Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Review Questions Environment Review Questions MCQs
Question 1. SI unit of pressure is
- Newton
- Pascal
- Bar
- Newton/Metre
Answer: 2. Pascal
Question 2. Pressure = Force/Area. With reference to this formula state which principle is applied in nail The to increase its pressure
- Area is increased
- Both area and force are increased
- Area is decreased
- Force is reduced
Answer: 3. Area is decreased
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 School Science
Question 3. Liquid flows from
- Lower pressure to higher pressure
- Higher pressure to lower pressure
- All of the above
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Higher pressure to lower pressure
WBBSE Class 6 Fluid Mechanics MCQs
Question 4. As the depth of water increases
- Only downward pressure would increase
- Only upward pressure would increase
- Only lateral pressure would increase
- Pressure in all directions would increase
Answer: 4. Pressure in all directions would increase
Question 5. Faster the rate of airflow, the ____________ the pressure.
- Higher
- Lower
- Same
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Lower
Question 6.If more force is applied on a certain surface area, pressure
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains the same
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Increases
Question 7. The lower portion of a dam’s wall is
- Thinner
- Same throughout
- Broader
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Broader
Question 8. The three surfaces of brick have an area of 50 sq. cm, 30 sq. cm, and 20 sq. cm respectively. The brick is released on mud in three ways so that its different surfaces come in contact with mud. The penetration of the brick inside the mud shall be maximum when it falls with its hot
- 50 sq. cm surface facing the mud
- 30 sq. cm surface facing the mud
- 20 sq. cm surface facing the mud
- Same in all of above
Answer: 3. 20 sq. cm surface facing the mud
Question 9. Fluid means
- Gas only
- Liquid only
- None of them
- Both of them
Answer: 4. Both of them
Question 10. The following is an airplane wing. Which of the following statements is true?
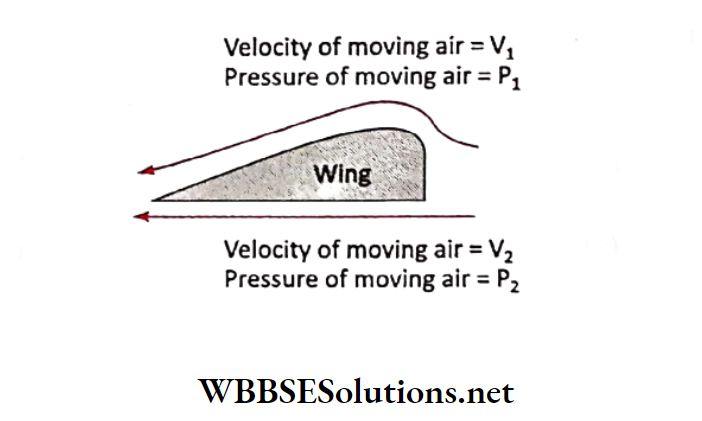
- V is greater than V, but P is smaller than P2
- V is smaller than V, but P is greater than P2
- V1 is greater than V2 and P, is greater than P2
- V is smaller than V, and P is smaller than P2
Answer: 1. V is greater than V, but P is smaller than P2
Question 11. The pressure exerted by a fluid depends on
- Quantity of the liquid
- Depth of the liquid
- The shape of the vessel
- The volume of the liquid
Answer: 2. Depth of the liquid
Understanding Statics and Dynamics of Fluids
Question 12. Pressure Force/Area In the light of this formula state which principle is applicable in the design of a camel’s feet.
- Area is increased
- Both area and force are increased
- Area is decreased
- Force is reduced
Answer: 1. Area is increased
Question 13. Application of Bernoulli’s theorem can be seen
- In making an airplane wing
- When tornados cause upliftment of roofs
- In a spray atomizer in a perfume bottle
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 14. According to Bernoulli’s principle, a moving fluid has
- No pressure
- More pressure where speed is more
- Less pressure where speed is more
- Constant pressure irrespective of speed
Answer: 3. Less pressure where speed is more
Question 15. 1 kilo Pascal =
- 1000 Pascal
- 1000 Newton per m2
- 0.1 Newton per cm2
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 16. The ground floor water tap of a building shows a pressure of 100 kPa. What will be the pressure in a tap on the tenth floor of the building?
- 100 kPa
- More than 100 kPa
- Less than 100 kPa
- None of these
Answer: 3. Less than 100 kPa
WBBSE Class 6 Science Question Answer
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. 1-kilo Pascal= __________ Pascal.
Answer: 1000
Question 2. The pressure of water __________ with the increase in depth of a well.
Answer: Increases
Question 3. Force = Pressure x __________
Answer: Area
Question 4. All __________ and __________ are regarded as fluids.
Answer: Liquids, Gases
Question 5. A moving fluid has less pressure at the place where its speed is __________
Answer: More
Question 6. The lower portion of a dam is made __________ than its upper portion.
Answer: Broader
Question 7. Fluid flows from a place with a __________ pressure to a place with a __________ pressure.
Answer: Higher, Lower
WBBSE Class 6 Science Question Answer
Question 8. The top of the wings of an airplane is somewhat __________ while the bottom is __________.
Answer: Curved, flat
Question 9. A force of __________ produces a pressure of 20 kPa when it acts on a surface having an area of 10 sq.m.
Answer: 200 kN
Question 10. A sharp knife generates __________ pressure at its cutting surface than a blunt knife.
Answer: More
Question 11. \(\frac{1 N}{1 sp.m}\) = ?
Answer: 1 Pa
Question 12. The pressure which a fluid exerts on the sides of the containing vessel below the free surface is called __________ __________.
Answer: Lateral Pressure
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Identify As True Or False
Question 1. Pressure in liquid decreases with depth.
Answer: False
Question 2. Thrust Pressure x Area
Answer: True
Question 3. Gases diffuse from a place of higher pressure to a place of lower pressure.
Answer: True
Class 6 WBBSE Science Question Answer
Question 4. A rubber sucker works on the principle of atmospheric pressure.
Answer: True
Question 5. Fluids do not exert pressure.
Answer: False
Question 6. Pressure is different at all points in a horizontal plane at a given depth within a liquid.
Answer: False
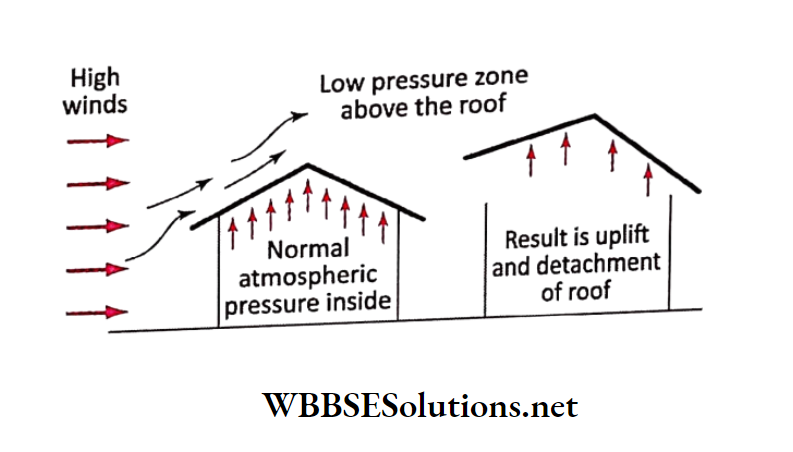
Question 7. Storms flow away thatched roofs of huts when inside pressure exceeds that in the outside.
Answer: True
Question 8. A pointed nail goes easily inside a wooden plank after hammering.
Answer: True
Question 9. Bernoullis’ principle has more application with regard to airflow than liquid flow.
Answer: False
Question 10. Increasing the applied force on the same area decreases the pressure.
Answer: False
Question 11. A blunt knife is more useful for cutting than a sharp knife.
Answer: False
Question 12. 1 kilo Pascal = 1000 Newton per square meter.
Answer: True
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Match The Columns
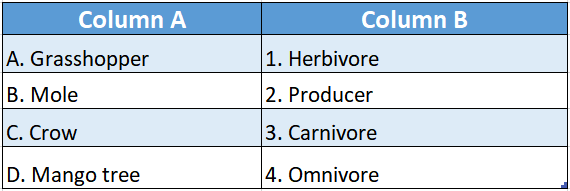
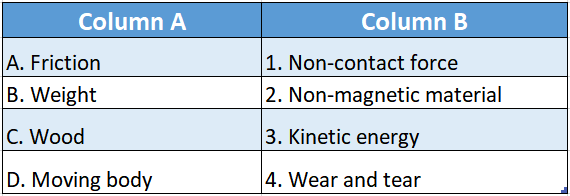
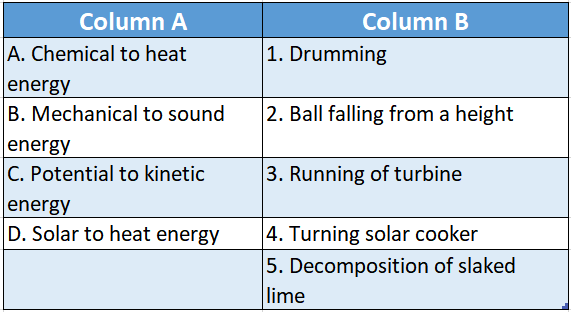
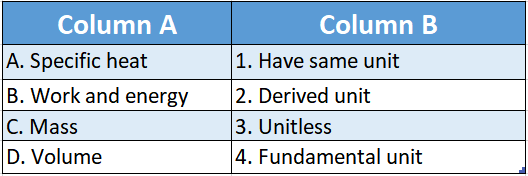
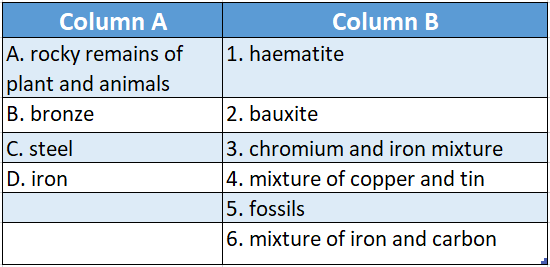
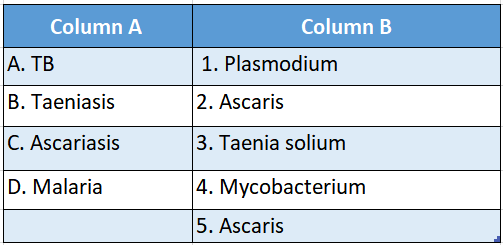
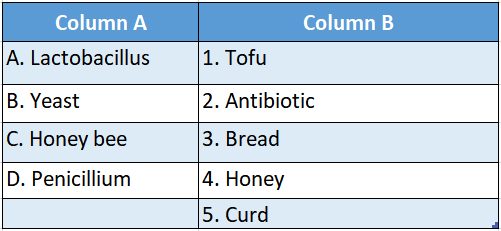
Question 1.
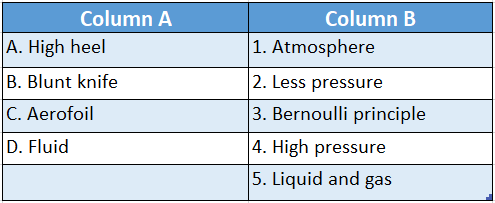
Answer: A-4,B-2,C-3,D-5
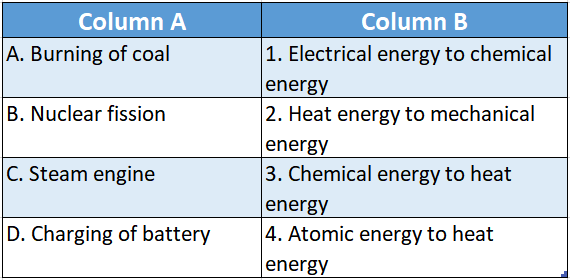
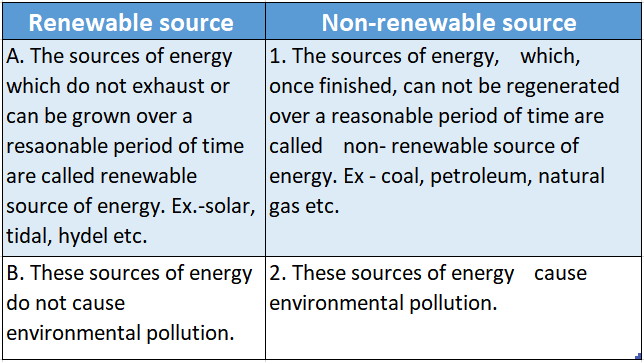
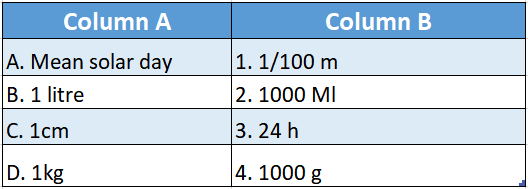
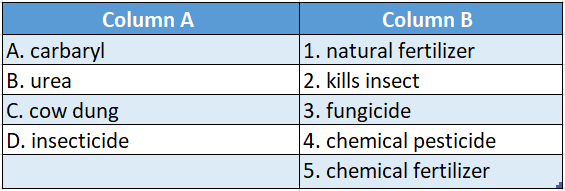
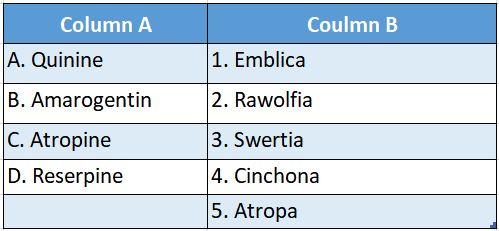
Question 2.
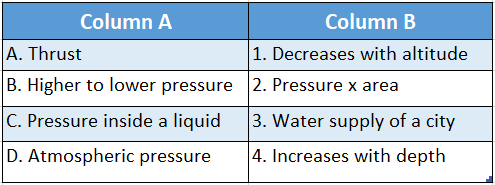
Answer: A-2,B-3,C-4,D-1
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Answer In Words Or A Sentence
Question 1. If the area is doubled keeping the applied force the same, what would be the change in pressure?
Answer: Pressure becomes half the previous.
Question 2. How does pressure change with the speed of moving liquid?
Answer: The pressure of liquid decreases with an increase in the speed of moving liquid.
Class 6 WBBSE Science Question Answer
Question 3. In which direction does air flow?
Answer: From a place of higher pressure to that of lower pressure.
Question 4. What are the units to express atmospheric pressure?
Answer: Atmosphere (atm), Pound per square inch (psi), and Bar (bar).
Question 5. In which direction does a liquid exert pressure at any point below its free surface?
Answer: In all directions.
Question 6. What is the pressure acting at the free surface of a liquid?
Answer: Atmospheric pressure.
Short Questions on Properties of Fluids
Question 7. What is the principle applicable behind the flight of a bird?
Answer: Bernoulli’s principle.
Question 8. If 100 N force is applied on a surface of 25 sq. m area, what is the applicable pressure?
Presure=\(\frac{Force}{Area}\)=\(\frac{100 N}{25 sq.m}\)=4 pa
Question 9. Which one is difficult to penetrate inside a block-a sharp-ended nail or a blunt-ended nail?
Answer: Blunt-ended nail.
Question 10. How does air pressure vary at a hill station compared to that of a plane landing at sea level?
Answer: Air pressure at the hill station is lesser than that at sea level.
Question 11. Flags flutter while there is a breeze-which principle does this phenomenon follow?
Answer: Bernoulli’s Theorem on fluid flow and pressure.
Class 6 WBBSE Science Question Answer
Question 12. On what factors does a pressure of a liquid depend?
Answer: At a certain place the pressure at a point inside a liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid.
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. A boy weighing 30 N falls on the sand. The area of his feet is 0.001 sq. m. What is the pressure exerted on sand?
Answer:
Pressure=\(\frac{Force}{Area}\)=\(\frac{100 N}{0.001 sq.m}\)
Question 2. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string? Pressure = Force/Area.
Answer: Thus as the area decreases, pressure increases. Since the contact surface area of a thin string strap is very small, it exerts large pressure on the shoulder making it difficult to carry.
Question 3. What makes house lizards stick to the wall when they crawl?
Answer: Lizards have hollow cavities inside the soles of their feet which help suck out the small pockets of air from the spots where they stand.
The higher atmospheric pressure helps them to stick to the surface of walls and ceilings.
4. Why are dams broader at the base than at the top?
Answer: Pressure at a point inside the liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid.
This lateral pressure multiplied by the area of the dam gives the force exerted by the water on the walls of the dam. The force at the base is higher than at the top.
Hence dams are constructed with a broader base to prevent the development of cracks.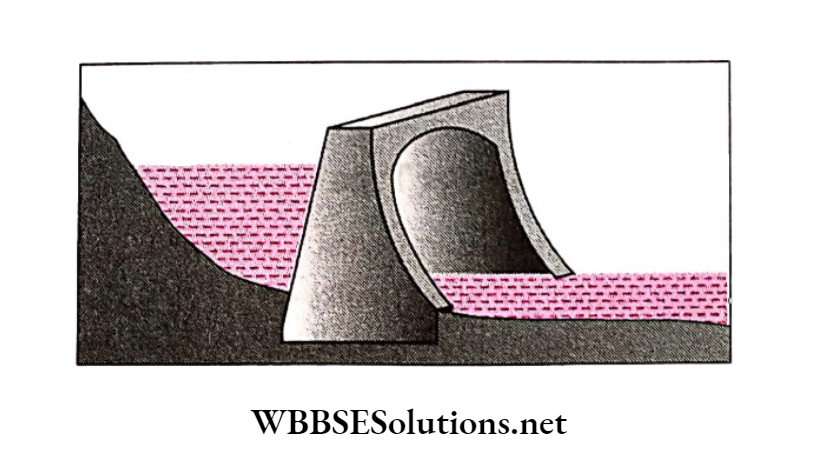
Examples of Real-Life Applications of Fluid Dynamics
Question 5. If force remains the same, how can pressure be increased?
Answer: If the area decreases, pressure increases when the force remains the same.
Question 6. Why does a capped plastic bottle filled with steaming hot water get deformed when it is allowed to cool?
Answer: As the steaming water in the bottle begins to cool, the pressure inside the bottle reduces.
However, the pressure outside the bottle remains the same. This excess outside pressure deforms the bottle.
Question 7. How is water supplied in cities?
Answer: The dependence of pressure in liquids on depth is made used in supplying water to different parts of a city. Water is stored in big tanks which are placed at great heights.
From these tanks, water is sent to different parts of the city through pipes.
Class 6 Science Question Answer WBBSE
As the water tanks are placed at great heights, the pressure in the water, being very large, forces the water to rise in multi-storied buildings.
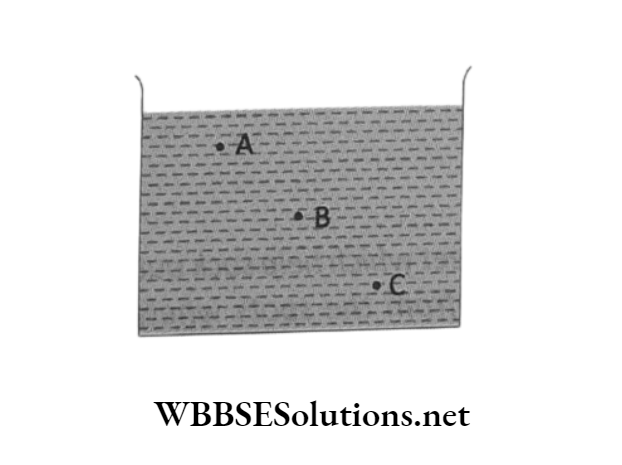
Question8. The figure shows a container filled with water. At which point is the pressure highest?
Answer: Point C is at maximum depth from the free surface of the water. Hence lateral pressure of water is highest at C
Question 9. Three vessels are shown in the following figure. The volume of water is the same in all of them. Arrange the
Answer: vessels in the order of increasing pressure at the base of each vessel.
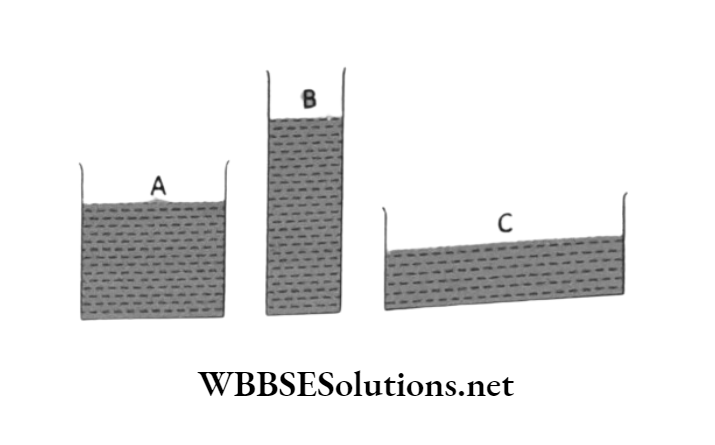
Conceptual Questions on Bernoulli’s Principle
The height of the water column is maximum in vessel B and minimum in vessel C. Accordingly pressure at the base shall be maximum in vessel B and minimum in vessel C.
Thus when arranged in the order of increasing pressure at the base, the vessels shall be Vessel C< Vessel A < Vessel B.
Question10. A liquid seeks its own level-explain it.
Answer: A liquid, irrespective of the shape of the container of a communicating vessel in which it is poured, attains its own level because the pressure applied at the bottom of each container remains the same.
The surface of the liquid in every container is found to be horizontal at rest. This fact is often known as liquid finding its own level.
Question 11. Why do flags flutter when air is blowing?
Answer: When air is blowing, the air layers are moving with unequal velocity on the two faces of the flag.
Class 6 Science Question Answer WBBSE
According to Bernoulli’s theorem, the air layers flowing at a slower speed have higher pressure while those flowing at a faster speed have lower pressure.
Thus a difference of pressure is created on both sides of the flag which results in fluttering of the flag.
Question 12. On what factors does the thrust exerted by a liquid on the base of a vessel depend?
Answer: Thrust or force exerted by a liquid on the base of a vessel depends upon
- the height of the liquid column in the vessel. More the height, the greater the thrust, and vice versa.
- the area of the base of the vessel. For a certain height of the liquid column, more thrust will be there on the base of the vessel having a bigger base area.
Chapter 7 Statics And Dynamics Of Fluid Liquid And Gas Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is pressure? What is its unit in the Sl system? When somebody walks on pebbles, he feels greater pain than walking on a flat floor explain.
Answer:
Pressure:
Force per unit area of surface is your whole foot, much more of the pressure is called pressure.
Pressure Force/Area.
The SI unit of force and area are Newton and square metres respectively. Hence SI unit of pressure shall be Newton per square meter.
It is also called Pascal or Pa. Multiple of Pascal is kilo Pascal.
1 kilo Pascal = 1000 Pascal = 1000 Newton per square metre.
Now we shall go back to the previous example and try to analyze what causes more pain to walk on pebbles than on sand and how is it related to pressure.
This is because of the applied to the small area that is actually touching the pebble. So, more pressure applied on a given area of your foot causes more pain.
Let us take another example. Try to hit two nails-one having a blunt end and another having a sharp end into a wooden block by a hammer.
You would observe that the sharp-ended nail penetrates the block more easily than the blunt-ended one.
Class 6 Science Question Answer WBBSE
Since the area of the sharp-ended nail is less compared to the blunt-ended one, it generates more pressure for penetration than the other nail and thus penetrates relatively easily.
Question 2. What is Bernoulli’s principle? Why are people warned to move away from the edge of a platform when a fast-moving train comes?
Answer: You know the behavior of a river in a wide, unconstricted region, it flows slowly, but if its flow is narrowed by canyon walls (for instance), then it speeds up dramatically.
Now imagine that fluid moves from a wider pipe to a narrower one. Certainly, the volume of that fluid that moves a given distance in a given time period does not change.
But since the width of the narrower pipe is smaller, the fluid must move faster in order to achieve that result.
Bernoulli’s principle states that a slow-moving fluid exerts more pressure than a fast-moving fluid.
Since “fluid” in this context applies equally to liquids and gases, the principle has as many applications with regard to airflow as to the flow of liquids.
We shall illustrate the above principle with another example. Suppose there is a room full of children.
If each child is asked to run at top speed, children will start bouncing off each other and the walls resulting in a number of collisions.
Now if those same children are taken out of the room and again asked to run down a wide hall at top speed, they would be all said? running together.
This time all collisions between children are much more gentle than before since they are all running in the same direction.
Hence Bernoulli’s conclusion The slower the rate of flow of a fluid, the higher the pressure, and the faster the rate of flow, the lower the pressure.
Take a piece of folded paper and hold them. in front of your mouth. Blow air in between the. papers, as shown in The papers, come.
closer instead of going apart. When air moves faster in between the papers (due to blowing), the pressure decreases in that region. The force.
exerted by air outside the papers act perpendicular to the outer surface of the two sheets and push them together.
One of the most common everyday applications of Bernoulli’s principle is in air flight. The main way that Bernoulli’s principle works in air flight has to do with the architecture of the wings of the plane.
In an airplane wing, the top of the wing is somewhat curved, while the bottom of the wing is totally flat. While in the sky, air travels across both the top and the bottom of the wing concurrently.
Because the top part and the bottom part of the wing are designed differently, this allows for the air on the bottom to move slower, which creates more pressure on the bottom, and allows for the air on the top to move faster, which creates less pressure.
This is what creates a lift, which allows planes to fly.
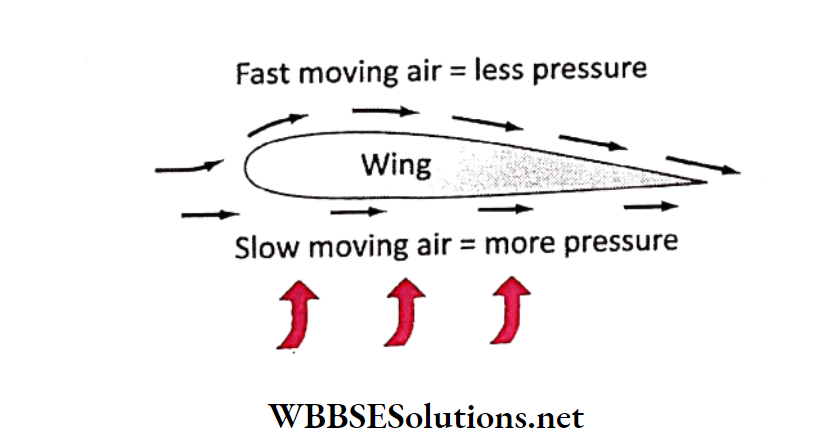
A person standing near the railway track is pulled towards the train when a fast-moving train passes close to him. The fast-moving train decreases the pressure between the person and the train.
Question 3. Define the lateral pressure of the liquid. Explain with a diagram what happens when three holes are made at varying heights in a bottle filled with water.
Answer: Any substance which has no fixed shape and can flow is called fluid. All liquids and gases are regarded as fluids.
Do fluids exert pressure? Does it also depend on the area on which the force acts? We have seen that a solid exerts pressure on another surface on account of its weight.
Real-Life Scenarios Involving Hydrostatic Pressure
Similarly, a fluid has weight and hence, it exerts pressure on the walls of the container in which it is kept or enclosed.
It may be demonstrated as shown in means that they need to reduce their Dit pressure on the ground. Large feet mean a large area of contact and thus less pressure.
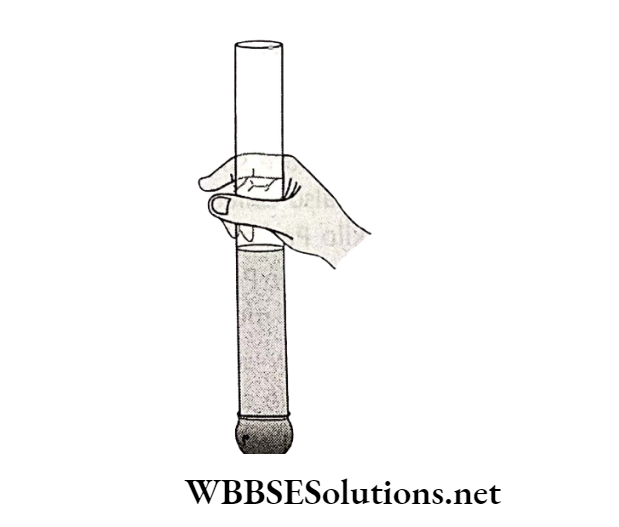
A piece of thin and good quality rubber sheet may be tied tightly over at one end of a long glass tube.
While holding the glass tube in the middle and in an upright condition, some water may be poured into the tube.
It would be seen that the rubber sheet would bulge out indicating that Statics and Dynamics of Fluid (Liquid and Gas) water exerts pressure.
While walking down the streets you must have come across situations. where fountains of water are seen to come out of the leaking joints or holes in municipal water pipes supplying water to the city.
This happens due to the pressure exerted by the water on the walls of the pipes. When you inflate a balloon, you have to tightly close the mouth immediately or else the balloon deflates rapidly leaking out all the air.
There are certain laws of liquid pressure. These are as follows:
- Pressure at a point inside the liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid.
- Pressure is the same at all points in a horizontal plane at a given depth within the liquid.
- A liquid flows from a place of higher pressure to a place of lower pressure.
- A liquid seeks its own level.
Now we would explain one after another with simple demonstrations. Let us take the first law which states that pressure increases with the depth of a liquid from the free surface.
Let us prove it with the following example. A plastic bottle filled with water may be taken similar to the one shown earlier.
Three holes shall be made in the bottle one above another from top to bottom in a line.
It would be found that the flow of water from the bottommost hole travels furthest because the pressure exerted at this point is the highest since this hole is situated at maximum depth from the free surface of the water.
Class 6 Science Question Answer WBBSE
Question 4. Why do we not feel tremendous atmospheric pressure? Why does a rubber sucker require a large force to pull it off a surface?
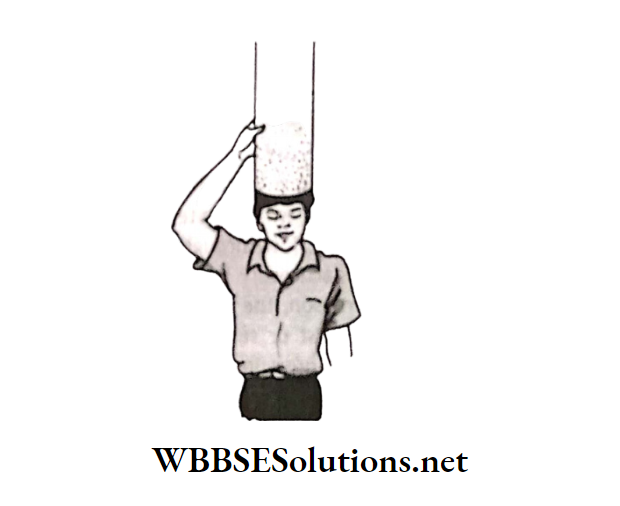
Answer: The envelope of air surrounding us is called the atmosphere. It extends up to many kilometers above the surface of the earth. The pressure exerted by this column of air is known as atmospheric pressure.
If we imagine a unit area on our head as shown in and a very long cylinder standing on it filled with air, then the weight of air belonging to this cylinder shall be the atmospheric pressure.
The reason we are not crushed under this weight of the air column is that the pressure inside our bodies is also equal to the atmospheric pressure and it cancels the pressure from outside.
Why do some passengers suffer from nose bleeding in pressurized aircraft cabins? As the altitude increases.
the air pressure decreases around passengers and therefore this can cause nose bleeding in some cases since the pressure inside the human body becomes more than that at the outside at higher altitudes.
The cabin is pressurized but not as much as it is at sea level. Therefore, it’s common among many people to have nose bleeding and is not usually a serious problem.
There are certain laws of liquid pressure. These are as follows:
- Pressure at a point inside the liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid.
- Pressure is the same at all points in a horizontal plane at a given depth within the liquid.
- A liquid flows from a place of higher pressure to a place of lower pressure.
- A liquid seeks its own level.
Now we would explain one after another with simple demonstrations. Let us take the first law which states that pressure increases with the depth of a liquid from the free surface.
Let us prove it with the following example. A plastic bottle filled with water may be taken similar to the one shown earlier.
Three holes shall be made in the bottle one above another from top to bottom in a line.
It would be found that the flow of water from the bottommost hole travels furthest because the pressure exerted at this point is the highest since this hole is situated at maximum depth from the free surface of the water.
Question 5. Draw a diagram to show how thatched roofs are blown away by high winds or tornadoes.
Answer: