Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Rest And Motion
In our daily life, we come across various objects; some of them move but others remain where they are. Suppose you enter a room.
A chair lying in the room does not move or change its position with respect to the surroundings of the room. We say that the chair is in a state of rest.
Now coming out of the room you go to your balcony and see a car speeding along the road from there.
It means that the car is changing its position with respect to you and your building both of which are stationary. Thus the car is in a state of motion.
Hence objects around us can either be in a state of rest or in motion. Let us define rest and motion to get a clear idea
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Notes For Class 6 School Science
Rest:
When an object does not change its position with respect to its surroundings, the object is said to be at rest.
Motion:
When an object changes its position with respect to its surroundings, the object is said to be in motion.
Thus objects associated with the states of rest and motion are known as stationary and moving objects respectively. These may be defined as
Stationary object:
An object which does not change its position with respect to time is called a stationary object.
Moving object:
An object which changes its position with respect to time is called a moving object.
Seemingly, rest and motion are opposed to each other, yet there is a close relation between them and it is very difficult to say, whether an object is in a state of rest or in a state of motion.
Think about the fact that whenever we describe the motion of a body or object we knowingly or unknowingly take another body to be at rest.
In fact to measure the distance traveled by a body or how fast the body is moving, we require another body at rest to do so.
For example, we say a car is moving speedily on the road. But how can we say that? The answer is that here the road is taken to be at rest and the car is described to be moving on the stationary road with a certain speed.
Let us take another somewhat more difficult instance. A boy is found running along the corridor of a moving train.
How can we describe his motion when both the train and the boy are moving together? Actually here, to describe the motion of the boy.
The train is assumed to be at rest and the distance of the moving boy is compared with respect to a certain object inside the train, say, the door of the compartment on one side.
This simplifies our understanding of rest and motion. Again let us analyze a somewhat similar sort of situation.
When traveling in a train we can very well say that we are at rest inside the compartment (since we are sitting inside it).
But somebody standing on the platform of a station says a different story since he sees that we are moving at a certain speed.
Who is correct then? In fact, both of them are correct.
The confusion arises since they are describing the same situation standing at different locations (for us it is the compartment of the train and for the man, it is the platform outside the moving train).
We are at rest if the train is supposed to be at rest and on the other hand, we are moving if the platform is supposed to be at rest.
Thus we see that the description of the motion of a body (static or dynamic position) changes if the location of the viewer changes.
Always noiensmib remember that the location of the viewer is of utmost importance in any description of motion.
WBBSE Class 6 Force and Energy Notes
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Force And It’s Unit
The use of the word ‘force’ is very common in our daily life. We use force to walk on the ground, lift a bucket full of water, push a heavy bookshelf, or throw a cricket ball.
In fact, it is our common experience that unless we apply force on a stationary body, it will not move out on its own and will remain stationary forever.
On the other hand, it is equally true that a moving body will continue its motion forever along a straight line unless it is disturbed by some force.
But unlike the previous case this time our senses cannot accept it since we never see such a motion.
Does a moving ball continue to roll forever? Before answering the puzzle let us discuss a commonly observed phenomenon.
You must have noticed that if a ball is rolled on a smooth floor, it goes further than it goes on ordinary ground.
Why does it happen like that? Actually, a ball gets various sorts of resistance while it is in motion-some may be due to the nature of the ground or floor and others may be due to the air surrounding the ball.
All these invisible resistances are actually forces that try to stop the motion of the ball. A ball thus does not roll forever because external forces retard the motion of the ball.

A smooth floor offers less retarding force compared to the ground and hence the ball goes further on it.
In this way, we can make a conception that if the external force be eliminated, the force-free ball would go on moving in a straight line forever.
Hence the lesson we get from the discussion is that an external force is required to change either the state of rest or of motion of a body.
A force can thus make a body move, or make a moving body stop, or make it move slower or faster, or change the direction of motion of the moving body.
Force:
A force may be defined as an external cause that changes or tends to change the state of rest or of the uniform motion of a body in a straight line.
In the CGS system, a unit of force is called dyne. In the SI system, the unit of force is called Newton.
carefully observe the fact that the word ‘force’ There are different types of forces, but generally denotes a push or a pull.
We can exert and apply a push through something rigid, while a push and pulls. We must pull can act through a non-rigid connector such as a rope or a wire.

Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Effects Of Force
A force can bring about the following effects as shown below:
1. It can set a stationary body into motion.
- A railway engine can move a stationary train by applying a pull or push.
- A boy can set a ball into motion by hitting it with a bat.
2. It can stop a moving body.
- A speeding car is stopped by the application of brakes.
- A boy can stop a rolling football directed towards him in the field.
3. It can change the speed or direction of the old movement of a moving body.
- A moving bicycle runs faster when
- A stone is thrown vertically upward slows down after attaining a height, Sal changes its speed and stops for an instant
4. It can bring about change in the dimensions of a body
A stretching force increases the length ady of a rubber band. A compressive force shortens the length of a spring
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Force Without Touch
Push and pull were discussed earlier. These forces are to be applied through something rigid or non-rigid. Hence these are called contact forces.
There are other forces that do not make contact with the objects and yet act on them through space. These are called non-contact forces or forces at a distance.
Gravity is an invisible force, with which a body is attracted or pulled towards the earth. There is nothing attached to the body by which the force is applied.
A body on the earth’s surface is in a very strong gravitational field of earth and hence, the body experiences the force of attraction due to the earth’s gravity.
This gravitational force is called the weight of the body. It has the same units as those of force stated earlier.
Another example of the non-contact type of force is found in a magnetic field. When a magnet attracts another magnet or a magnetic substance (such as Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, etc.), there is nothing visible, which is pulling them together or separating them.

Thus around a magnet, there is a magnetic field that is responsible for this type of non-contact force. The magnetic field pushes or pulls other magnets or magnetic materials.
Electromagnetism and nuclear force are other two examples of non-contact forces.
Electromagnetism is the force that causes the interaction between electrically charged bodies or between an electrically charged body and a magnet.
The area inside which this force is active is called the electromagnetic field. The nuclear force is active between fundamental particles like protons, neutrons, etc inside the nucleus of an atom.
It is charge independent. However, its range is very very small compared to gravity and electromagnetic forces.
Based on the above examples some characteristics of non-contact type of forces may be mentioned as under :
- The gravitational force is always attractive in nature, while the electromagnetic, magnetic, and electrostatic forces can be either attractive or repulsive.
- The non-contact forces depend on the distance of separation between the bodies. It decreases with the increase in separation and increases with the decrease in separation.
- These are action-reaction types of forces,90107 to atole. they are mutual.
- The forces may be long-range or short-range forces.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Energy Its Different Forms Energy Sources And Energy Crisis
When we wake up in the morning after a good night’s sleep we are full of capacity to start
the day’s work. As the day progresses, gradually our capacity to do work diminishes.
At night our capacity reduces to a minimum. We say that we are extremely tired since our energy is exhausted throughout the day in doing various jobs.
Similarly, if we do not eat for a long time, we feel tired and hence lose the capacity to do any work. These happen due to a lack of energy.
Thus energy may be defined as follows:
Energy The capacity of a body to do work is called energy.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Types of Energy
For the sake of understanding, energy is divided into two kinds: Kinetic energy and Potential energy.
A shooting arrow can pierce through a log. A wall may collapse if a speeding car collides with it. A stone thrown towards an earthen pot from a distance can break it when it hits it. These are known to us.

Now think about the above cases in a different way. Can an arrow pierce a log if it vans gently touches it?
Can a wall collapse if a comes in contact with it extremely slowly Can a stone break a pot if it is gently kept on it? The answer is ‘no’ in all the cases.
What then is the cause behind these phenomena whereby a work is done by a moving body? The arrow, the car, or the stone acquires kinetic energy due to motion by virtue of which they are able to perform the intended work.
Hence, when a body does work by virtue of its motion, it is said to have kinetic energy.
Similarly, the destruction of huts by fast-blowing stormy wind, carrying of load by running water in its path, etc., are other indign examples of kinetic energy.
Let us now understand what is potential energy by an example. Keep a nail on a wooden plank. Gently touch the head of the nail with a hammer.

Understanding Force and Energy
Nothing happens. The nail does not penetrate into the plank. The hammer sainerbandiser ofni bolondr af ygrone fralstoola nin s 19ns frant una lesinedasin is now raised a bit and the nail is hit with it i botrovic.

It is seen that the nail gets penetrated into the plank. The change in position of the hammer makes it accumulate energy which does the work in the latter case.
Hence, if a body does work by virtue of its position or configuration, it is said to have potential energy. Another example may be a catapult and a stone.
The stone is set in the catapult by stretching the string. When the string is released, the stone flies off due to the stretched string.
Here it is the change of shape of the string which provides potential energy to the string to do work on the stone.
When a spring is pressed forcefully, it undergoes compression. Pressure changes the shape of the spring and it contracts.
Thus it gains potential energy. This potential energy develops an ability inside the spring to do some work. For this reason, it jumps away when the pressure is removed and it recovers its normal shape.
If a block is used to pressurize the spring, the block flies away as the spring elongates and jumps back to its normal shape and configuration.
Kinetic energy and potential energy are together called Mechanical energy.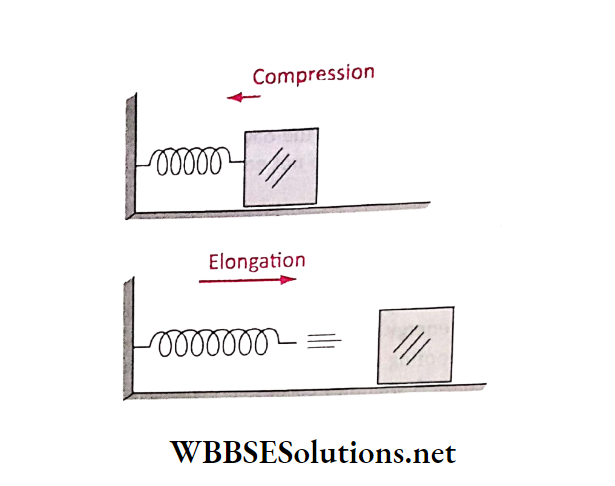
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Transformation Of Energy
In actual practice, there are 8 forms of energy prevalent in nature such as mechanical energy, heat energy, light energy, sound energy, electrical energy, magnetic energy, chemical energy, and atomic energy.
Whenever work is done anywhere in the universe, one form of energy gets converted to another form of energy. No new energy is created or destroyed in the universe.
Important Definitions Related to Force and Energy
1. Conversion of mechanical energy into other forms of energy:
- When palms are rubbed, the mechanical energy due to rubbing is converted into heat energy and palms become warm.
- During hitting a drum with sticks, mechanical energy is transformed into sound energy.
- When a knife is rubbed against the grinding stone mechanical energy changes into heat, light, and sound energy.
2. Conversion of heat energy into mechanical energy:
In a steam engine heat energy is converted into mechanical energy.
3. Conversion of electrical energy into other forms of energy:
- When a motor is run, electrical energy is converted into mechanical and heat energy.
- When a fan rotates, electrical energy is transformed into mechanical and heat energy.
- When light is put on, electrical energy changes into light and heat energy.
- During the charging of a battery, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
4. Conversion of light energy into other forms of energy:
- During photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- In photovoltaic cells, light energy is transformed into electrical energy.
5. Conversion of chemical energy into other forms of energy:
- When fuels are burnt, chemical energy is converted into heat and mechanical energy.
- When the cracker explodes, chemical energy changes into heat, light, and sound energy.
- When water is poured on quick lime, chemical energy is converted into heat energy which vaporizes the water.
6. Conversion of magnetic energy into other forms of energy:
When a magnet attracts iron particles, magnetic energy is converted into mechanical energy.
7. Conversion of atomic energy into other forms of energy:
During nuclear fusion or fission, atomic energy changes into heat and light energy.
8. Conversion of sound energy into other forms of energy:
When an explosion occurs, sound energy is converted into mechanical energy and vibration occurs.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Sources of Energy
All forms of energy which are available on Earth have their origin from the sun. The solar energy that Earth receives every day, gets transformed into various sources of energy.
The transformation of solar energy into other forms of energy is depicted in the flow chart. it may be described as follows:
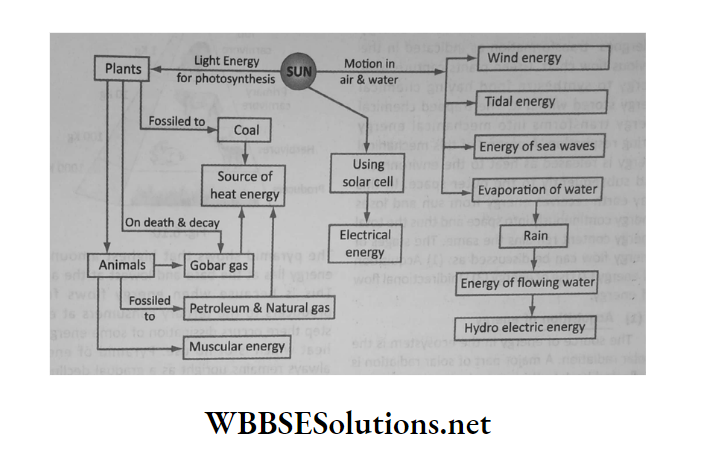
1. Solar energy is stored in green plants during photosynthesis as chemical energy. Hence they are termed as producers.
2. The chemical energy stored inside plants remains intact when they are buried for very long periods under the surface of the earth to form fossil fuels such as coal.
Coal is excavated out and used as a source of energy in thermal power plants or in domestic and other industrial sectors.
3. If the green plants do not form fossils after death, they can be converted into biogas. This process converts the stored chemical energy of dead plants into heat energy on burning.
4. When plants are consumed by animals, the chemical energy of plants changes into heat energy during respiration.
This heat energy supplies the necessary mechanical energy required to perform the daily work and keeps the body warm.
5. When animals die, their bodies get buried under the earth for a long period to be converted into petroleum and natural gas. These are the sources of heat energy for all industries and automobiles.
6. Remains of dead animals can be utilized to generate biogas.
7. Solar energy provides light energy which helps us to see things around.
8. Solar energy is directly converted into electrical energy by solar photovoltaic cells.
9. Solar energy provides wind energy, tidal energy, and energy from sea waves.
10. Solar energy maintains the water cycle. It causes large-scale evaporation of water from water bodies. The water vapor condenses to form clouds.
Clouds cause rain which ultimately creates running or flowing streams. The energy of flowing streams is utilized to produce hydroelectric power and to drive water mills.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept of Energy Flow
The sun is the source of all energy. Energy never goes back to its source. In other words, the incoming solar energy to Earth never returns back to the sun.
The solar energy undergoes a transformation as indicated in the previous flow chart. Green plants capture solar energy to synthesize food having chemical energy stored within it.
The trapped chemical energy transforms into mechanical energy during respiration. A portion of this mechanical energy is released as heat to the environment and subsequently to outer space.
In this way, the earth receives energy from the sun and loses energy continuously into space and thus the total energy content remains the same.
The stages of energy flow can be discussed as:
- Acquisition of energy
- Use of energy
- Unidirectional flow of energy.
1. Acquisition Of Energy
The source of energy in the ecosystem is solar radiation. A major part of solar radiation is reflected back to space due to the presence of clouds, smoke, dust particles, etc.
Some portion of the solar energy is absorbed by the suspended solid particles of the atmosphere and some part is reflected by the surface of the earth.
Thus the remaining portion of the solar energy is entrapped by the chlorophyll of leaves where photosynthesis takes place.
As a result, light energy gets transformed into chemical energy and this chemical energy remains stored as potential energy inside the carbohydrate food matters produced by the green plants.
The green plants are called producers. Primary production is the amount and the rate of energy produced by the producers.
2. Use Of Energy
The transfer of energy takes place through the consumption of food. Producers are consumed by herbivorous animals and thus the potential energy of producers enters into the system of herbivores.
Herbivores are termed primary consumers. When carnivores feed on the herbivores they also acquire potential energy.
Thus the carnivores are termed secondary consumers. Thus when tertiary consumers consume secondary consumers, a similar flow? to School Science of potential energy takes place.
The representation of the energy flow in an ecosystem is called a pyramid of energy.
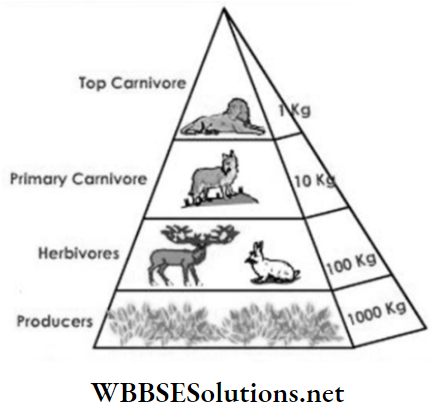
The pyramid shows that the highest amount of energy lies at the base and the lowest at the apex.
This is because when energy flows from producers to the tertiary consumers at each step there occurs dissipation of some energy as heat which is of no use.
The pyramid of energy always remains upright as a gradual decline of energy takes place from initiation to termination.
The energy stored by the various types of consumers in their tissues is known as secondary production.
The transfer of food energy from the source in green plants (producer) through a series of organisms (consumers) with repeated eating and being eaten occurs through the food chain.
The sequence of the eaters being eaten in an ecosystem is called the food chain.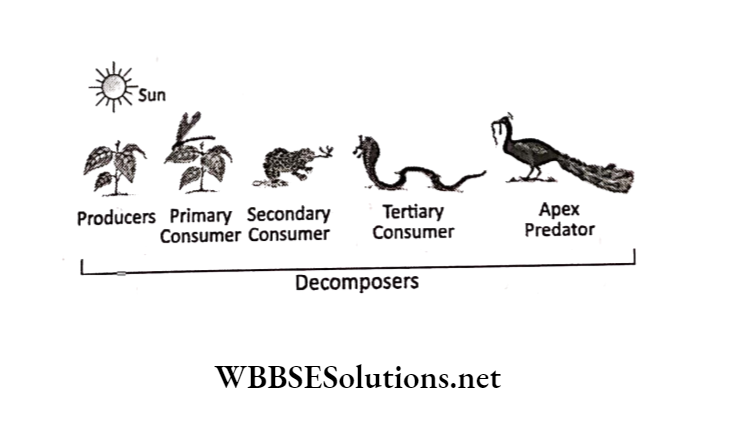
In an ecosystem the producer-consumer arrangement represents the trophic structure and each food level is called the trophic level.
Green plants at the base of the energy pyramid occupy the first trophic level.
Herbivores or primary consumers are second trophic level, carnivores or secondary consumers are at the third trophic level and tertiary consumers are fourth trophic level.
In the year 1942, Raymond Lindemann formulated the law called the 10 percent law.
According to this law, about 10% of total energy is transmitted during energy flow through several trophic levels to be used up for building the body mass, and the rest is dissipated as heat energy.
That is why we notice a diminution in the amount of energy from the first trophic level at the base to the fourth trophic level at the apex of the pyramid.
Energy used up by a body in order to function properly is called respiratory energy.
For example, 100 kg biomass in the grass will make 10 kg biomass for herbivorous animals (ex. Deer) and 1 kg biomass for carnivorous animals (ex. Tiger).
When different food chains of the same habitat are interconnected with each other to form a complicated network then the feeding relationship is known as a food web.
Examples of Real-Life Applications of Force
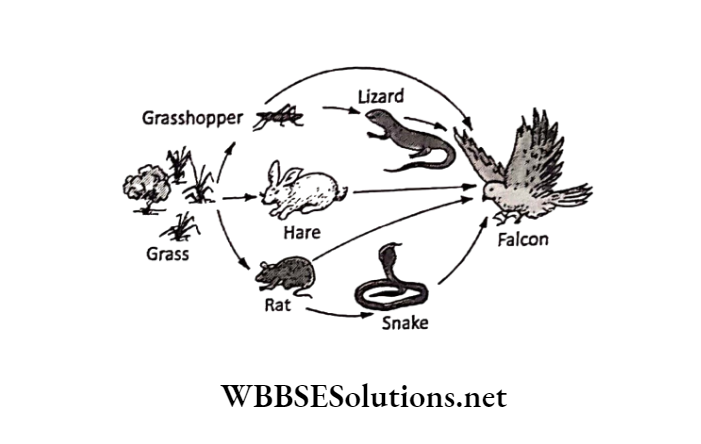
The interconnection and the inter-dependency in the food web make it more fundamental than the food chain.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Energy Crisis
The energy needs of human beings are increasing day by day because the use of energy provides comfort to modern life. The increasing population is leading to the growth of cities.
This, coupled with technological innovations, is resulting in the setting up of more industries.
The growth of transport and the modernization of agriculture are putting a heavy demand on energy consumption.
Because of this heavy demand and limited resources, the prices of energy sources are steadily increasing.
The indiscriminate use of energy resources on the one hand is leading to an energy crisis and on the other hand to global environmental pollution.
Unless some clean and cheap sources of energy are developed this energy crisis is likely to continue.
There are two types of resources of energy:
1. Non-renewable resources and
2. Renewable resources.
1. Non-renewable resources The sources of energy that, once finished, can not be.
Hence food web is more stable than a food chain. It is through the food web only that one animal of a food chain depends on many animals of other food chains and also of different trophic levels as food.
Regenerated over a reasonable period of time are called non-renewable resources of energy. Coal and petroleum fall in this category.
2. Renewable resources The sources of energy which do not exhaust or can be grown over a reasonable period of time are called renewable resources of energy. These resources include solar, tidal, hydel, wind, biomass, etc.
The need for non-conventional or renewable energy sources arises because:
- It was the energy crisis of 1973 and 1978 which forced people to recognize the vulnerability of oil-based energy solutions all over the world and sincere efforts were undertaken to develop renewable sources of energy.
- Conventional sources of energy like coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc are non-renewable and they’re on a wide scale. use is invariably associated with severe environmental pollution.
- Hydroelectric power generation is limited by topography and seasonal factors.
- The use of wood in villages leads to deforestation.
- Renewable sources provide energy in a decentralized manner to small areas and can be cultivated in places where it is difficult to carry fossil fuels or power lines.
- Large-scale use of renewable sources of energy can enlarge the life spans of fossil fuels and thereby, can reduce the burden of future energy crises.
For this reason, to cater to the energy crisis, the whole world, including India, is now conducting research on renewable resources of energy.
The major thrust is centered around the following sources
- Utilization of solar energy
- Conversion of solar energy into electricity
- Wind energy
- Biomass-based energy sources.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Frictional Forces In Our Daily Life
When a ball is rolled on the ground its speed decreases gradually and ultimately it stops after going through a certain distance.
If the same ball is rolled on a smooth floor, it goes further than it goes on the ordinary ground before stopping altogether.
Hence it does not roll forever whatever may be the surface. What causes it to stop after going through a certain distance? There must be an opposing force acting on the ball while it rolls which causes its speed to decrease gradually.
This retarding force is called friction. This retarding force also acts on a body while it is stationary. For example, if you are asked to push a heavy almirah you would see that a gentle push does not serve the purpose.
Even if you go on increasing the push, the heavy almirah moves only when your push exceeds a certain limit.
Hence friction prevents the almirah from being moved while it is stationary. It is therefore a contact force.
Friction: The force developed along the surface of contact of two bodies, which opposes the tendency of relative motion.
and the relative motion of the two bodies is called the force of friction or simply friction.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Phenomena Associated With Friction
Real-Life Scenarios Involving Energy Transformation
1. Friction produces heat:
1. When two palms are rubbed together, they become warm.
2. If a stone is rubbed on a metallic surface for some time, the metal becomes hot.
3. When we want to ignite a matchstick, we rub the stick on the rough surface of a matchbox.
The rough surface of the matchbox and the head of the matchstick both contain gunpowder on them. Rubbing causes the temperature to increase and heat is produced which ignites the matchstick.
2. Friction causes erosion of contact surfaces:
1. The tires of cars or cycles get eroded after a long run.
3. The smoother the surface the lesser is the friction:
1. If a ball is rolled on a smooth floor, it goes further than it goes on the ordinary ground before stopping altogether.
4. Friction Depends On the Mass Of The Body:
1. It is easier to push a single book on the
the surface of a table then pushing a number of books placed one on top of the other.
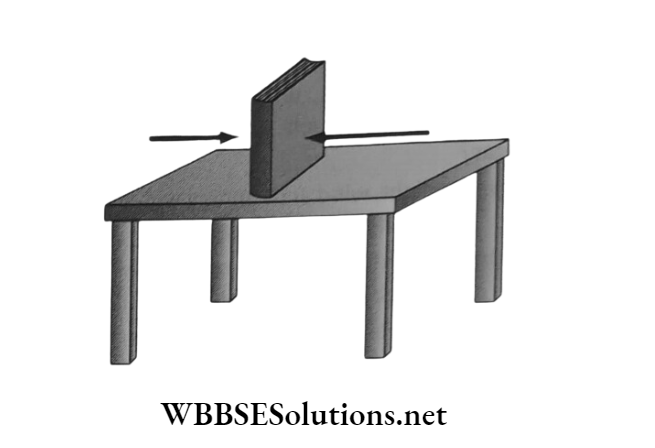
5. Friction Does Not Depend On Surface Area Of Contact:
1. If a book is pushed with its broader flat surface on the table and in another instance, its shorter flat surface on the table, on both occasions, it would be found that the same force is required to overcome friction through the same distance.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Causes Of Friction
The cause of friction is the roughness of the surfaces in contact. A surface is rough means there are irregular small projections (hills and dells) on the surface.
When one body is resting on another there is interlocking between these projections. So to move the body, it must be dislodged continuously from those interlockings.
An additional force is necessary. Hence we feel the friction.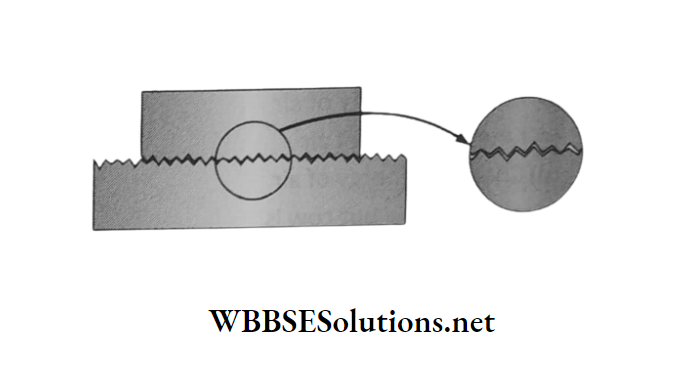
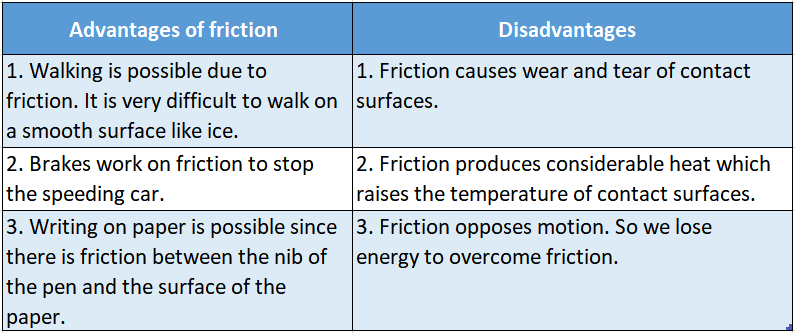
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Friction Advantages Of Friction: