions
Question 11. Mention the types of water pollution. Explain the effects of water pollution on human health.
Answer:
Types of water pollution:
Based on the source, water pollution can be classified into five categories. These are-
- Underground water pollution,
- Marine water pollution,
- River water pollution,
- Lake water pollution and
- Pond water pollution.
Effects of water pollution on human health:
1. The harmful effects of using polluted or contaminated water while drinking, cooking, bathing, washing hands, rinsing mouth, etc. are mentioned in the next table.
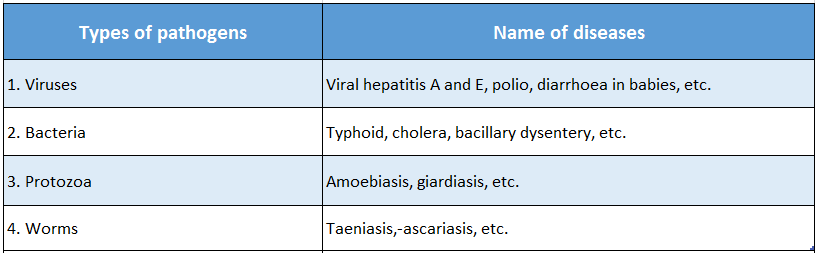
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
2. Different elements like mercury, cadmium, lead, copper, nickel, arsenic, iron, chlorine, etc. cause moderate to severe nervous, gastroenteric, blood and skin-related diseases.
Excess fluorine in drinking water causes allergy, renal impairment, bone deformity and form a permanent brown layer on teeth.
Question 12. What is soil pollution? State three causes of soil pollution.
Answer:
Soil pollution:
The undesirable change in the land, is caused mainly by human activities, resulting in to the mixing of non-biodegradable or partially degradable harmful materials, like-chemical fertilisers, pesticides, herbicides, solid industrial wastes, etc.
Into it, making it infertile and unsuitable for living of soil- dwelling organisms, is called soil pollution or land pollution.
Causes of soil pollution:
Soil pollution may occur in different ways. Out of those, only three causes are mentioned below.
1. Edaphic microbes:
Municipality sewage, medical wastes and domestic wastes contain numerous pathogenic germs. Several of these can survive over the soil surface for a certain period of time.
If these pathogens are transferred directly or with the help of flies, rats, cats or any other vectors to the human body, many diseases may occur.

2. Chemical fertilisers and pesticides:
To increase crop production, farmers use to apply fertilisers much more than the recommended dose. This indiscriminate use of chemical fertilisers makes the soil acidic. Similar is in the case of pesticides and herbicides.
The leftover of these toxic chemicals makes the soil toxic. In lower pH and high toxicity, several beneficial microbes die, making the soil infertile.

Soil Pollution: Causes and Effects
3. Increased salinity:
Excessive pumping out of underground water increases the salinity of the soil. But a more prominent incidence has also been observed in recent days that many of the artificially irrigated crop fields are losing their fertility gradually as a result of excessive irrigation.
Question 13. Describe the harmful effects of soil pollution.
Answer:
Harmful effects of soil pollution:
Different harmful effects of soil pollution are mentioned below.
1. Effect on human health:
Soil pollution has many harmful effects on human health. These are as follows-
Infection by pathogens:
Number of pathogens increases faster in polluted soil. These pathogens can enter into human body directly or by any vector like flies, cockroaches, rats, etc. Clostridium tetani is an edaphic pathogen that causes tetanus.
Clostridium perfringens enter in to the human body through wounds to cause gas-gangrene. Spores of Aspergillus sp., cause a disease called aspergillosis.
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Decrease in productivity of food:
The fertility of soil is inversely proportional to the pollution level of the soil, i.e. as soil becomes more polluted, its fertility decreases. Therefore, soil pollution is one of the most noteworthy causes of food scarcity.
2. Biomagnification:
Gradual increase in the content of any pollutant through the food chain from the lower to upper trophic level is called biomagnification. It occurs in the following two ways-
Bioaccumulation:
Certain non-biodegradable pollutants can’t be metabolised within the animal body. Instead, these are accumulated in the adipose tissues of those animals. In the course of time, the content of these pollutants reaches a fatal limit. This is called bioaccumulation.
The flow of pollutants through trophic level:
Prey and predators remain interconnected in a food chain. The pollutant accumulated in any trophic level is transferred to the next higher trophic level through the food chain.
By this process, the maximum quantity of pollutants reaches the topmost trophic level. The biomagnification of DDT is mentioned in the following flowchart as an example.
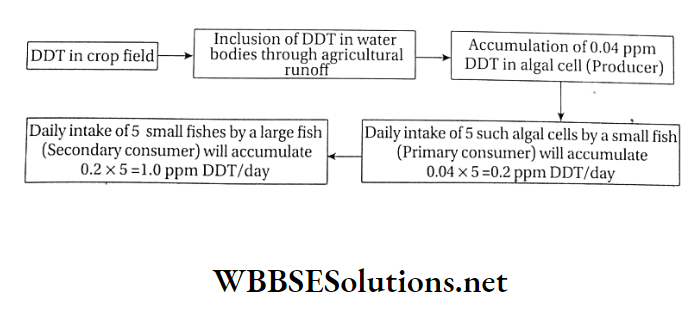
Question 14. Briefly state the harmful effects of water pollution.
Answer:
Harmful effects of water pollution:
The harmful effects of water pollution are mentioned below.
1. Occurence of diseases:
Polluted water is a breeding area for several disease-causing microbes. Germs of typhoid, cholera, hepatitis (A and E), amoebiasis, giardiasis, gastroenteritis, etc. contaminate the polluted water. Intake of this water may lead to these diseases.
2. Skin diseases:
Polluted water containing sulphur, copper, mercury, etc. may cause different skin diseases. Arsenic in water causes incurable black foot disease.
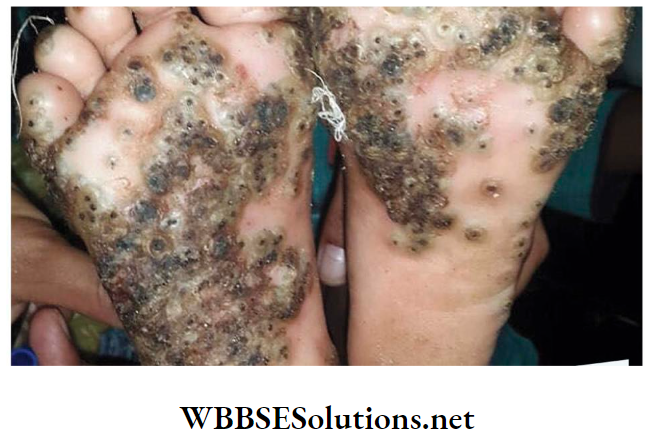
3. Eutrophication:
Detergent and runoff water from crop fields contain various nutrients like phosphates and nitrates. These nutrients facilitate the formation of algal bloom. This process is known as eutrophication.
The water of eutrophic pools becomes odorous and it has very low oxygen content. Moreover, the algae release neurotoxins in those water bodies. Therefore, aquatic animals cannot survive in eutrophic ponds and lakes.
4. Soil infertility:
If polluted water containing toxic chemicals percolates in soil, several soil-dwelling beneficial bacteria and animals like earthworms die. In the long run, it also may be the cause of soil infertility.
5. Decline in fish production:
Most fishes prefer to live in clear, unpolluted, oxygen-rich water. The addition of pollutants in water results in their death and thus, decreases fish population.
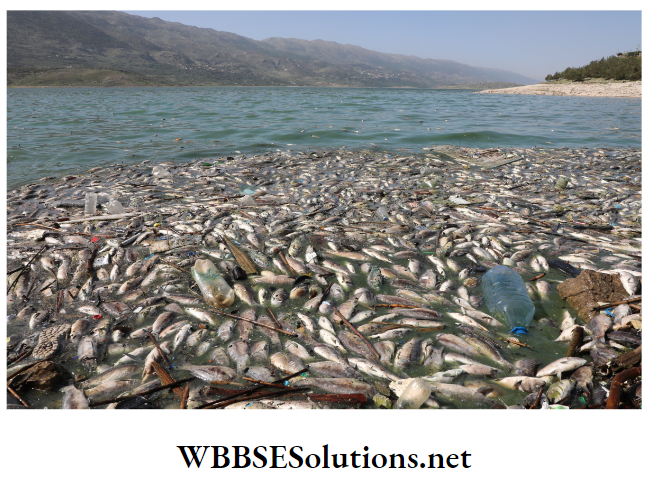

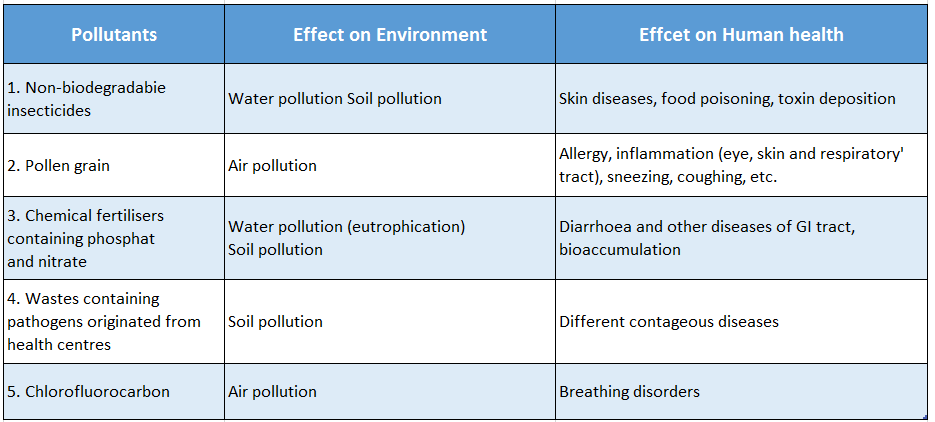
Question 15. Evaluate the effects of the following pollutants on the environment and human health.
- Non- biodegradable insecticide,
- Pollen grain,
- Chemical fertilisers containing phosphate and nitrate,
- Wastes containing pathogens originated from health centres and
- Chlorofluorocarbon.
Answer:
Effects of Pollutants on environment and human health
Thermal Pollution and Its Impact
Question 16. What is noise pollution? Mention a few causes of noise pollution.
Answer:
Noise pollution:
Any undesirable and disturbing high-frequency or high-intensity noise, that is harmful for human health as well as for wildlife, is called noise pollution.
Causes of noise pollution:
Noise pollution is caused by different agents, which are as follows.
1. Motor vehicles:
The number of motor vehicles increases in accordance with the global population. We see a huge concentration of traffic especially in urban areas. The sound created by horns and engines of motor vehicles such as motorcycles, cars, buses, lorries, trams, tempo, etc., taking off and landing of aircraft, etc.
well exceeds the permissible noise limit of 65 dB in commercial areas by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
2. Industrial factories:
The friction of different instruments, the sound of engines, and the hammering of metals create very high-intensity sound. CPCB has fixed the sound intensity at an average of a maximum 75 dB for 8 hours in a day for industrial zones.
Whereas, much more sound is created by different factories and mechanical workshops resulting in noise pollution.
3. Electrical appliances:
Different domestic electrical appliances like mixture grinders, vacuum cleaners, washing machines, and power generators create high-intensity sound.
Besides these, loudspeakers, high-watt sound systems, radio, TV, etc. can generate harsh sound above the permissible limit of noise of 55 dB in residential areas and create noise pollution.

4. Firecrackers:
As a powerful firecracker burst, it suddenly creates a very high-intensity sound reaching up to 150 dB or above. This type of polluting sound may damage the cochlea of the inner ear and can develop permanent deafness, called acoustic trauma.
Question 17. Mention the adverse effects of noise pollution on humans and other animals. What are the harmful impacts of sound pollution can exert on the ears and heart in a human body?
Answer:
Adverse effects of noise pollution on man:
The adverse effects of noise pollution on humans are mentioned below.
1. Effect on the ear:
- Hearing a high-frequency sound for a prolonged period causes the sound-sensory cells of the organ of Corti inactive. In this case, the person may gradually become deaf. Drivers of metro rail face similar problem.
- A sudden sound of more than 150 dB may rupture the eardrums and may damage the cochlea to cause permanent deafness. Survivors of bomb blasts often face similar consequences.
2. Effect on heart:
- Hearing high-intensity noise causes excitement which in turn increases heartbeat.
- Continuous hearing a noise above 90 dB increases systolic pressure.
- Prolonged listening to a sound above 60 dB may cause myocardial infarction to the listener.
- Hearing high-intensity sounds for some time increases the chance of a heart attack.
3. Other effects:
- Noise pollution leads to mental depression.
- High-intensity sound causes a lack of concentration.
- It may lead to insomnia.
- Noise curtails physical ability and enhances fatigue.
- A person may become ill-tempered with the effect of noise pollution.
Adverse effects of noise pollution on animals
The adverse effects of noise pollution on animals are mentioned below.
1. Deafness:
A high-intensity sound may cause deafness in animals.
2. Hampered reproduction:
Noise changes the reproductive behaviour of many animals. The population of birds and several other animals has shrunk significantly due to noise pollution.
3. Effect on foetal growth:
It is experimentally proved that high-intensity sound restricts foetal development in rats. Speculate the probable causes of each of the following phenomena
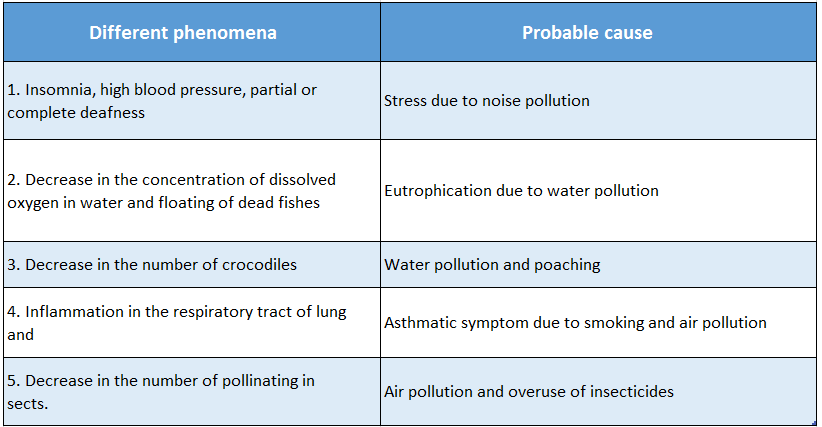
Question 18. Speculate the probable causes of each of the following phenomena.
- Insomnia, high blood pressure, partial or complete deafness,
- Decrease in the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water and floating of dead fishes,
- Decrease in the number of crocodiles,
- Inflammation in the respiratory tract of lungs and
- Decrease in the number of pollinating insects.
Answer:
Probable causes of different phenomena
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by environmental pollution?
Answer:
Environmental pollution:
The state of the environment, when different materials, harmful for the normal existence of plants and animals, reach beyond the admissible level, is called environmental pollution. Presently this is the most alarming environmental issue all over the world.
Question 2. What is meant by pollutants?
Answer:
Pollutants:
The substances which cause undesirable changes in the environment by harming the biosphere are called pollutants. The huge amount of pollutants on earth is the main cause of environmental pollution.
Example-Sand particles, CO2, NO2, SO2, lead, mercury, pollen grains, etc.
Question 3. Into how many types did environmentalist EP Odum classify the environmental pollutants?
Answer:
E P Odum, the famous environmentalist, classified environmental pollutants into two main types. These are
- Biodegradable pollutants and
- Non-biodegradable pollutants.
Question 4. What is meant by biodegradable pollutants?
Answer:
Biodegradable pollutants:
There are certain complex polluting compounds, which are degraded easily into. simple compounds by biological decomposition with the help of bacteria and other microbes. These are known as biodegradable pollutants.
Example-Household organic wastes.
Question 5. What is meant by non-biodegradable pollutants?
Answer:
Non-biodegradable pollutants:
There are certain complex, polluting substances which do not degrade easily into simple compounds by biological decomposition. These compounds are recycled in the food chain for a very long time. These are known as non-biodegradable pollutants.
Example-DDT, polythene.
Question 6. What are primary air pollutants?
Answer:
Primary air pollutants:
The air pollutants, which are produced directly by natural processes or man-made ones and mix in the atmosphere to cause air pollution, are called primary air pollutants.
Example-CO2, SO2, suspended particulate matter, ozone, etc.
Question 7. What are secondary air pollutants?
Answer:
Secondary air pollutants:
Several primary air pollutants present in the atmosphere undergo reactions among each other in the presence or absence of sunlight to produce more harmful polluting substances. These are called secondary air pollutants.
Example-Sulphuric acid, nitrous acid, smog, peroxyacetyl nitrate, etc.
Question 8. What is meant by polluted air?
Answer:
Polluted air:
The air, which contains pollutants like carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, different oxides of nitrogen, dust particles, hydrogen sulphide, etc. beyond the admissible limit is called polluted air.
It has harmful effects on human beings, animals and plants. Polluted air is a major issue of health concern in all developing countries.
Question 9. What is meant by pollution-free air?
Answer:
Pollution-free air:
The air, which is either pollutant-free or may contain a few of it well below the admissible limit, is called pollution-free air. Pollution-free air is abundant in seacoasts and hilly areas.
Question 10. What is an ozone hole?
Answer:
Ozone hole:
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), halone, etc. released due to human activities break the ozone gas of the ozonosphere into O2, making holes in the ozone layer. It is called an ozone hole. The decrease of concentration of the ozone layer is called ozone depletion.
Question 11. Write the harmful effects of the ozone hole.
Answer:
Some of the harmful effects of ozone hole are-
- The UV ray of sunlight easily enters into the earth through the ozone hole. This UV ray causes skin cancer, cataract, etc.
- UV ray destroys certain good bacteria of soil and air causing loss of crop production.
Question 12. How is PAN produced in the atmosphere?
Answer:
PAN produced in the atmosphere As Follows:
In the presence of sunlight, nitrogen dioxide reacts with hydrocarbons in the atmosphere to produce a colourless gas called PAN or peroxyacetyl nitrate. PAN is a secondary air pollutant causing irritation in eye, and inflammation in the respiratory system, especially in the trachea, etc.
Question 13. How does automobile exhaust cause air pollution?
Answer:
Automobile exhaust cause air pollution:
Automobile exhaust contains various harmful gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, etc. All these gases cause air pollution. About 40% of total air pollution occurs due to the gases released from automobiles.
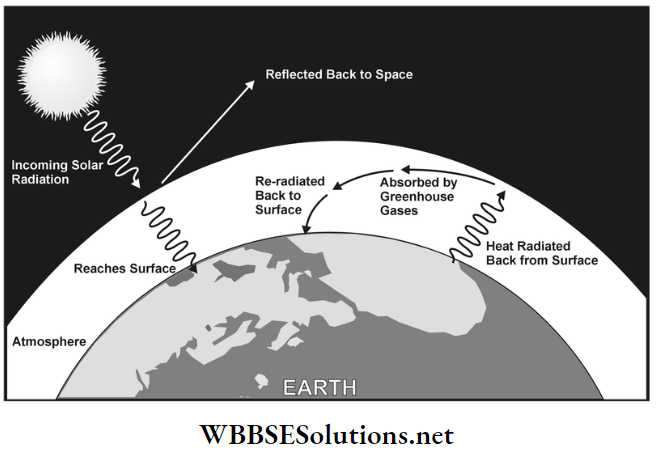
Question 14. What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer:
Greenhouse effect:
Accumulation of gases like carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbon, water vapour, etc. creates a gaseous layer in the atmosphere. This layer does not allow heat to escape from Earth.
Instead, it is reflected back to the earth’s surface continuously. This heat increases the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere. This is known as the greenhouse effect.
Question 15. What are the different components of SPM? Or, Give some examples of common SPM.
Answer:
The different components of SPM
SPM are very fine, amorphous particles, that are light enough to be suspended in air. These include pollen grains, fly ash, coal dust, soil dust, metal oxide particles, asbestos particles, unburnt carbon particles or soot, etc.
Question 16. Mention various sources of SPM.
Answer:
Various sources of SPM:
Some common sources of SPM in the atmosphere are automobile exhaust, emissions from factory chimneys, soil dust, dust from agricultural fields, carbon dust from oil refineries, and pollen grains from forests.
Question 17. What are the harmful effects of SPM?
Answer:
Different harmful effects of SPM are as follows-
- SPM lesser than 10 μm can enter into the bloodstream and can cause cancer.
- SPM cause harm to the nasal passage, pharynx, trachea and lungs. These substances cause bronchitis, laryngitis, tuberculosis, black lung disease, lung cancer, etc.
- Changes in heart rate and heart attack are some of the severe harmful effects of SPM.
- SPM also creates smog which in turn reduces visibility and causes acid rain.
Question 18. What is aerosol?
Answer:
Aerosol:
Several very fine, colloidal, solid particles, and microdroplets of volatile liquids and vapours remain suspended in the air. These are called aerosols. These particles have a diameter of less than lu. Dust, smoke, etc. are some examples of aerosols.
Question 19. What is smog?
Answer:
Smog:
In the presence of sunlight, air-borne hydro-carbons undergo a photochemical reaction with nitrogen oxides that have been released especially by automobiles to produce a smoky gaseous substance in the atmosphere.
This smoky gas mixes with atmospheric moisture to make a greyish misty surrounding which blurrs our vision. This is called smog. Simply we can say that smog is a mixing of fog and smoke.
Question 20. Mention two causes of an increase in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
Answer:
Two causes of the increase in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are as follows-
- Excessive burning of different fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, mineral oils, natural gases, etc.
- Indiscriminate deforestation also increases carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.

Question 21. How does acid rain cause damage to the Taj Mahal and other marble architecture?
Answer:
The chief component of marble is calcium carbonate (CaCO3). When these marble objects are exposed to nitric acid and sulphuric acid of acid rain, calcium carbonate reacts with these acids to form calcium nitrate and calcium sulphate respectively.
As a result, the marble gets corroded and loses its lustre. This is called ‘stone leprosy’ or ‘stone cancer.
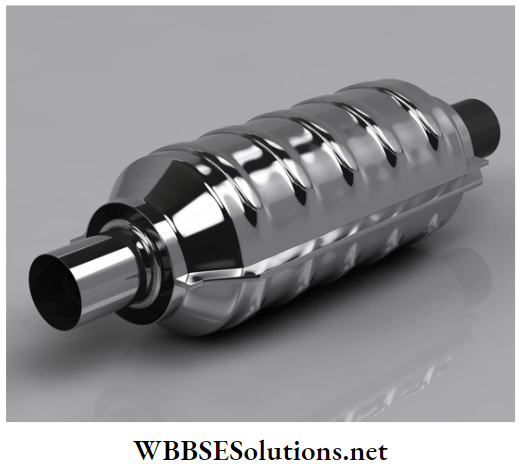
Question 22. Name two devices used to remove air pollutants.
Answer:
Devices used to remove air pollutants
Certain instruments are now used to remove various pollutants from the air. Two of the common air pollution-controlling devices are electrostatic precipitators and catalytic converters.

Question 23. What is water pollution?
Answer:
Water pollution:
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies (example-lakes, rivers, oceans, underground water, etc.). It occurs when pollutants are directly or indirectly discharged into waterbodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful
compounds from water.
Consumption of this polluted water causes various health hazards in different organisms including human beings.
Question 24. Mention two causes of water pollution.
Answer:
Two causes of water pollution are-
- Mixing of agricultural wastes including fertilisers, pesticides, herbicides, etc.
- Mixing of industrial wastes including various toxic chemicals, boiling water, radioactive wastes, etc. in waterbodies.
Question 25. What is meant by physical pollution of water?
Answer:
Physical pollution of water:
The pollution, in which water of any waterbody becomes turbid, foul-smelling with a bad taste due to the accumulation of different polluting substances, is called physical pollution of water.
Physical pollution makes water unsuitable for drinking and survival of several aquatic species.
Question 26. What is algal bloom?
Answer:
Algal bloom:
The process or situation in which a large and excessive growth of algae on or near the surface of fresh and saline waterbodies naturally or as a result of the oversupply of nutrients from organic pollution.
Harmful effects of algal bloom are blocking of sunlight, depletion of oxygen levels and sceretion of toxins in the water. Thus algal bloom very often results into the eutrophication of waterbodies.
Question 27. What is eutrophication?
Answer:
Eutrophication:
Water pollutants often contain inorganic phosphates and nitrates, which, when get mixed to any stagnant waterbody increase the nutrient level of the water.
In this nutrientrich water bodies, different phytoplanktons grow very fast, which results into the deterioration of water quality and oxygen levels. This condition is called eutrophication.
Question 28. Mention a few characteristic features of eutrophic water bodies.
Answer:
A few characteristic features of eutrophic waterbodies are as follows-
- Presence of excess nutrients in water and development of algal bloom. This turns the colour of the water into the green.
- Eutrophic waterbodies have a reduced level of dissolved oxygen which causes the death of aquatic animals, mainly fishes.
- The decomposition of algal bodies produces a substance) which reduces biodiversity in aquatic toxic substances, viz, strychnine (a toxic ecosystem.
Question 29. Why does oxygen level decrease in eutrophic waterbodies?
Answer:
In eutrophic waterbodies, the algal bloom occurs very fast. After the death of these algae and other plankton, a huge amount of organic matter decompose and accumulate in the floor.
A large quantity of dissolved oxygen is consumed during this decomposition process by decomposing bacteria and that is why, the oxygen level decreases in eutrophic waterbodies.
Question 30. Name the pollutants present in crop field wastes.
Answer:
The pollutants present in crop field wastes are
- Insecticides like DDT, BHC, etc.,
- Nitrate and phosphate-containing different inorganic fertilisers.
Question 31. What does agricultural runoff mean?
Answer:
Agricultural runoff:
The excess fertilisers, pesticides, crop remnants, soil particles, etc. are washed off from the crop fields during heavy rain or overflooding of irrigation water. This is called agricultural runoff. Agricultural runoff is one of the most principal agents of water pollution.
Question 32. What does BOD or biological oxygen demand mean?
Answer:
BOD:
After mixing of industrial wastes in any waterbody, the population of plankton and microorganisms increases. For respiration, these organisms absorb excess oxygen from the water body.
As a result, a need for dissolved oxygen increases in the water which is called BOD or Biological Oxygen Demand.
Question 33. What is COD? What is its significance?
Answer:
COD:
The Chemical Oxygen Demand or COD is an indicative measure of the available amount of oxygen consumed during a reaction in a definite measured solution. SI unit of COD is mg/L.
Significance:
COD is a measure of water and wastewater quality. It helps in deciding the disposal of organic and inorganic effluents of domestic and industrial origin.
Question 34. How does infection of cholera occur? Mention its symptoms.
Answer:
Infection of cholera:
Cholera is a bacterial disease. Its causative agent, Vibrio cholerae is a water-borne bacterium. The person may get infected with cholera when consuming water directly or indirectly contaminated with Vibrio cholera.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of cholera are severe diarrhoea, vomiting followed by extreme dehydration and even death.
Question 35. How does Infection of typhoid occur? Mention its symptoms.
Answer:
Infection of typhoid:
Typhoid is a bacterial disease. The causative agent is a water-borne bacterium, Salmonella typhi. The person may get infected with typhoid when intakes water contaminated with Salmonella typhi.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of typhoid are high fever with headache, abdominal pain and diarrhoea.
Question 36. Mention two main causes of soil pollution.
Answer:
Two main causes of soil pollution are as follows-
- Pathogenic germs-The medical wastes and municipal wastes contain thousands of germs, which pollute soil.
- Chemicals- Chemical fertilisers, pesticides, industrial and household wastes contain different harmful non-biodegradable chemicals that cause ‘soil pollution.
Question 37. How does atomic pollution occur in soil?
Answer:
After atomic explosion or by dumping of byproducts from atomic reactors and atomic power plants, different radioactive substances mix in soil. By this process, atomic pollution occurs in soil.
Question 38. Which type of pesticides causes maximum soil pollution?
Answer:
Organochlorine pesticides, like DDT, BHC, aldrin, etc. cause maximum soil pollution. These are highly stable compounds, which retain their harmful effect for a long time within the soil. without any degradation.

Question 39. Which metallic elements cause soil pollution?
Answer:
Different metallic elements and their salts, released through industrial wastes, cause serious type of soil pollution. These elements include lead, mercury, cadmium, nickel, zinc, copper, etc.
Question 40. Which metallic elements mix with soil from pesticides?
Answer:
Various pesticides contain metallic elements, like copper, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, etc. as compounds. During the application of such pesticides, these elements get mixed in soil and result in soil pollution.
Question 41. What are the effects of soil pollution?
Answer:
The effects of soil pollution are as follows-
- Diseases like tetanus, gas-gangrene, and aspergillosis occur.
- Bioaccumulation of non-biodegradable pollutants takes place in an animal body. Their quantity gets increased with time, that finally causes toxicity.
Question 42. What is meant by edaphic pathogens?
Answer:
Edaphic pathogens:
Certain soil-dwelling microbes those cause numerous health hazards are called edaphic pathogens. Example-Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax disease, is an edaphic pathogen.
Question 43. What is meant by rodenticides?
Answer:
Rodenticides:
There are certain chemicals that are used to kill rodents, especially the field rats. These are called rodenticides.
Example-Endrin, phosphide compounds, etc.
Question 44. What is meant by biomagnification?
Answer:
Biomagnification:
The process by which various biodegradable chemical substances relentlessly into different trophic levels through the food chain and gradually increase their quantity in different living organisms at higher trophic level is called biomagnification.
DDT is one of those chemicals, which undergoes biomagnification.
Question 45. What is meant by bioaccumulation?
Answer:
Bioaccumulation:
Bioaccumulation is the net accumulation of harmful substances in an organism from all the resources, like water, air or food. Certain pollutants, enter into animal bodies through food and do not undergo metabolic changes.
Without being excreted, these compounds accumulate in certain animal tissues, especially the adipose tissues. In the course of time, the quantity of these compounds increases in many folds in the animal bodies causing bioaccumulation.
Question 46. How does fly ash cause environmental pollution?
Answer:
Fly ash causes environmental pollution in two ways, which are as follows-
- Soil pollution- Fly ash does not contain any nutrients. If this dust is piled to fill up a low land, the soil underneath it becomes infertile.
- Air pollution-The particles of fly ash are very light. Hence are flown away by the wind. As a result, it adds SPM in the air.
Question 47. Differentiate between biomagnification and bioaccumulation.
Answer:
Differences between biomagnification and bioaccumulation-
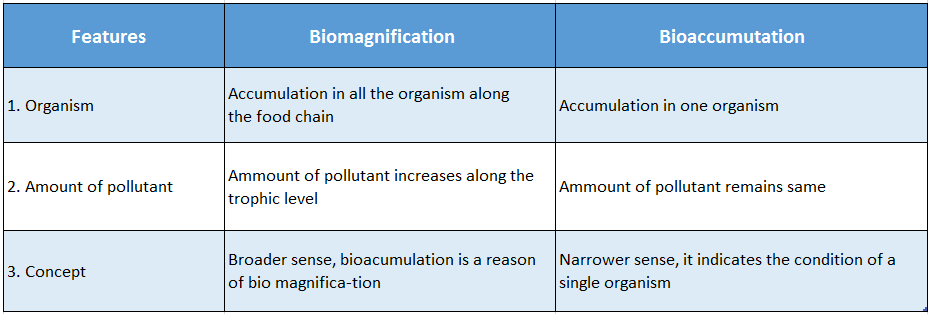
Question 48. List the harmful effects of the following pollutants-
- Greenhouse gas,
- SPM,
- chemical fertilisers used in agriculture,
- Non- biodegradable insecticides.
Answer:
The harmful effects of some pollutants are as follows-
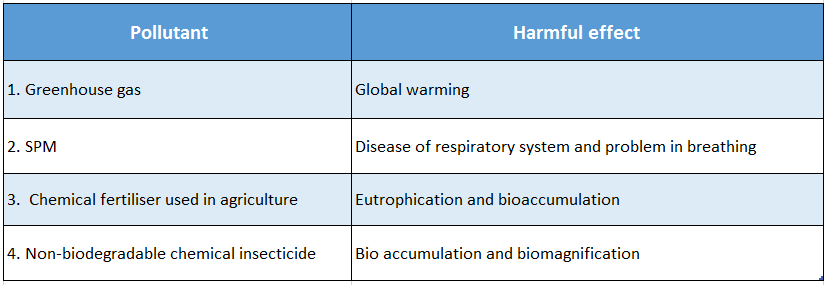
Question 49. What is meant by audible sound?
Answer:
Audible sound:
The sound with a frequency ranging between 20 Hz to 20000 Hz is audible to the human ear. This is called an audible sound. The human ear is unable to detect any sound with a frequency below or above this range.
Question 50. What is meant by acoustic trauma?
Answer:
Acoustic trauma:
A sudden sound of very high intensity may cause permanent damage to the cochlea of the internal ear which may results in complete hearing loss. This is called acoustic trauma.
Question 51. What is bel and decibel?
Answer:
Bel and decibel:
Bel and decibel are the units to measure the intensity of sound. Decibel (dB) is one-tenth of a bel which is popularly used to measure sound intensity. The term bel is coined to honour the great scientist Alexander Graham Bell.

Preventive Measures for Environmental Pollution
Question 52. Which home appliances may cause noise pollution?
Answer:
Washing machines, vacuum cleaners, mixer grinders, high-wattage music systems, etc. are a few common home appliances, which cause noise pollution.
Question 53. What is meant by auditory fatigue?
Answer:
Auditory fatigue:
When sound waves of high frequency are received by our ear for a prolonged period, the sensory cells of the ear become temporarily inactive. This situation is called auditory fatigue. A sound, with an intensity higher than 90 dB can cause such distress.
Question 54. What is meant by PM-10 and PM-2.5?
Answer:
PM-10 and PM-2.5:
PM-10 indicates the larger suspended particulate matter in air, which are less than 10 μ in diameter. Dust particles, asbestos fibres etc. belong to PM-10.
Whereas, PM-2.5 denotes the diameter of smaller air-borne particulate matter, which are less than 2.5 μ in diameter. PM-2.5 includes diesel particulate matter that are released through the exhaust of diesel engines.
Question 55. Mention the harmful effects of PM-10 -10 what are the harmful effects of PM-2.5?
Answer:
Harmful effects of PM-10:
These suspended particulate matters cause cough, burning sensation in the throat, breathing distress, asthma, etc.
Harmful effects of PM-2.5:
These finer particulate matter can reach the alveoli of the lungs. Therefore, these are more harmful than PM-10. These may cause asthma, blood-related diseases, lung cancer, etc.
Question 56. What is the masking effect?
Answer:
Masking effect:
The masking effect is noise pollution in which any undesired noise of higher intensity hinders the impact of other desired sounds.
Example-In a noisy class, students cannot listen to the teacher properly.
Question 57. What is a silence zone?
Answer:
Silence zone:
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has decided that the maximum sound intensity should be 50 dB during the day near hospitals, schools, courts, etc. This zone is called the silence zone.
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution MCQs
Question 1. The main greenhouse gas is—
- Oxygen
- Ozone
- Carbon dioxide
- Chlorofluorocarbon
Answer: 3. Carbon dioxide
Question 2. The gas emitted from refrigerator and air- condition industries is—
- N2O
- SO2
- CFC
- H2O2
Answer: 3 CFC
Question 3. The normal amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide is about—
- 0.1%
- 0.01%
- 0.03%
- 0.3%
Answer: 3. 0.03%
Question 4. Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
- Methane
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
Answer: 2. Oxygen
Question 5. The main source of methane in the environment is—
- Anaerobic respiration by microorganisms in marshy land
- Bacterial decomposition in hot springs
- Volcanic eruption
- Lightning
Answer: 1. Anaerobic respiration by microorganisms in marshy land
Question 6. Which of the following is fossil fuel?
- Methane
- Mineral oil
- Coal
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Question 7. Gas produced by the incomplete oxidation of fossil fuel is—
- Nitric oxide
- Hydrogen sulphide
- Carbon monoxide
- Chlorofluorocarbon
Answer: 3. Carbon monoxide
Question 8. A poisonous breath-choking gas is—
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Carbon monoxide
Answer: 4. Carbon monoxide
Question 9. The ozone layer is present in the—
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Exosphere
- Mesosphere
Answer: 2. Stratosphere
Question 10. The gas that causes maximum damage to the ozone layer is—
- Carbon dioxide
- PAN
- Chlorofluorocarbon
- Carbon monoxide
Answer: 3. Chlorofluorocarbon
Question 11. CFC gas is emitted from—
- Oil refineries
- Refrigerator factories
- Automobiles
- Smog
Answer: 2. Refrigerator factories
Question 12. The microorganisms of wetlands produce—
- Methane
- Aerosol
- Elinver
- Butane
Answer: 1. Methane
Question 13. The pollutant emitted from foam, mattress factories is—
- PAN
- Lead
- CFC
- NO
Answer: 3. CFC
Question 14. The plant part responsible for air pollution is—
- Flower
- Fruit
- Leaves
- Pollen grains
Answer: 4. Pollen grains
Question 15. The full form of PAN is
- Para acetyl nitrate
- Peroxyacetyl nitrate
- Peroxy acid nitrate
- Para acidic nitrogen
Answer: 2. Peroxyacetyl nitrate
Question 16. CO2, SO2 and NO are
- Primary pollutant
- Secondary pollutant
- Tertiary pollutant
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Tertiary pollutant
Question 17. PAN, SO3, HNOX are
- Primary pollutant
- Secondary pollutant
- Portial polutant
- Not polllutant
Answer: 2. Secondary pollutant
Question 18. An example of SPM is
- Lead
- Pollen grain
- Aerosol
- Plastic
Answer: 2. Pollen grain
Question 19. Which type of pollution is caused by SPM?
- Air pollution
- Soil pollution
- water pollution
- Sand pollution
Answer: 1. Air pollution
Question 20. The diameter of aerosol is—
- Less than 1μ
- 1.5μ
- 5-15μ
- More than 15μ
Answer: 1. Less than 1μ
Question 21. The main components of acid rain are—
- Hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid
- Maleic acid and formic acid
- Sulphuric acid and nitric acid
- Citric acid and tartaric acid
Answer: 3. Sulphuric acid and nitric acid
Question 22. The gas which is abundant in industrial area is—
- Oxygen
- Argon
- Sulphur dioxide
- Neon
Answer: 3. Sulphur dioxide
Question 23. A harmful effect of sulphur dioxide is—
- Inflammation of the respiratory tract
- Black spots on the skin
- Pancreatic disease
- Gastric ulcer
Answer: 1. Inflammation of the respiratory tract
Question 24. Natural source of sulphur dioxide is—
- Waterbodies
- Lightning
- Volcanoes
- Chemical factories
Answer: 4. Chemical factories
Question 25. Which of the following is the main source of sulphur dioxide in the air?
- Thermal power plants
- Hydropower plants
- Atomic power plants
- Chemical industries
Answer: 1. Thermal power plants
Question 26. Due to acid rain, maximum damage occurs to
- Wooden houses
- Glasswares
- Marble sculptures
- Porcelain articles
Answer: 3. Marble sculptures
Question 27. The diseases associated with air pollution
- Diarrhoea, typhoid, hepatitis
- Hepatitis, bronchitis, deafness
- Bronchitis, asthma, lung cancer
- Lung cancer, polio, malaria
Answer: 3. Bronchitis, asthma, lung cancer
Question 28. In underdeveloped countries, water pollution is caused mainly due to—.
- LIuman and cattle wastes
- Thermal power plants
- Industrial by-products
- Atomic power plants
Answer: 1. LIuman and cattle wastes
Question 29. An example of a biochemical water pollutant is—
- Brick
- Sand
- Stone
- Detergent
Answer: 4. Detergent
Question 30. A water-insoluble pollutant is—
- Hydrogen sulphide
- Salt
- Arsenic
- Plastic
Answer: 4. Plastic
Question 31. The component of detergent that causes maximum water pollution is—
- Alkali
- Sulphate
- Phosphate
- Nitrate
Answer: 2. Sulphate
Question 32. The metallic particles, which cause maximum water pollution, are—
- Lead and mercury
- Sodium and potassium
- Iron and copper
- Magnesium and silver
Answer: 1. Lead and mercury
Question 33. Living water pollutants are—
- Wood pieces
- Pebbles
- Worms, protozoans, aquatic insects
- Insecticides and detergents
Answer: 3. Worms, protozoans, aquatic insects
Question 34. Maximum water pollution is caused by—
- Mineral plants
- Paper and leather industries
- Electronic Industries
- Steel Industries
Answer: 2. Paper and leather industries
Question 35. The recommended pH of drinking water is—
- 3.5 to 5.5
- 6.5-8.5
- 9.5-11.5
- 15.5-13.5
Answer: 2. 6.5-8.5
Question 36. The dissolve O2 (DO) of normal water is—
- 1 ppm
- 3 ppm
- 8 ppm
- 10 ppm
Answer: 3. 8 ppm
Question 37. The full form of COD is—
- Common Oxygen Demand
- Common Oxygen Development
- Chemical Oxygen Demand
- Chemical Oxygen Development
Answer: 3. Chemical Oxygen Demand
Question 38. COD is measured to know the level of—
- Water pollution
- Air pollution
- Soil pollution
- Noise pollution
Answer: 1. Water pollution
Question 39. BOD is used to measure—
- Demand of CO2
- Demand of hydrogen
- Demand of oxygen
- Demand of nitrogen
Answer: 3. Demand of oxygen
Question 40. An increase in BOD of water indicates—
- Distilled water
- Water pollution
- Drinking water
- Presence of excess minerals in the water
Answer: 2. Water pollution
Question 41. With the increase in BOD, the amount of dissolved oxygen in water—
- Decreases
- Increases
- Remains unchanged
- All of these
Answer: 1. Decreases
Question 42. The bacterium used as a bio-indicator of water pollution is—
- Bacillus subtilis
- Thiobacillus denitrificans
- E. coli
- Rhizobium leguminosarum
Answer: 3. E. coli
Question 43. A water-borne disease is—
- Measles
- Hepatitis
- pox
- Malaria
Answer: 2. Hepatitis
Question 44. Cholera is a type of—
- Air-borne disease
- Soil-borne disease
- Water-borne disease
- Protozoan disease
Answer: 3. Water-borne disease
Question 45. The harmful toxin released by algae is—
- Neurotoxin
- Phyllotoxin
- Oxytocin
- Coli
Answer: 1. Neurotoxin
Question 46. A protozoon present in waterbodies is
- Ebtamoeba histolytica
- Salmonella typhi
- Vibrio cholera
- E. coli
Answer: 1. Ebtamoeba histolytica
Question 47. Amoebiasis and giardiasis are caused by—
- Protozoa
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Algae
Answer: 1. Protozoa
Question 48. The source of underground water pollution is—
- Mercury
- Cadmium
- Arsenic
- Fluorine
Answer: 3. Arsenic
Question 49. The acceptable limit of arsenic in drinking water is—
- 0.15 ppm
- 0.05 ppm
- 0.20 ppm
- 0.09 ppm
Answer: 2. 0.05 ppm
Question 50. Black foot disease is caused by which of the pollutant?
- Arsenic
- Lead
- Mercury
- Cadmium
Answer: 1. Arsenic
Question 51. The event of rapid reproduction and growth of phytoplanktons in a waterbody is called—
- Fungal bloom
- Bacterial bloom
- Algal bloom
- Protozoal bloom
Answer: 3. Algal bloom
Question 52. Eutrophication results in the increase of—
- Algae
- Fungi
- Mosses
- Ferns
Answer: 1. Algae
Question 53. An increase in nutrient levels in water bodies is known as—
- Biomagnification
- Eutrophication
- Nutrition
- Nitrification
Answer: 2. Eutrophication
Question 54. A large amount of eutrophication is caused by—
- Carbon compounds
- Sulphate compounds
- Phosphate compounds
- Nitrate compounds
Answer: 3. Phosphate compounds
Question 55. Which of the following effect is the result of water pollution?
- Global warming
- Eutrophication
- Deafness
- Bronchitis
Answer: 2. Eutrophication
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Question 56. Among the following, excessive soil pollution is caused by—
- Iron, copper and silver
- Lead, arsenic and cadmium
- Calcium, magnesium and sodium
- Calcium, potassium and magnesium
Answer: 2. Lead, arsenic and cadmium
Question 57. The organism which is mostly affected due to soil pollution is—
- Crab
- Fish
- Earthworm
- Microbes
Answer: 3. Earthworm
Question 58. The waste matter from a thermal power plant that causes soil pollution is—
- Mineral oil
- Radioactive matters
- Fly ash
- Hot water
Answer: 3. Fly ash
Question 59. The cause of soil pollution is—
- Increase in pH
- Increase in salinity
- Droppings of birds
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 60. A non-biodegradable substance is—
- Leather
- Wood
- Plastic
- Paper
Answer: 3. Plastic
Question 61. Use of ammonium nitrate fertiliser causes—
- Increase in soil acidity
- Increase in soil fertility
- Decrease in soil acidity
- Decrease in soil salinity
Answer: 1. Increase in soil acidity
Question 62. A human disease caused by nitrogenous fertilisers is—
- Pneumonia
- Anaemia
- Methemoglobinemia
- Scurvy
Answer: 3. Methemoglobinemia
Question 63. Soil acidity increases—
- Due to the plantation of the eucalyptus plant
- Due to the plantation of evergreen plants
- Due to the cultivation of vegetable plants
- Due to the cultivation of paddy plants
Answer: 1. Due to the plantation of the eucalyptus plant
Question 64. The best way to prevent soil pollution is by
- Performing chemical farming
- Performing organic farming
- Using tractor
- Performing inorganic farming
Answer: 2. Performing organic farming
Question 65. The fertiliser that reduces soil acidity is
- Potassium-containing fertiliser
- Urea-containing fertiliser
- Phosphorus-containing fertiliser
- Sulphur-containing fertiliser
Answer: 1. Potassium-containing fertiliser
Question 66. The water retention capacity of soil is increased by using—
- Chemical fertilisers
- Organic manures
- Insecticides
- Weedicfdes
Answer: 2. Organic manures
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Question 67. Which type of plants increases soil fertility by nitrogen fixation?
- Leafy vegetables
- Leguminous crops
- Paddy plants
- Wheat plants
Answer: 2. Leguminous crops
Question 68. Parallel cultivation of Azolla in paddy fields increases the quantity of—
- Potassium
- Phosphate
- Sulphur
- Nitrogen
Answer: 4. Nitrogen
Question 69. Application of urea fertilisers supplements the need of—
- Copper
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
- Nitrogen
Answer: 4. Nitrogen
Question 70. An insecticide available from plants is—
- Malathion
- BHC
- Lindane
- Pyrethin
Answer: 4. Pyrethin
Question 71. DDT is a type of—
- Organic manure
- Insecticide
- Inorganic fertiliser
- Biofertiliser
Answer: 2. Insecticide
Question 72. The insecticide that undergoes maximum biomagnification is—
- Carbamate
- Organophosphate
- Chlorinated hydrocarbon
- Organosulphate
Answer: 3. Chlorinated hydrocarbon
Question 73. Decide which of the following if remains for a long time in the environment, the probability of its biomagnification increases—
- Newspaper
- Faecal matters of animals
- Rotten leaves
- Chlorinated insecticide
Answer: 4. Chlorinated insecticide
Question 74. Which of the following is associated with biomagnification—
- Phosphate
- Detergent
- DDT
- CFe
Answer: 3. DDT
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Question 75. Gradual increase in the quantity of pollutants in the food chain is called—
- Bioaccumulation
- Biomagnification
- Biodiversity
- Acidification
Answer: 2. Biomagnification
Question 76. The unit of measuring sound intensity with respect to noise pollution is—
- Millibel
- Centibel
- Decibel
- Decibel
Answer: 4. Decibel
Question 77. The sound intensity of the electric air horn is about—
- 40 dB
- 70 dB
- 140 dB
- 100 dB
Answer: 3. 140 dB
Question 78. The intensity of sound that causes the physiological disorder is—
- 35-45 dB
- 45-55 dB
- 80-90 dB
- 60-70 dB
Answer: 3. 80-90 dB
Question 79. By using earplugs, the intensity of sound can be reduced up to—
- 45-60 dB
- 10-45 dB
- 60-75 dB
- 50-100 dB
Answer: 2. 10-45 dB
Question 80. The most harmful effect of noise pollution is—
- Partial loss of hearing
- Complete loss of hearing
- Tremor of hands and legs
- Cardiac palpitations
Answer: 2. Complete loss of hearing
Question 81. Hearing high-intensity sound for a long time causes—
- A tremor in hands and legs
- Auditory fatigue
- Nervous disorder
- Anaemia
Answer: 2. Auditory fatigue
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Question 82. The part of the ear which is affected the most due to noise pollution is—
- Retina
- Valve
- Organ of Corti
- Auditory nerve
Answer: 3. Organ of Corti
Question 83. The type of disease caused due to noise pollution is—
- Only physical disease
- Only mental disease
- Both physical and mental disease
- Dental disease
Answer: 3. Both physical and mental disease
Question 84. The decrease in the number of birds in the urban area is due to—
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Air pollution
- Noise pollution
Answer: 4. Noise pollution
Question 85. The intensity of sound that increases systolic pressure, is more than—
- 65 dB
- 85 dB
- 90 dB
- 110 dB
Answer: 3. 90 dB
Question 86. To prevent noise pollution, cars are fitted with—
- Silencer
- Condenser
- Converter
- Compressor
Answer: 1. Silencer
Question 87. Educational institutions and hospitals are considered as silence zones up to a periphery of—
- 50 m
- 100 m
- 300 m
- 400 m
Answer: 2. 100 m
Question 88. To protect ears from noise pollution, one should use—
- Eardrum
- Earplug and earmuff
- Hearing aid
- Gloves
Answer: 2. Earplug and earmuff
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution VSAQs
Question 1. Which substances cause maximum air pollution?
Answer: Automobile exhausts and gases emitted from chemical industries cause maximum air pollution.
Question 2. Name two greenhouse gases.
Answer:
Two greenhouse gases
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) and methane (CH4) are two greenhouse gases.
Question 3. Which are the main sources of air polluting hydrocarbons?
Answer: Combustion of fossil fuel and emission from chemical factories are the main sources of air polluting hydrocarbons.
Question 4. Which are the two main air pollutants in urban cities?
Answer: Hydrocarbons and aerosols are the two main air pollutants in urban cities.
Question 5. What is the main cause of air pollution in metro cities?
Answer: Automobile emission is the main cause of air pollution in metro cities.
Question 6. What is fly ash?
Answer:
Fly ash
Fine solid particles of ashes, dust and soot produced from burning fossil fuels, like- coal, mineral oils in thermal power plants or paper are called fly ash.
Role of Legislation in Controlling Pollution
Question 7. What is the name of the gas responsible for the Bhopal gas tragedy?
Answer: The gas which is responsible for the Bhopal gas tragedy is methyl isocyanate.
Question 8. Name the fine particulate matter liberated due to the incomplete combustion of petroleum from oil refineries.
Answer: Petcoke dust are the fine particulate matter liberated due to the incomplete combustion of petroleum from oil refineries.
Question 9. How do SPM cause harm to human respiration?
Answer: The SPM, suspended in air, cause irritation in the pharynx and breathing distress.
Question 10. Which pollutant of automobile exhaust prevents haemoglobin formation in blood?
Answer: Lead, liberated from automobile exhaust prevents haemoglobin formation in blood.
Question 11. Name a symbiotic association that acts as a bio-indicator of air pollution.
Answer: Lichen is a symbiotic association that acts as bio-indicator of air pollution.
Question 12. Which pollutant reduces chlorophyll content in green plants?
Answer: Sulphur dioxide
Life Science Class 10 Wbbse
Question 13. Name two gases responsible for acid rain.
Answer: Two gases responsible for acid rain are sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide.
Question 14. Name two famous architectures in India, which are vulnerable to acid rain.
Answer: The Taj Mahal of Agra and the Victoria Memorial of Kolkata are two famous. architectures in India, which are vulnerable to acid rain.
Question 15. Which gas is emitted during a volcanic eruption?
Answer: Sulphur dioxide
Question 16. What is the full form of COPD?
Answer: The full form of COPD is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Question 17. Mention two adverse effects of carbon monoxide on human health.
Answer: Two adverse effects of carbon monoxide on human health are breathing distress and fatal blood toxicity.
Question 18. Name a gas which causes lung cancer.
Answer: Sulphur dioxide gas causes lung cancer.
Question 19. Name the harmful component that enters in to the lungs during smoking.
Answer: During smoking, the harmful component named chlorobenzene enters into lungs.
Question 20. Which disease often occurs among the miners of coal mines?
Answer: Black-lung disease often occurs among the miners of coal mines.
Question 21. Name three main types of insecticides.
Answer: Organochlorine, organophosphate carbamate
Question 22. What is the full form of DDT?
Answer: The full form of DDT is dichloro- diphenyltrichloroethane.
Question 23. Name two organochlorine insecticides.
Answer: Two organochlorine insecticides are DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) and BHC (Benzene hexachloride).
Question 24. Name two water-insoluble bio-pollutants.
Answer: Dry leaves and algae
Question 25. What is sewage?
Answer:
Sewage
The domestic waste matters and human excreta, which are discharged through municipal waste disposal systems, are collectively Answer: called sewage.
Question 26. Name two water-borne viral diseases.
Answer:
Two water-borne viral disease
Hepatitis A and polio
Question 27. Name two water-borne bacterial diseases.
Answer: Cholera and bacillary dysentery are two water-borne bacterial diseases.
Question 28. Name two water-borne protozoan diseases.
Answer: Amoebiasis and giardiasis are two water-borne protozoan diseases.
Question 29. Name two water-borne helminthic diseases.
Answer: Taeniasis and ascariasis are two water-borne helminthic diseases.
Question 30. Name the bacterium which causes typhoid.
Answer: Salmonella typhi
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Solutions
Question 31. Name the bacterium which causes cholera.
Answer: Vibrio cholera
Question 32. Name two harmful toxins produced by algae.
Answer: Neurotoxin and hepatotoxin
Question 33. What depth of a tube well is unlikely to contain arsenic?
Answer: A tube well with a depth of 500-600 ft is unlikely to contain arsenic.
Question 34. What is the acceptable limit of fluorine in drinking water in India?
Answer: The acceptable limit of fluorine in drinking water in India is less than 1.2 mg/L.
Question 35. Which salt is predominant in seawater?
Answer: Sodium chloride is predominant in seawater.
Question 36. With which type of pollution is arsenic concerned?
Answer: Arsenic is concerned with water pollution.
Question 37. When does eutrophication occur?
Answer: When excess amounts of nutrients mix in waterbodies by the addition of various water pollutants, eutrophication occurs.
Question 38. What happens to the level of dissolved oxygen in case of eutrophication?
Answer: In the case of eutrophication, the level of dissolved oxygen is decreased in water bodies.
Question 39. Name two types of fertilisers responsible for eutrophication.
Answer: Phosphate and nitrate-containing fertilisers
Question 40. What is the accumulation of pollutants in a trophic level known as?
Answer: The accumulation of pollutants in a trophic level is known as bioaccumulation.
Question 41. In which animal tissue generally bioaccumulation occurs?
Answer: Generally, in the adipose tissue of animals bioaccumulation occurs.
Question 42. Which disease is caused due to cadmium pollution?
Answer: Itai-itai
Question 43. What is commonly meant by land pollution?
Answer: Land pollution is commonly meant by soil pollution.
Question 44. Which worms are released from infected human body that contaminate soil?
Answer: Roundworms and hookworms
Question 45. Which method is applied to burn pollutants to cut down the chance of soil pollution?
Answer: To cut down the chance of soil pollution, pollutants are burnt by the incineration method.
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Solutions
Question 46. What happens when excess nitrogenous fertilisers are added to fields?
Answer: Adding excess nitrogenous fertilisers to fields increases the acidity of the soil.
Question 47. What happens when excessive irrigation is done on a crop field?
Answer: The soil becomes saline if excessive irrigation is done on a crop field.
Question 48. Name the worm which causes ascariasis.
Answer: The roundworm named lumbricoides causes ascariasis.
Question 49. Name the sound-receiving structure in the ear.
Answer: The sound-receiving structure in the ear is the organ of Corti.
Question 50. Which disease may occur as an adverse effect of noise pollution?
Answer: Myocardial infarction may occur as an adverse effect of noise pollution.
Question 51. In India, what is the acceptable intensity of sound during the daytime?
Answer: In India, the acceptable intensity of sound during the daytime is 65 dB.
Question 52. What is the admissible limit of motor vehicle-generated sound, fixed by the Central Pollution Control Board in India?
Answer: The admissible limit of motor vehicles- generated sound, fixed by the Central Pollution Control Board in India is 70 dB.
Question 53. What is the full form of NIHL?
Answer: The full form of NIHL is Noise Induced Hearing Loss.
Question 54. Which measures should we take to avoid the adverse effects of noise pollution?
Answer: To avoid the adverse effects of noise pollution, we must use earplugs and earmuffs.
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. From refrigeration industry, ________ is evolved.
Answer: CFC
Question 2. ________ is a nitrogenous greenhouse gas.
Answer: Nitrous(N2O)
Question 3. By the combustion of fossil fuels, a greenhouse gas named ________ the atmosphere.
Answer: CO2
Question 4. An inflammable greenhouse gas produced from paddy fields is ________.
Answer: Metliane (CH4)
Question 5. The fine droplets of smoke, ashes, dust, pollen grains, etc. suspended in air collectively called ________, which cause various lung diseases.
Answer: Suspended particulate matters (SPM)
Question 6. The air-borne particulate matters less than a diameter of ________ are called aerosols.
Answer: 1μ
Question 7. ________ gas is produced due to the decomposition of garbage.
Answer: Methane
Question 8. The pH of water bodies ________ after acid rain.
Answer: Reduces
Question 9. The architecture built of ________ and limestone are damaged by acid rain.
Answer: Marble
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Solutions
Question 10. The ________ present in marble reacts with acid rain to produce sulphate and nitrate.
Answer: Calcium carbonate
Question 11. SO2, NOX, etc. increase the occurrence of ________ among people living in industrial area.
Answer: Asthma
Question 12. A respiratory disease caused due to air pollution is ________.
Answer: Bronchitis/Asthma
Question 13. The miners of coal mines often develop ________ diseases.
Answer: Black lung
Question 14. The disease caused due to squeezing of the trachea is called ________.
Answer: COPD
Question 15. Pollution due to silica fibres is responsible for ________ disease.
Answer: Silicosis
Question 16. DDT is an ________ pesticide.
Answer: Organic
Question 17. ________ is a toxic material released by algae.
Answer: Neurotoxin
Question 18. Salmonella typhi causes ________ disease.
Answer: Typhoid
Question 19. Cholera is caused by the ________ bacterium.
Answer: Vibrio cholera
Question 20. The pathogen causing amoebiasis is ________.
Answer: Entamoeba histolytica
Question 21. Mixing of arsenic with groundwater causes ________ disease.
Answer: Arsenicosis
Question 22. In ________ disease, blisters and black marks are seen on palms and feet.
Answer: Arsenicosis
Question 23. To produce the bottled cold drinks widely sold in the market, a lot of ________ water is wasted.
Answer: Fresh
Question 24. The soil-dwelling microbes are called ________ microbes.
Answer: Edaphic
Question 25. To kill field rats, ________ insecticide is used.
Answer: Endrin
Question 26. Paris green is an ________ pesticide.
Answer: Inorganic
Question 27. Sodium arsenite is a ________.
Answer: Weedicide
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Solutions
Question 28. ________ is an insecticide that causes soil
Answer: DDT
Question 29. Soil pollutants enter into the human body by direct ________.
Answer: Touch
Question 30. Fungal spores of Aspergillus mostly affect the ________ system of humans and poultry.
Answer: Respiratory
Question 31. Aspergillus causes a lung disease called ________.
Answer: Aspergillosis
Question 32. Clostridium tetani is a/an ________ bacterium that causes tetanus.
Answer: Edaphic
Question 33. ________ is a disease caused due to soil pollution.
Answer: Tetanus
Question 34. A soil-dwelling worm is ________.
Answer: Ascaris sp.
Question 35. The pathogen of anthrax is a/an ________ bacteria.
Answer: Edaphic
Question 36. In India, the admissible level of intensity of sound in an industrial area is ________.
Answer: 90 dB
Question 37. Hearing a sound beyond ________ for a prolonged period may cause myocardial infarction.
Answer: 60 dB
Question 38. High intensity sound ________ heart rate.
Answer: Increases
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution State True Or False
Question 1. Methane is a greenhouse gas.
Answer: True
Question 2. O3, is used in aerosol spray.
Answer: False
Question 3. In SPM disease, the trachea is inflamed.
Answer: True
Question 4. Acid rain is caused by SO2, and NO2 gases formed due to air pollution.
Answer: True
Question 5. The Taj Mahal is adversely affected by acid rain.
Answer: True
Question 6. Black lung disease is a water-borne disease.
Answer: False
Question 7. A decrease in pH of waterbodies hampers the ecological balance.
Answer: True
Question 8. Aldrin is an inorganic pesticide.
Answer: False
Question 9. High fever is a significant symptom of cholera.
Answer: False
Question 10. Arsenicosis is caused due to mercury pollution.
Answer: False
Question 11. In the case of eutrophication, the colour of the water bodies becomes bluish.
Answer: False
Question 12. Amoebiasis is caused by the infection of Entamoeba.
Answer:True
Question 13. Neurotoxin is usually secreted by fungi.
Answer: False
Wbbse Class 10 Life Science Solutions
Question 14. Algal bloom indicates the high growth of algae.
Answer: True
Question 15. A degradable pollutant is responsible for biomagnification.
Answer: False
Question 16. Bacillus anthracis is a water-borne bacterium.
Answer: False
Question 17. Echinococcus.is a type of fungus.
Answer: False
Question 18. Ascaris is a type of roundworm.
Answer: True
Question 19. Toxic pollutants generally accumulate in the adipose tissue of animals.
Answer: True
Question 20. The unit, used to measure air pollution is decibel.
Answer: False
Question 21. Noise pollution is the second most dangerous polluting hazard.
Answer: True
Question 22. CPCB has laid down the permissible sound intensity level at 40 dB for motor vehicles.
Answer: False
Question 23. If sound intensity reaches beyond 90 dB, it may cause a rise in systolic pressure.
Answer: True
Question 24. A sound of more than 150 dB caused by firecrackers may lead to acoustic trauma.
Answer: True
Question 25. Myocardial infarction is caused due to water pollution.
Answer: False
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Match The Columns
Question 1.
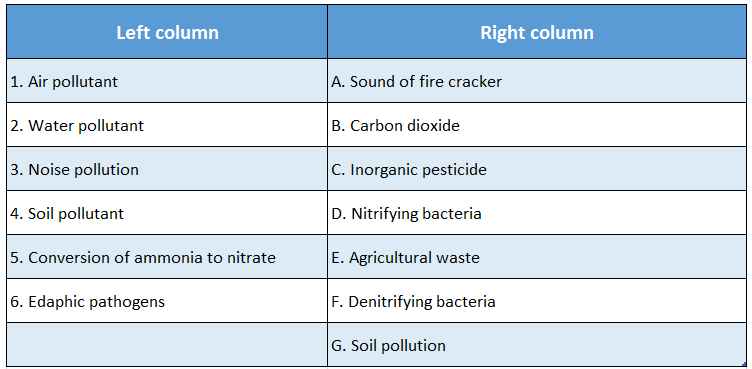
Answer: 1-B; 2-E; 3-A; 4-C; 5-D; 6-G
Question 2.
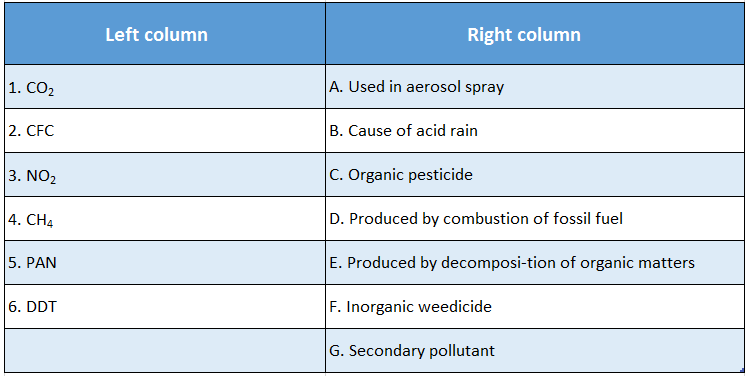
Answer: 1-D; 2-A; 3-B; 4-E; 5-G; 6-C
Question 3.
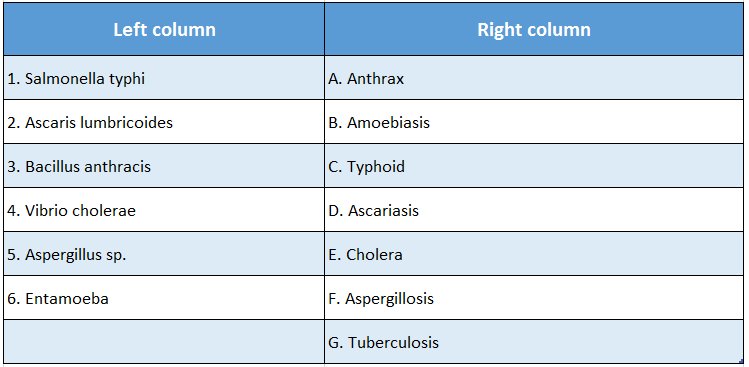
Answer: 1-C; 2-D; 3-A; 4-E; 5-F; 6-B
Question 4.
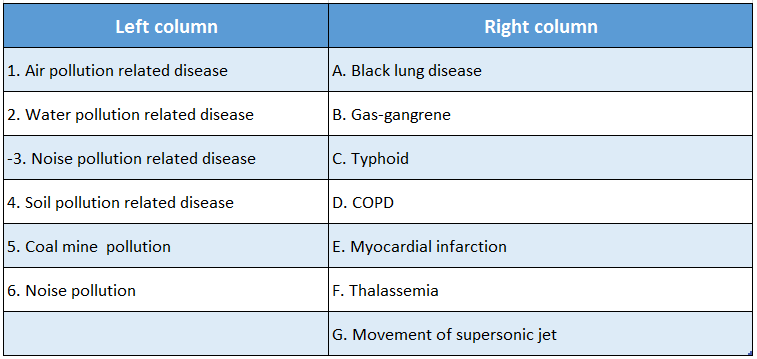
Answer: 1-D, 2-C, 3-E, 4-B, 5-A, 6-G
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Find The Odd One Out
Question 1. SPM, CO2, N2O, CH4
Answer: SPM
Question 2. Corrosion of marble structures, Acidification of soil, Acidification of water, Breathing distress
Answer: Breathing distress
Question 3. Nitrous oxide, Ammonia, Carbon dioxide, Methane
Answer: Ammonia
Question 4. Emphysema, Asthma, Amoebiasis, Bronchitis
Answer: Amoebiasis
Question 5. Taenia solium, Bacillus anthracis, BHC, PAN
Answer: PAN
Question 6. Arsenic, Bioaccumulation, Lead, PAN
Answer: PAN
Question 7. Eutrophication, Algal bloom, Gastrointestinal infection, COPD
Answer: COPD
Question 8. O3,SO2,CH4, CO2
Answer: SO2
Question 9. Metal Particle, Rain, Pollen grains, Dust particle
Answer: Rain
Question 10. Refrigeration industry, CFC, Aerosol spray,CH4
Answer: CH4
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Fill In The Blanks By Looking At The First Pair
Question 1. CFC: Greenhouse effect:: Sulphur dioxide: _________
Answer: Acid rain
Question 2. SPM: Air pollution:: Algal bloom: _________
Answer: Water pollution
Question 3. Carbon monoxide Air pollution:: DDT: _________
Answer: Biomagnification.
Question 4. Lead: Dyslexia:: Mercury: _________
Answer: Minamata
Question 5. Eutrophication: Water pollution:: Bronchitis: _________
Answer: Air pollution
Question 6. Clostridium tetani: Soil pollution:: Entamoeba histolytica: _________
Answer: Water pollution
Question 7. Myocardial infarction: Sound pollution:: Typhoid: _________
Answer: Water pollution
Chapter 5 Topic 2 Environmental Pollution Among The Four Concepts Given Three Of Them Belong To One Find That
Question 1. Emphysema, Air pollution, Asthma, Eye irritation
Answer: Air pollution
Question 2. SPM, Air pollution, Greenhouse gas, Lung disease
Answer: Air pollution
Question 3. Acid rain, H2SO4, HNO3, H2O
Answer: Acid rain
Question 4. Eutrophication, Water pollution, Algal bloom, Detergent
Answer: Water pollution
Question 5. Pesticides used in agriculture, Typhoid, Water pollution, Liquid wastes from factories
Answer: Water pollution
Question 6. Entamoeba sp., Water pollution, Vibrio choleriae, Arsenic contamination
Answer: Water pollution
Question 7. Arsenic, Copper, Cadmium, Bioaccumulation
Answer: Bioaccumulation
Question 8. DDT, BHC, Urea, Soil pollution
Answer: Soil pollution
Question 9. Deafness, Myocardial infarction, Noise pollution, Increased heart rate
Answer: Noise pollution
